It is no secret that one of my favourite places in the world is Tuscany. There are many reasons for this, including the pace of life, the wine, the food, the people and, of course, the idyllic countryside.
There is also the history and archaeology.
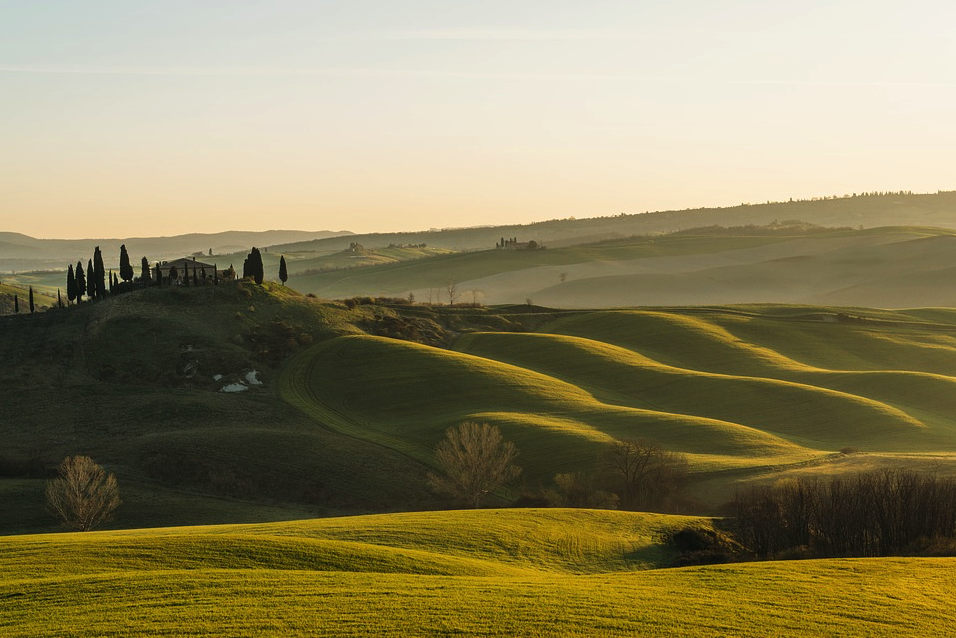
Over the years I have dearly missed Tuscany, especially in the dark days of a long, Canadian winter. I’ve often found myself longing for its rolling hills and spear-thrusting cypresses in a world exploding with colour and light.
