We’re heading back into the province of Africa Proconsularis this week with a brief look at one of the best preserved ‘small towns’ of Roman North Africa – Thugga.
I visited Thugga (also spelled ‘Dougga’) a few years ago, when I was doing research in Tunisia for Children of Apollo and Killing the Hydra.
I was with a small group that headed out in two 4x4s from the ruins of Carthage, south to Thysdrus (El Jem), across the great salt plains of Chott El Jerid and into the soft, sand-seas of the Sahara.
When we turned north again, skirting the edge of the guarded Algerian border, we came once more into the lush plains of northern Tunisia where grey mountains sprout from green, olive-dotted valley floors, and where low clouds hovered comfortably around their peaks in what was the mildest January I’ve ever experienced.
The countryside was beautiful and lonely, and I missed the desert dunes very much by that point, our time in the South having been all-too-short.
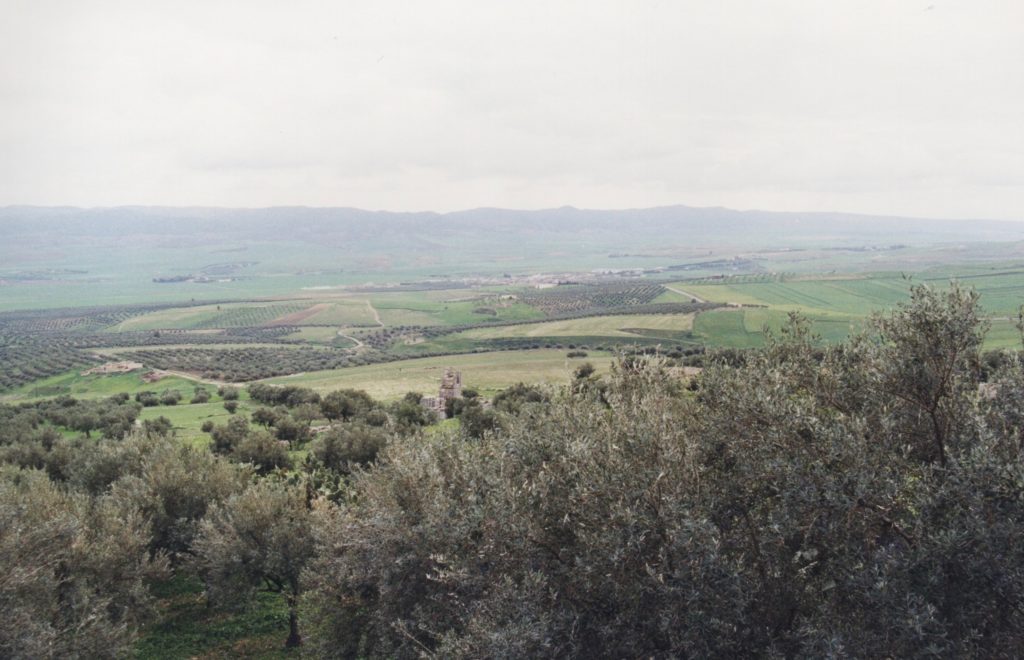

Countryside of Northern Tunisia
Admittedly, I had not heard of our next destination, ‘the place of Dougga’ as our guide called it. Our truck pounded along the winding, potted roads, climbing higher and higher, the land getting greener by the mile.
I also had a fever at this point in the journey, the result of having opted for what I thought was boiled soup, rather than camel meat a couple nights before.
Quick tip: they don’t boil the soup, and eating it is equivalent to drinking a murky glass of Saharan tap water.
