Greetings everyone!
This week, I’m pleased to welcome author Glyn Iliffe back on Writing the Past.
It’s been a couple of years since I interviewed Glyn on the old website around the time of the release of the fourth book in his series, The Adventures of Odysseus.
This time, Glyn is back with a special guest post that I know you will find fascinating!
He has just released book five, The Voyage of Odysseus, which I am reading right now and cannot put down.
Homer’s Odyssey is one of the foundational works of western literature, and the story of Odysseus’ journey back home after the Trojan War is one that has fascinated people for ages.
One of the terrifying elements of this story is the hero’s journey into Hades, and that is what Glyn is going to talk about today.

Katabasis – The Descent into Hell
By Glyn Iliffe
According to Benjamin Franklin only two things in life are certain: death and taxes. The latter we can grumble about and try to dodge, but death is a different question. You might say it’s the question. Being aware of the finite nature of our existence is what separates us from the rest of the animal kingdom and, essentially, makes us human. Death – and what lies beyond it – is the great unknown. The anticipation or fear of it has shaped every culture across the world and throughout time.
To understand the psychology of a culture you need look no further than its art, and a lot of art focuses on death. Enter any Catholic church and you will see depictions of Jesus on the Cross. The tombs of the ancient Egyptians are filled with hieroglyphs illustrating the journey into the afterlife. Indeed, the reason we know so much about our ancestors is because of their obsessions with death, culminating in the desire to take their treasures with them into the next world, or leave monuments to the lives they led before death took them. But the clearest insights into a culture’s views on death come from its stories.
In particular, there is one type of story that appears again and again in the texts of different civilizations from different eras: the descent into Hell. I’m thinking here of a physical journey to the underworld, rather than a symbolic or psychological descent into madness or suffering. Possibly the earliest is Gilgamesh’s visit to Utnapishtim. The Egyptians had the Book of the Dead. The Roman poet Virgil told of Aeneas’s visit to his death father, Anchises; and in the Renaissance Dante’s Divine Comedy describes one of the most memorable and terrifying visions of Hell ever depicted. The most defining katabasis of all, for Western culture, was that of Jesus Christ, who spent three days in Hell after taking mankind’s sins onto himself on the Cross.
The term katabasis comes from the Greek words κατὰ ‘down’ and βαίνω ‘go’, and it is the Greeks we must thank for the most numerous and vivid myths on the subject. In the case of Orpheus, the greatest of all poets and musicians, the journey was undertaken for love. When his wife died after being bitten by a viper, he descended into the Underworld and so charmed Hades and Persephone – King and Queen of the Dead – with his music that they agreed to release her back to him. There was one condition, though: that Orpheus walked ahead of his wife and did not look at her until they had both reached the world of the living. In his anxiety after reaching the upper world, he turned to look at her before she had crossed the threshold of Hades. She disappeared in an instant, and this time it was forever.
A less tragic visitation was made by Heracles, the greatest of all Greek heroes. As a penance for slaying his own family in an episode of madness (induced by the gods, of course), Heracles was forced to serve his weakling cousin, King Eurystheus, for twelve years. Eurystheus set him several labours, the twelfth of which was to capture Cerberus, the three-headed hound of Hell. Hades agreed to let Heracles attempt the feat, but only if he fought without weapons. Despite the fearsome nature of the beast, Heracles succeeded and carried Cerberus back to his cousin. Eurystheus was so frightened he agreed to set no more labours if Heracles would take the hound back!

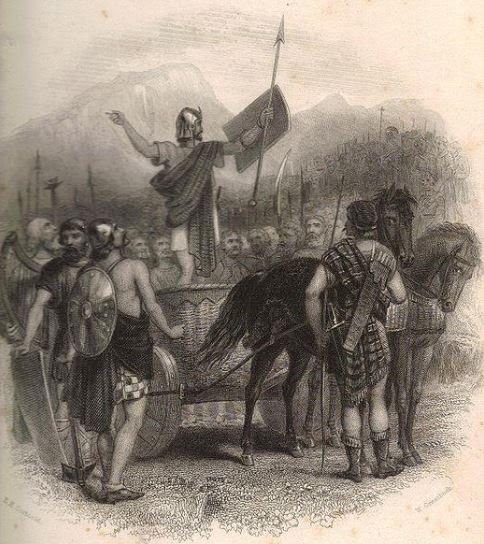
Teiresias speaks to Odysseus
The most famous katabasis features in Book 11 of Homer’s Odyssey. Odysseus descends into the Underworld to seek the ghost of Teiresias, who will tell him how to find his way home to Ithaca. There he encounters his dead mother and many of the heroes who died during the Trojan War. Chief among them is Achilles, who in life had been the greatest of all the Greek warriors and covered himself in martial glory. But in Hades he is a mournful phantom, scornful of what he had achieved on the battlefield:
‘…We Argives honoured you as though you were a god: and now, down here, you have great power among the dead. Do not grieve at your death, Achilles.’
‘And do no make light of death, illustrious Odysseus’ he replied, ‘I would rather work the soil as a serf on hire to some landless impoverished peasant than be King of all these lifeless dead.’
Odysseus comes away from the Underworld without learning the way back home, which makes the reason for his visit to such a bleak and terrifying place seem pointless. But was it pointless? Indeed, why do some heroes have to descend to Hades? What’s the meaning underlying these myths?
Though later Greeks softened their ideas, in the Bronze Age they believed one thing: that death was followed by an eternity of misery and regret in Hades, relieved only by forgetfulness. Knowing this, many sought the one form of immortality available to them – a reputation that would be honoured from generation to generation. This could only be achieved in battle, by defeating enemies and accumulating honour. This is the driving force for many of the characters in my own novels about the Trojan War.
The katabasis, though, is about symbolic immortality. Importantly, the hero does not reach Hell by the usual route (death). Instead, he seeks to enter the Underworld as a mortal, fulfilling a quest that requires him to take or retrieve something of great worth, such as an object, a person or a piece of knowledge. Interestingly, Odysseus does not return with the knowledge he went in search of, but emerges with something of possibly greater worth: an understanding of the value of life. By achieving his quest the hero proves himself to be exceptional, and by overcoming a figurative death he also becomes more than just mortal. He is reborn into a new life, similar to the Christian baptism ceremony, where the lowering into and rising up again from water is symbolic of death and rebirth.