This land has been a big part of my life, and the setting for many of my books.
Recently, I was blessed enough to be able to go back to Tuscany after twenty years away, and I was reminded once more why I love it so.
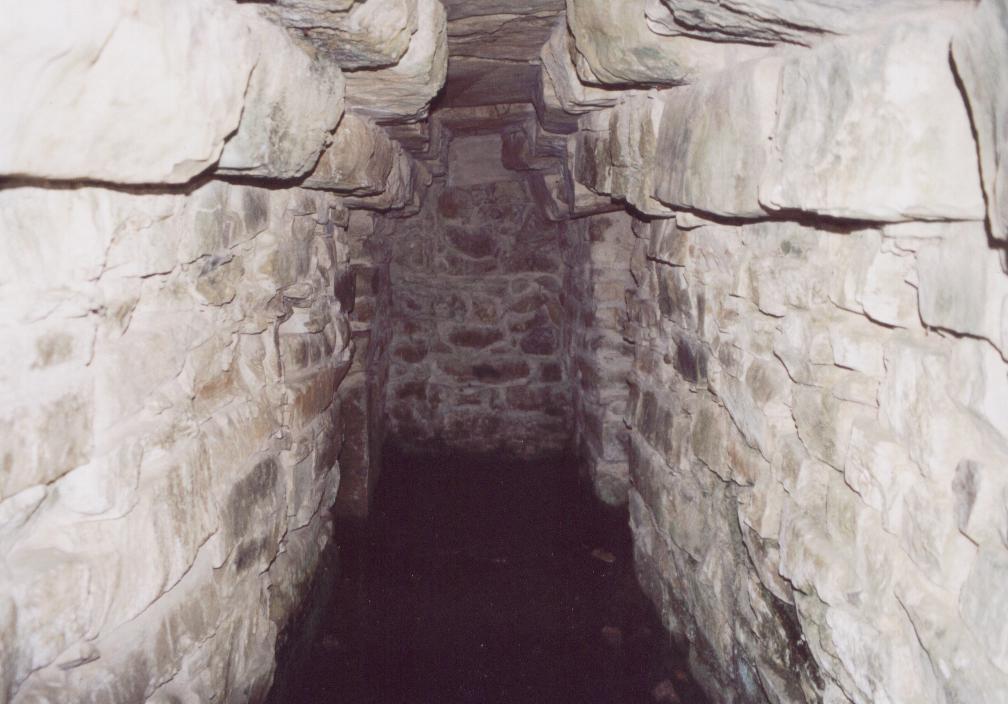
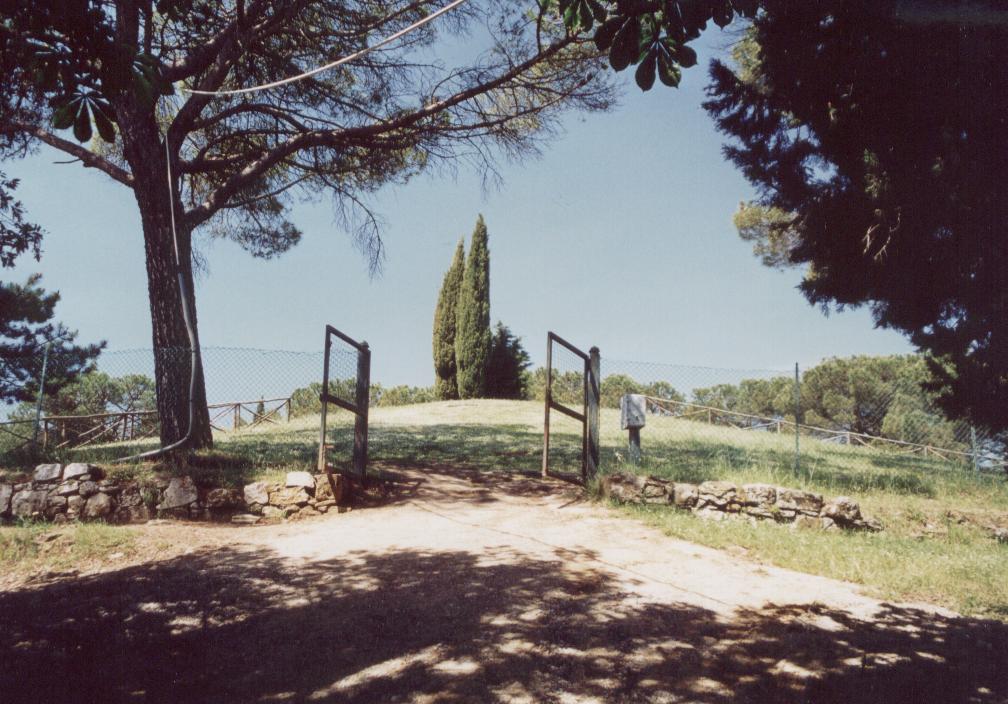
In this blog post, I want to share a bit about my return visit to one site in particular: the Etruscan tomb of Montecalvario.
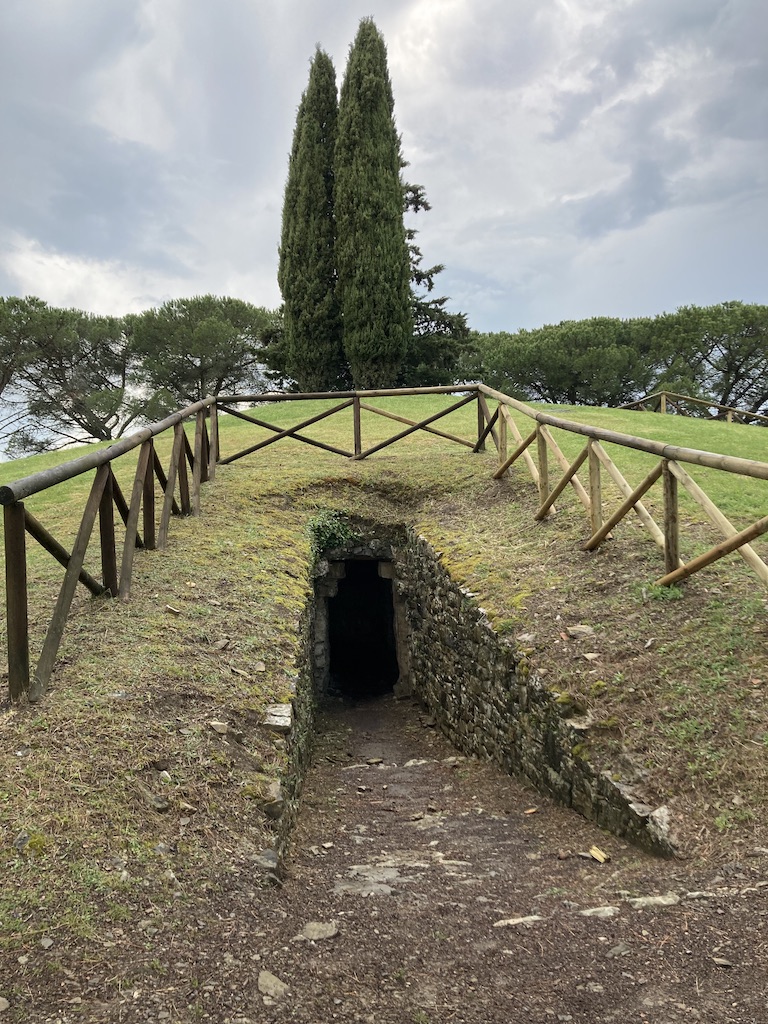

One of the four entrances to the tomb of Montecalvario