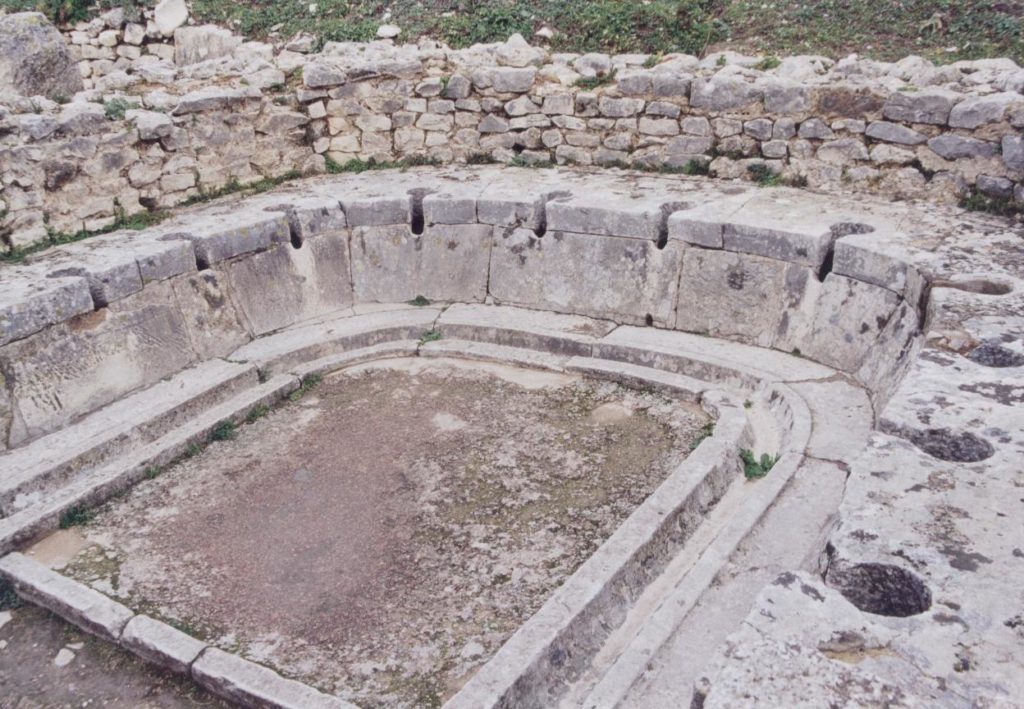

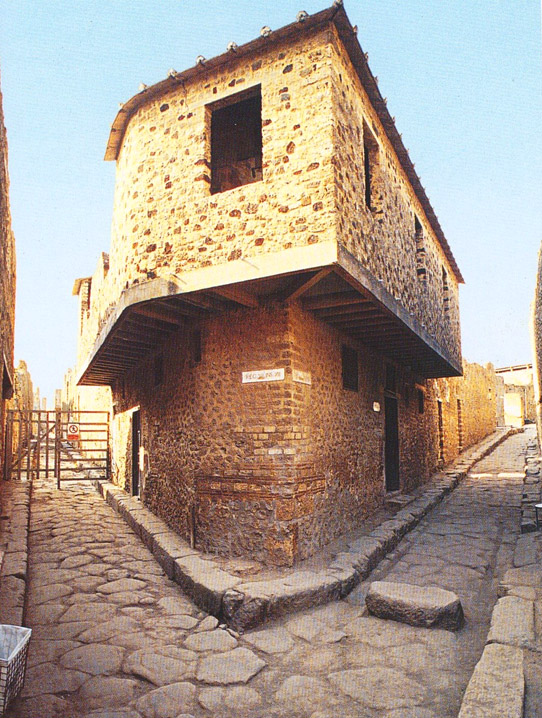
A public latrine in Thugga
Nevertheless, the historian in me could not help but spot the distant ruins perched on a hillside in the distance. As we came closer, and the road got rougher, it became apparent that there was much more to ‘the place of Dougga’ than we had been led to believe.
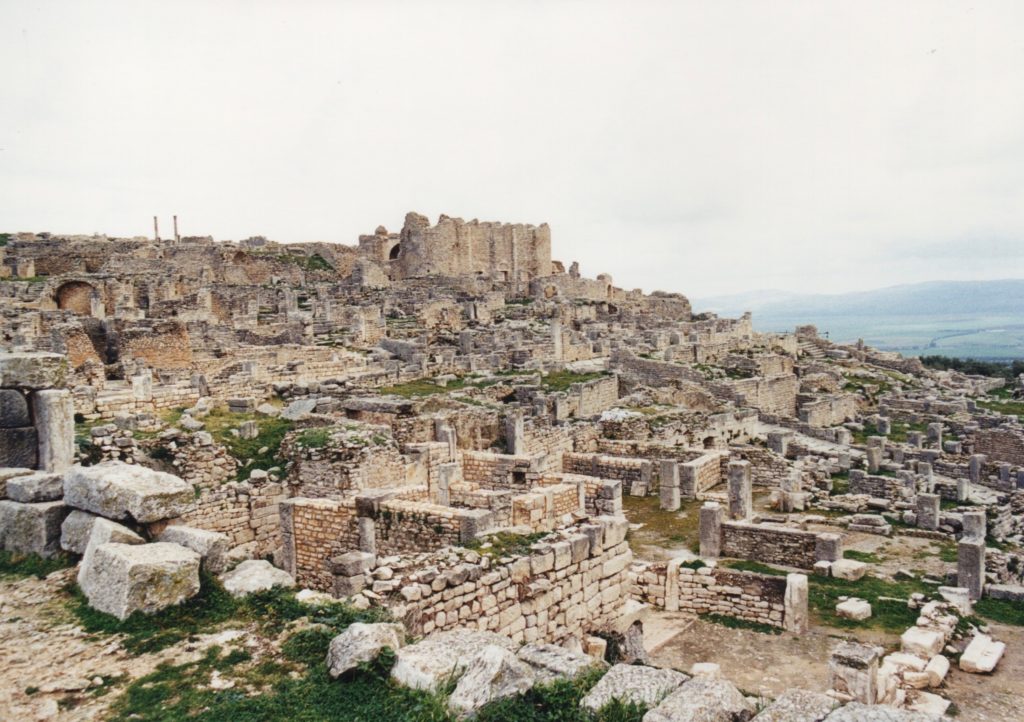

The sprawling remains of Thugga
This wasn’t a small gathering of weathered ruins – it was a city! Or rather, it felt as such in that lonely, windswept place.