Wilfred Owen
Such deep themes have inspired many modern retellings of the katabasis. Though the themes are no longer Greek, such stories are still reflective of their own times. Wilfred Owen was an officer in the Manchester Regiment during the Great War. His poetry is full of hell-like visions from the mud and slaughter of trench warfare, but in Strange Meeting there are clear parallels with Odysseus’s descent into Hades:
Yet also there encumbered sleepers groaned,
Too fast in thought or death to be bestirred.
Then, as I probed them, one sprang up, and stared
With piteous recognition in fixed eyes,
Lifting distressful hands, as if to bless.
And by his smile, I knew that sullen hall,
By his dead smile I knew we stood in Hell.
The speaker, like Odysseus with Achilles, tries to comfort the dead man; but like Achilles, the unhappy spirit will have none of it:
‘Strange friend,’ I said, ‘here is no cause to mourn.’
‘None,’ said that other, ‘save the undone years,
The hopelessness.’
The twist comes at the end, where the dead man informs the speaker ‘I am the enemy you killed, my friend’. Though only a glimpse of a descent into Hell, and one from which we don’t know whether the “hero” returns, Owen nevertheless plays on Homer’s suggestion that death is hollow and empty, and that any kind of life is rich by comparison.
A more recent katabasis appears in Phillip Pullman’s The Amber Spyglass, in which Lyra enters the Land of the Dead to rescue her best friend, Roger, who has been murdered. This already has echoes of Orpheus and Eurydice, but there are also other allusions to Greek mythology in the Harpies that patrol this terrible underworld, as well as the phantom-like figures of the dead that populate it. But there are heavy Christian references, too. Like Christ, Lyra leads the lost souls to a form of redemption. Through Lyra’s katabasis Pullman tries to offer an atheistic view of what lies beyond death – very different from traditional descents into Hell – but ironically still relies very heavily on Christian beliefs about redemption.
In The Voyage of Odysseus I retell the story of Odysseus’s long and arduous journey home to Ithaca. The previous books in the series have attempted to draw the full story of the Trojan War into one narrative, focussed on Odysseus. As a fan of Greek mythology, it has always been my intention to be faithful to the original myths and make them accessible, regardless of what the reader may or may not already know about the story. And yet it will always be my take. This is particularly true of the scene in which Odysseus enters the Underworld.
I have had a fear of Hell since childhood. This was probably instigated by seeing Hieronymus Bosch paintings, and reinforced in my teenage years by Dennis Wheatley novels. The notion that Hell is not merely a place of suffering, but a place where the relief of light, love and peace do not exist, is even more frightening. I have incorporated these fears in my retelling of Odysseus’s katabasis – as well as my terror of enclosed spaces!

The Garden of Earthly Delights by Hieronymus Bosch

Glyn Iliffe studied English and Classics at Reading University, where he developed a passion for the stories of ancient Greek mythology. Well travelled, Glyn has visited nearly forty countries, trekked in the Himalayas, spent six weeks hitchhiking across North America and had his collarbone broken by a bull in Pamplona. He is married with two daughters and lives in Leicestershire. He is currently working on the concluding book in the series.
Connect with him on Facebook, or visit his website at www.glyniliffe.com
Be sure to check out The Adventures of Odysseus books at any of the following outlets:
I’d like to thank Glyn for taking the time to write such an interesting piece for us. I know that whenever I read or write about a character’s descent into Hell or the Underworld, I will be doing so through a new lens.
If you haven’t already read Glyn’s work, I highly recommend The Adventures of Odysseus books. It is definitely one of the best historical fantasy series out there, and despite these being very old stories and characters, Glyn manages to give them new life. Trust me on this one, folks!
As ever, do be sure to leave your questions or comments for Glyn or myself in the comments section below.
Thank you for reading!