For fans of the Eagles and Dragons historical fantasy series, this particular tomb was the inspiration for Metellus family tomb which plays such an important and mysterious role in the books.
The first time I visited this archaeological site, hidden away on a lonely road outside of Castellina in Chianti, I knew right away that I wanted to use it in the novels.
Little did I know, how much of an inspiration it would be!
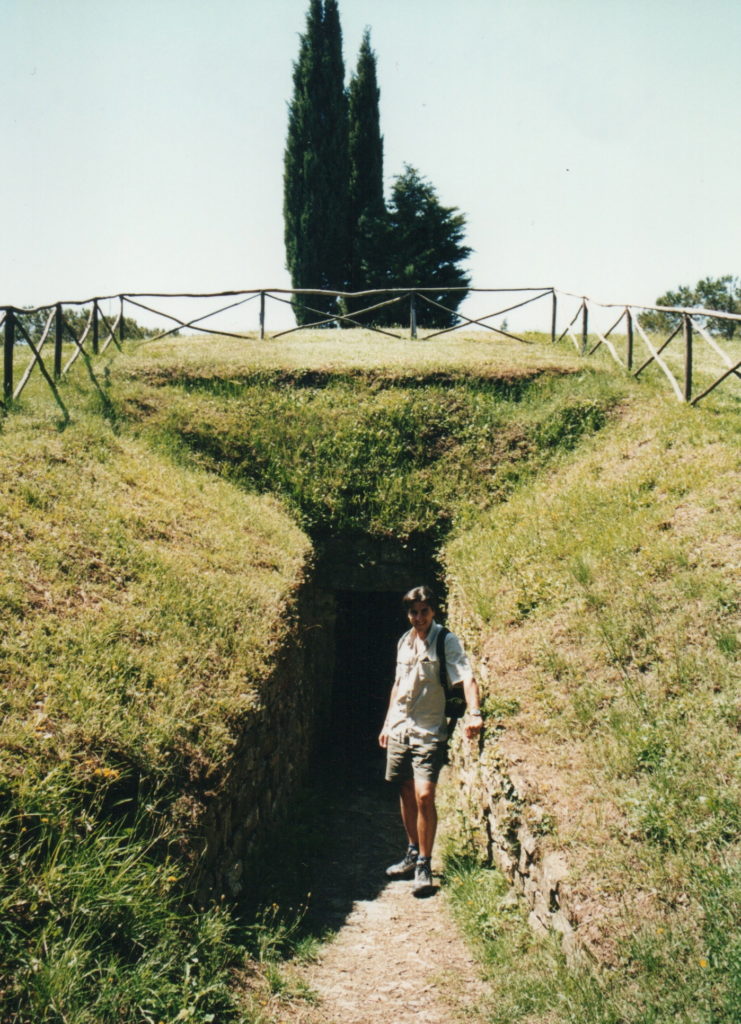

Adam going into the Etruscan tomb at Castellina in Chianti 20 years ago!
Before I get into my return visit, let’s briefly discuss the site.