I stepped out of the truck, grateful that the ‘Couscous Beats’ soundtrack our driver had been torturing us with since the beginning of the trip finally stopped. Everything was quiet, but for the wind, and the crunch of gravel beneath our feet as we approached the small, shuttered kiosk.
When I saw no one was there, I wondered if we would be able to get in, and craned my neck to try and see the tantalizing view beyond the gates.
From the side came a man with a shot gun slung over his shoulder. We had just woken him from his obviously important duty. He smiled however, and spoke in hushed tones with our guide who evidently knew the man, or appeared to know him.
Our man turned to us and nodded. “You have one hour,” he said, and the gates opened.
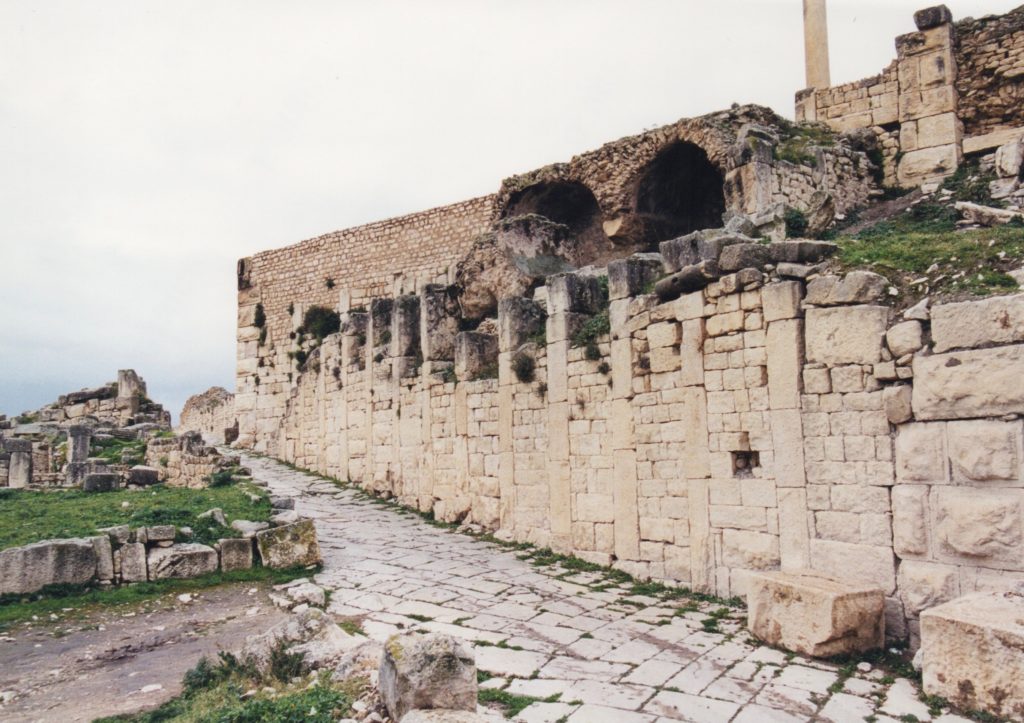

One of the main streets of Thugga
I’m not going to go into the history of Thugga a great deal here – there is an uncharacteristically good Wikipedia page on this site which you can read by CLICKING HERE.
But, before we walk the streets of this Roman ghost town, there are a few things worth mentioning.
Thugga has had a long a varied history of settlement, having gone from its origins as a Numidian-Berber settlement, to a place under Punic control during the ages of Carthaginian hegemony, to a major Roman town, and finally under Byzantine control prior to Arab dominance in the region.
In the first century B.C., the Greek historian, Diodorus Siculus mentioned the “beautiful enormity” of Thugga.
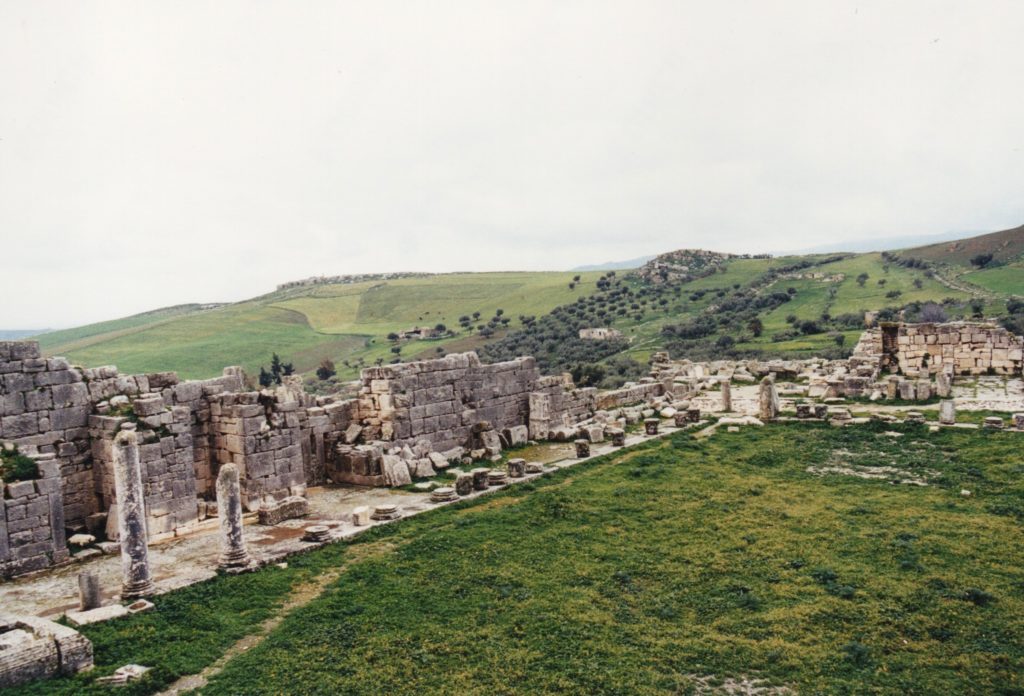

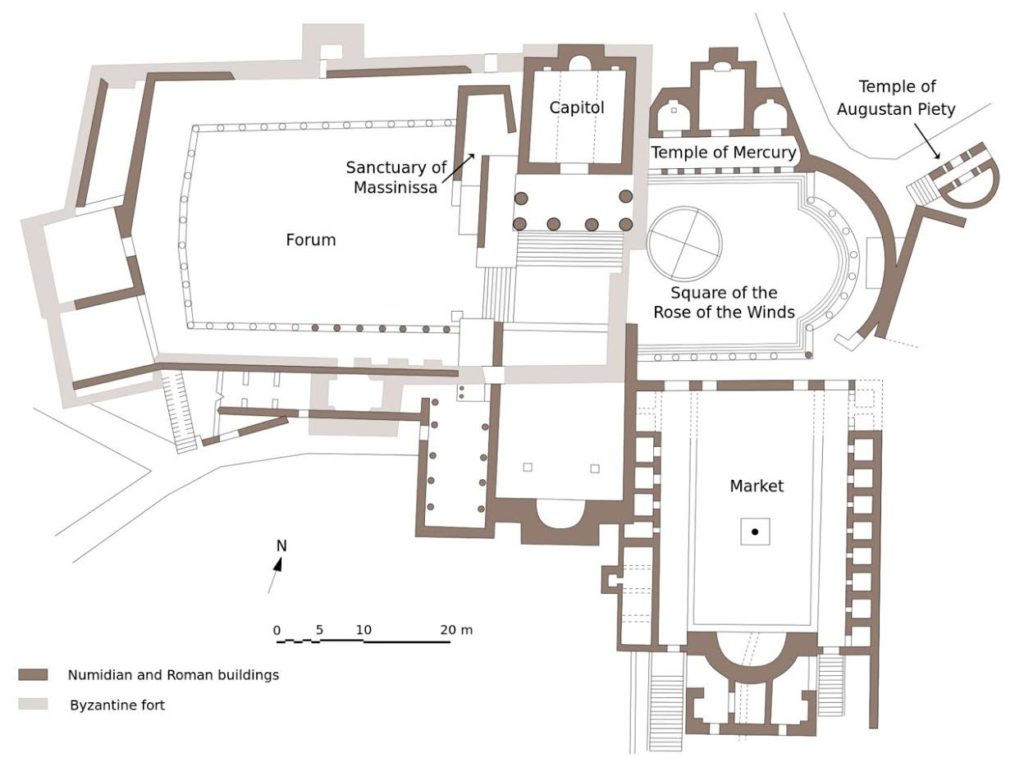
The Forum of Thugga
It is a big site – about sixty-five hectares (about 161 acres) – which makes it surprising that Thugga is considered a ‘small’ Roman town. Its population when it was at its most prosperous in the 2nd and 3rd centuries A.D. is said to have been about five thousand residents.