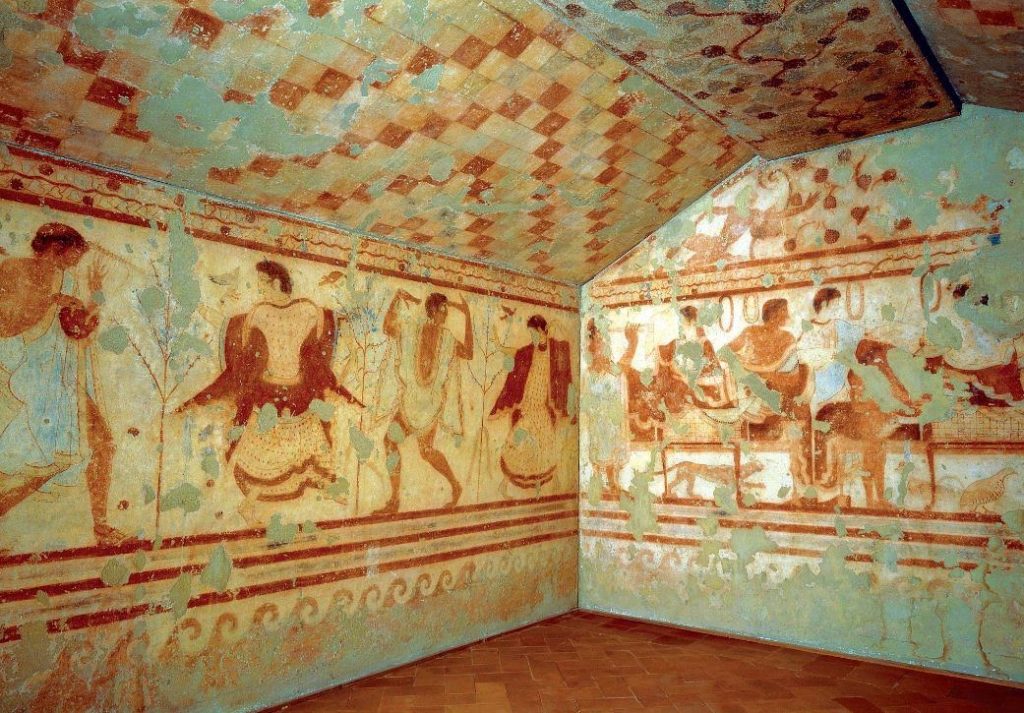
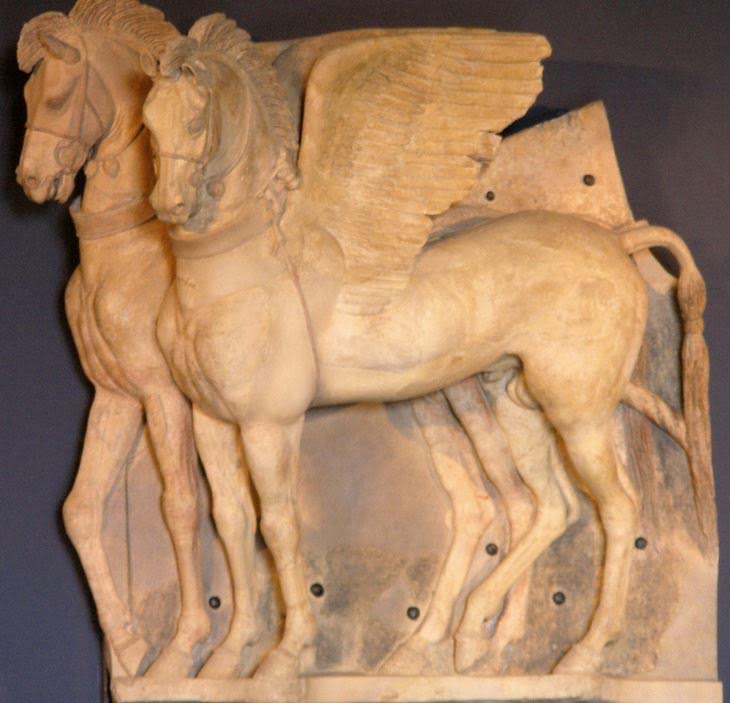
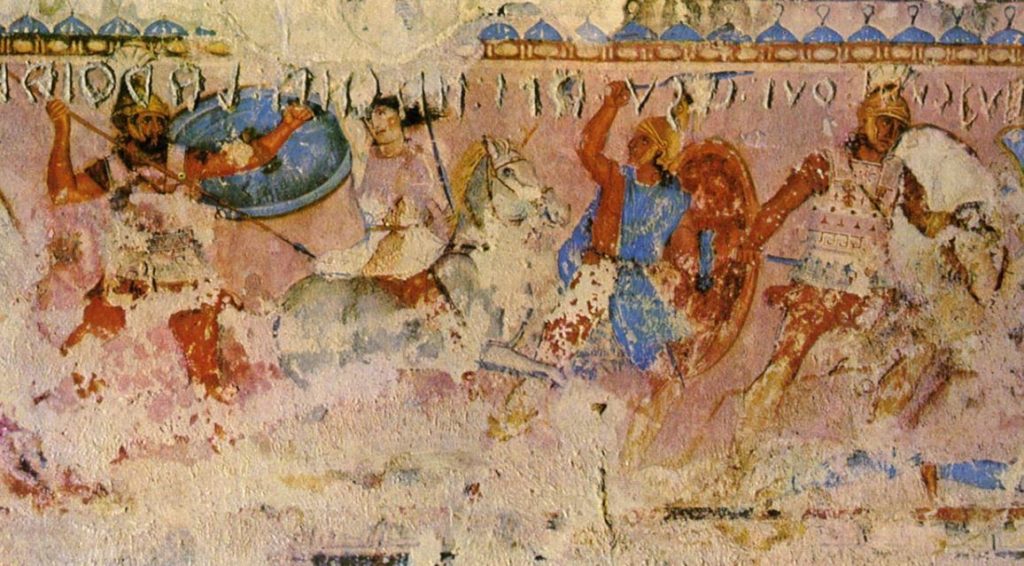
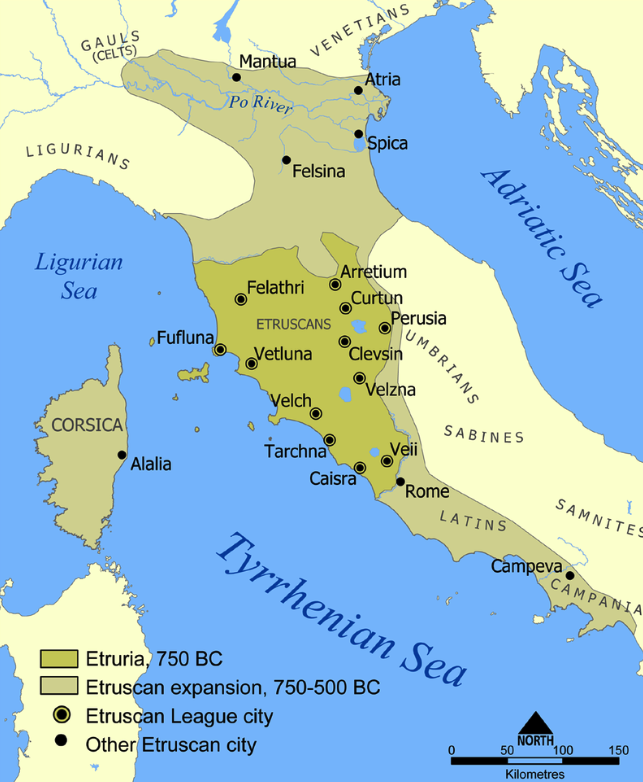
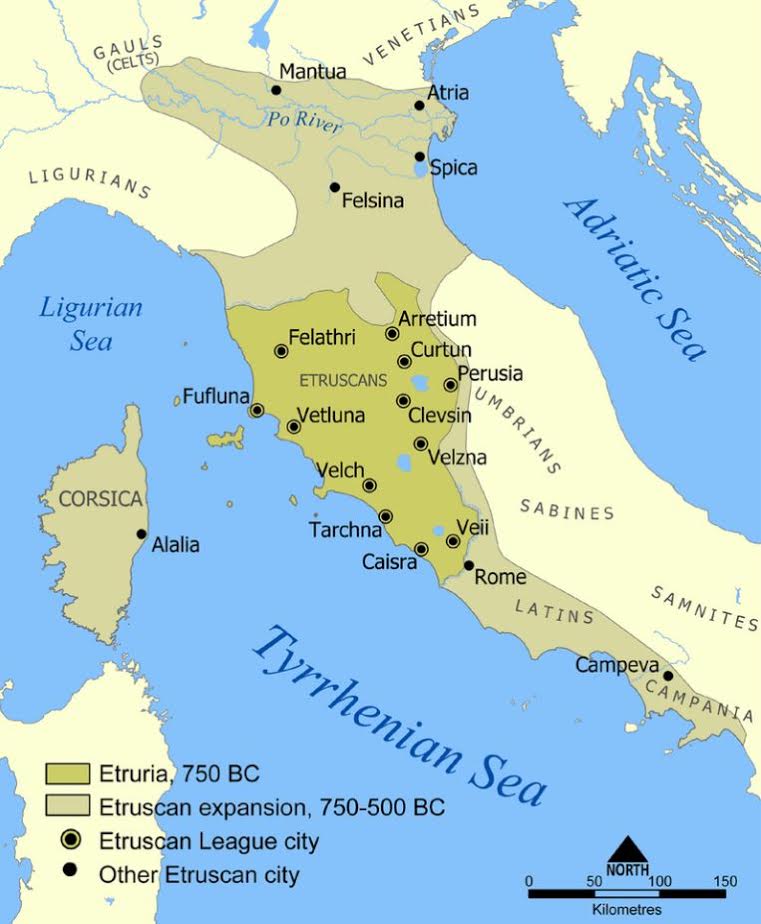
As many of you know, Tuscany, or rather Etruria, is named for the Etruscans, the ancient people who lived and ruled there long before the Romans dominated the Italian mainland. I won’t go into the history of the Etruscan here, but you can read the full blog post entitled The Elusive Etruscans for a brief history of that fascinating people.