UNESCO made it a World Heritage Site in 1997, and cited it as the “best preserved Roman small town in North Africa”.
Thugga was a thriving settlement because of agriculture, its location on the fields of northern Tunisia ideal for crops. But its fortunes took an even better turn in A.D. 205 when it was made a municipium by order of Septimius Severus and his son, Caracalla, acquiring the title of Municipium Septimium Aurelium Liberum Thugga. After that, Thugga received more rights and freedoms, and magistrates of the town were made Roman citizens.
Thugga didn’t enjoy the imperial favour that Severus’ hometown of Leptis Magna did, but it did prosper under Severus, aided by the fertile landscape that surrounded it, olives, oil, and grain being key to the running of the Empire.
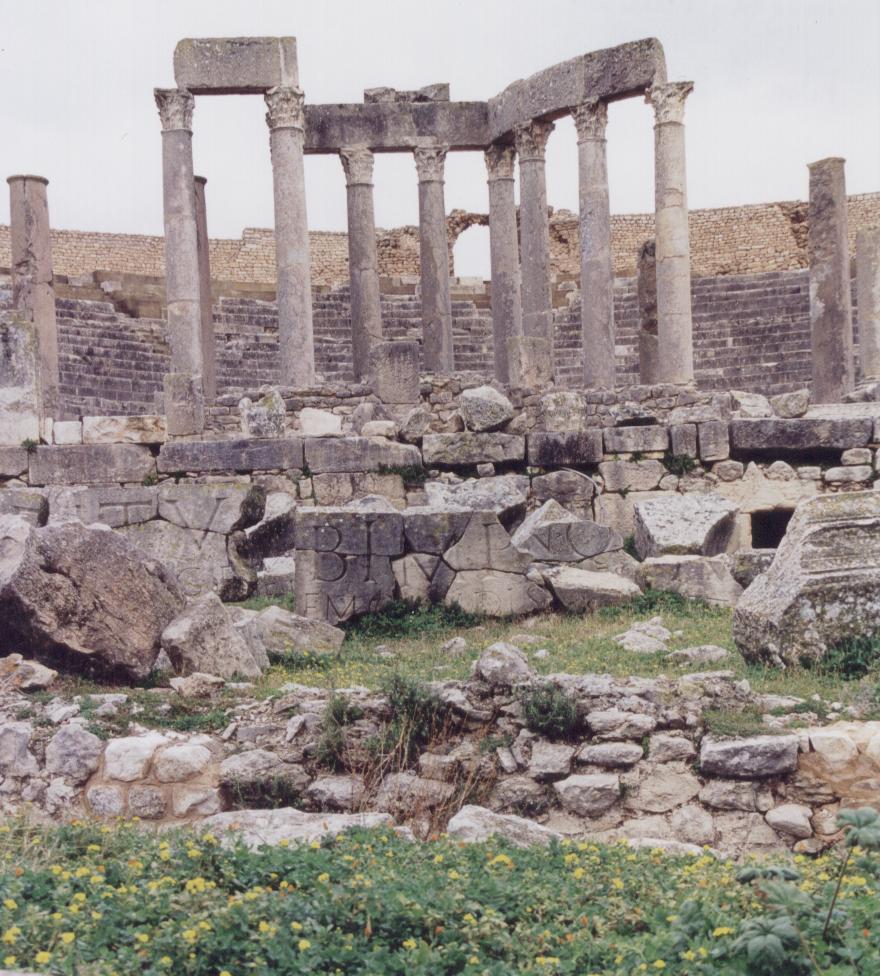

Theatre of Thugga
I didn’t know any of this however, as I stepped through the gate of the archaeological site and entered the labyrinthine streets of Thugga as our guide settled himself beneath an olive tree and left us to our own devices.
One hour was not nearly enough time!
Our small group quickly broke apart as people set about exploring the site with confidence, as if they were walkers in some sort of past-life recollection, certain of where they needed to go.
For myself and my friend, it was more a feeling of overwhelm that snared us. The streets stretched out before us in great slabs of polished white and grey stone. We didn’t know where to start, so we headed in the direction of the biggest monument near the entrance – the theatre.
The theatre of Thugga is incredibly intact, and as we climbed the concentric rows of seating to the top, the picture of Thugga became much more clear as it spread out before us.
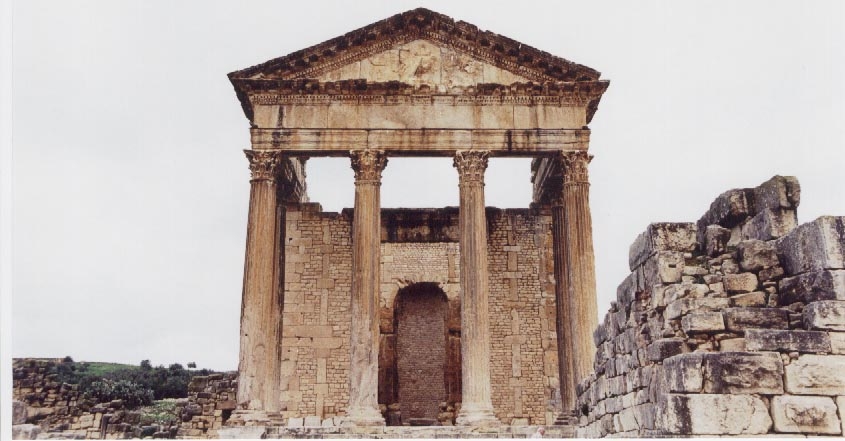

The Capitol of Thugga – the Temple of Jupiter, Juno, and Minerva
From the top row of the theatre I could see the high part of the town with the capitolium and agora beside it, the market place, the curve of one of the main streets passing the baths and going farther down into the residential part of ancient Thugga.
Five thousand residents may not seem like many, but when you look at a sprawling site like this, so quiet and complex, you begin to hear the voices of the past in a way that makes visiting an isolated archaeological site a truly unique experience.
To me, Thugga is a place of ghosts.
At every turn, I felt like I was intruding upon someone – a priest sacrificing in the Temple of Jupiter, Juno and Minerva, a slave buying supplies in the marketplace, a couple of locals discussing business in the agora, or two ladies whispering in hushed tones in the baths where they stand upon the black and white geometric mosaic floor that was open to the sky. From the marble-framed doorway of a private domus, a mother watches me pass while her child plays on the stoop at her feet… It was the same, everywhere we went.
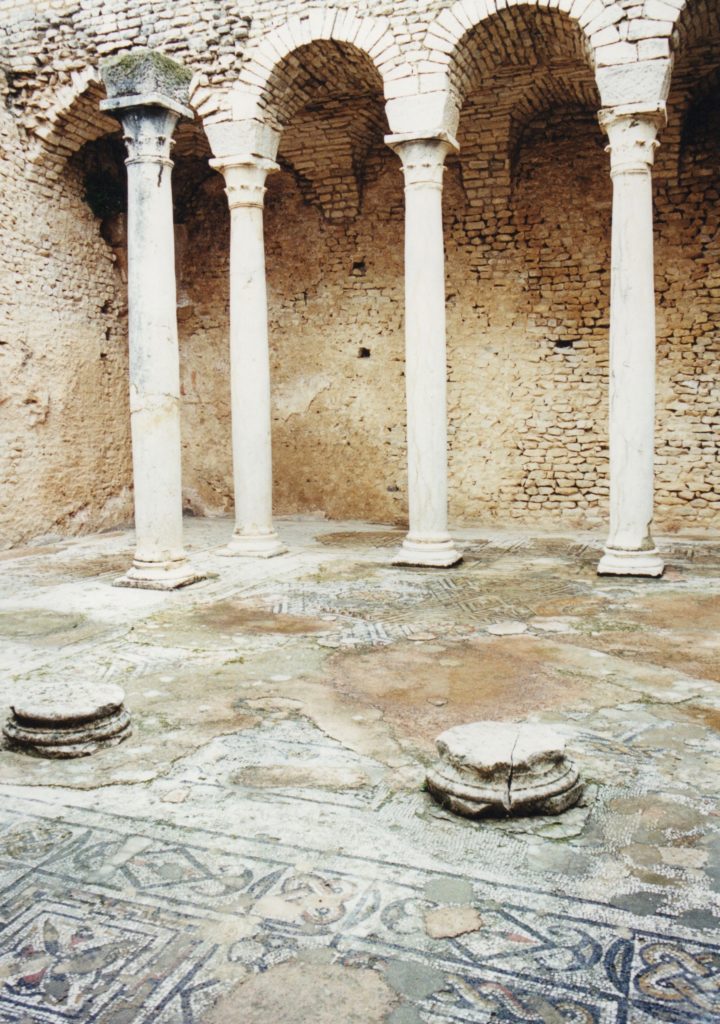

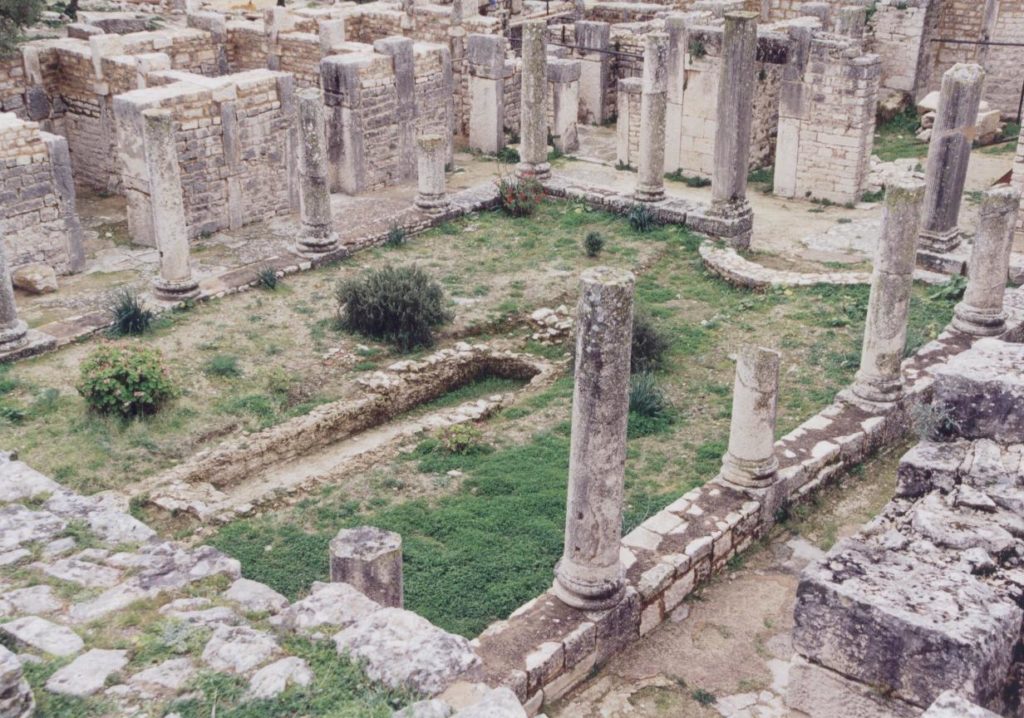
Inside one of the public baths, mosaics open to the sky!
As we walked around, the voices Thugga’s residents became louder in my ears, their shades passing around me as they went about their daily business.
I was blown away by the fact that this almost completely intact city was just sitting there, deserted, its mosaics open to the sky.
Even more shocking was that as I walked around, the seeds of my story began to take shape in my mind. I saw Lucius walking through these very streets, visiting the temple, the marketplace, being pursued by local thugs.
What I didn’t see was the young prostitute who would approach him on that very street I was walking on, and how she would be the only person who could help him in a time of need.
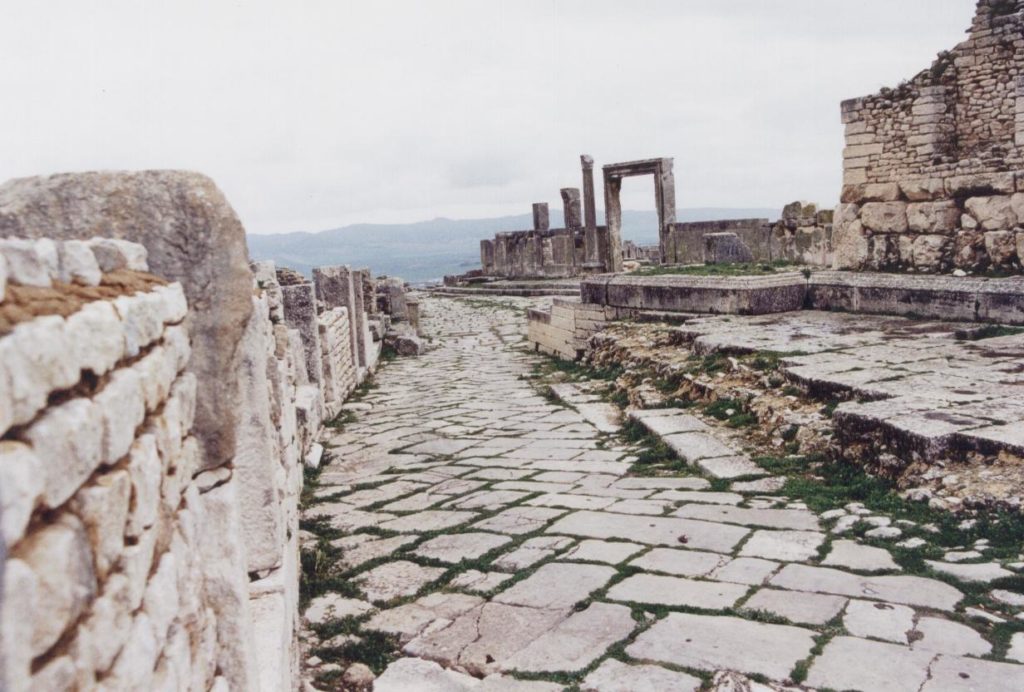

Seeing my characters wander down this main street…
As a writer, it’s a magnificent experience to have your story take shape like that. I didn’t realize it fully at the time as I stepped into the ruins of the brothel, or the public latrine, following the road down toward the second century B.C. Libyan-Punic mausoleum to look out over the valley.
As I stood there, our short, almost cruel, hour hard upon us, I can’t recall hearing any birdsong, tractors in neighbouring fields, or distant cars.
What sticks with me from my time in Thugga, apart from the wondrous physical remains, is the sound of the wind and the ghostly whispers of its citizens in my ears.
It really is one of the most amazing places I have ever travelled to, and the fact that it was deserted was a gift.
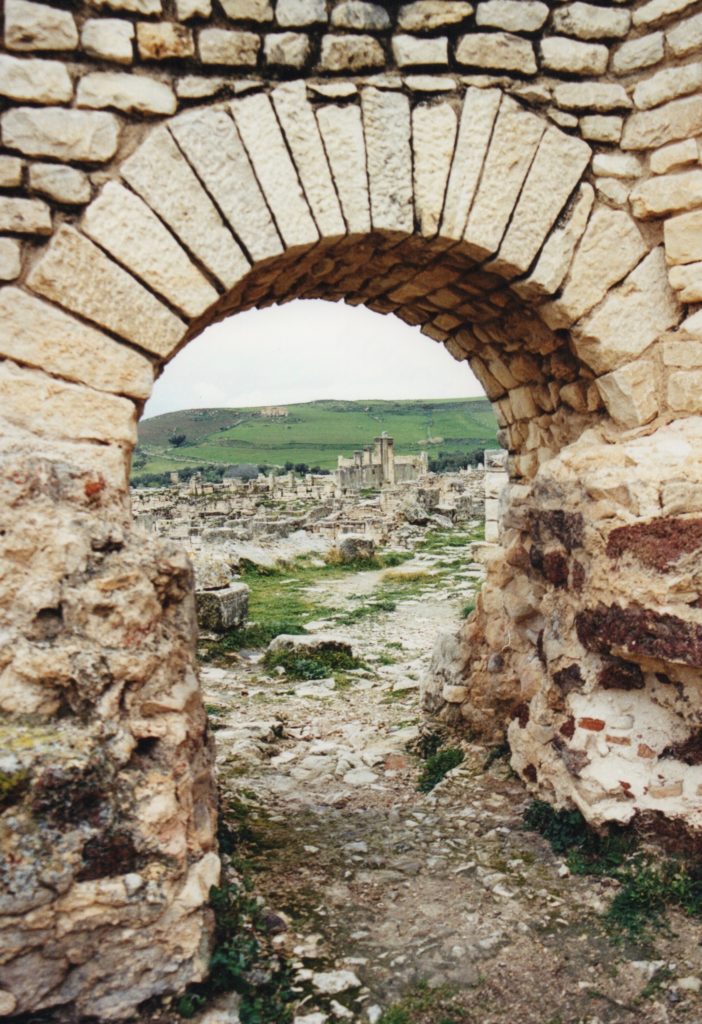

View of the lower town from the baths