Tuscany is full of Etruscan archaeological sites that you can explore, including countless tombs, large and small.
The tomb of Montecalvario is one of them.
It is located in the province of Siena, on the outskirts of Castellina in Chianti, one of the main towns of the Chianti Classico wine region, on the road between Poggibonsi and Radda, the latter being the heart of Chianti Classico.
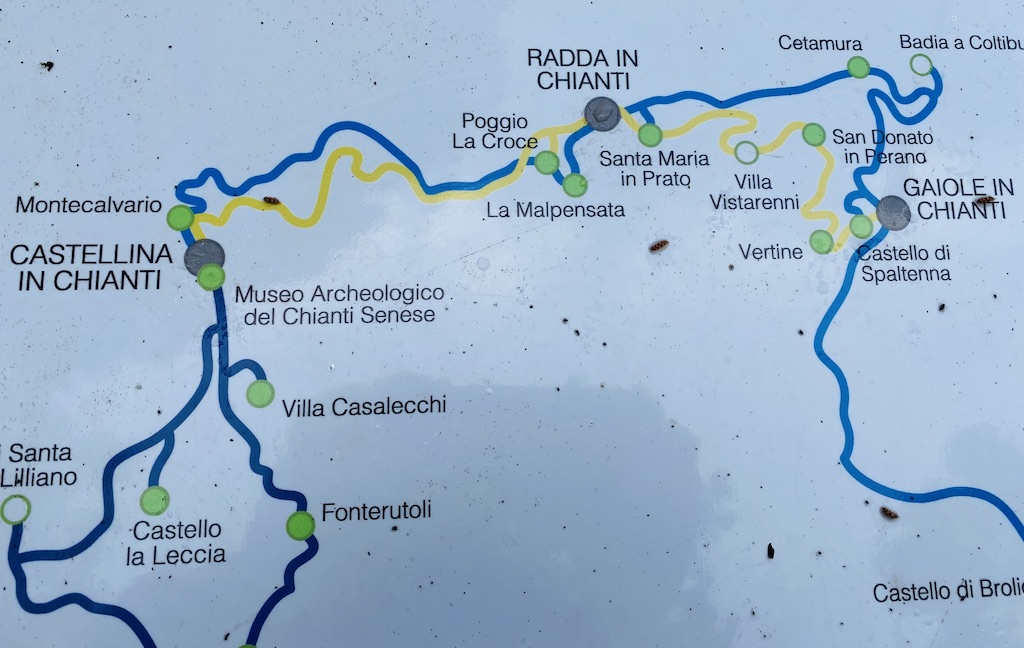
Chianti Classico region with Castellina in Chianti and Montecalvario in the top left corner (from site interpretation)
The hill of Montecalvario is actually named for a Christian chapel that had been built on top of the hill in the Middle Ages which was the last stop on the Via Crucis, or the ‘Way of the Cross’, the ‘Mount of Calvary’ being the site of Christ’s cruxifixction, but also the final stop for pilgrims along this particular trail.
The chapel is gone now, the remains of this majestic tomb visible once more.
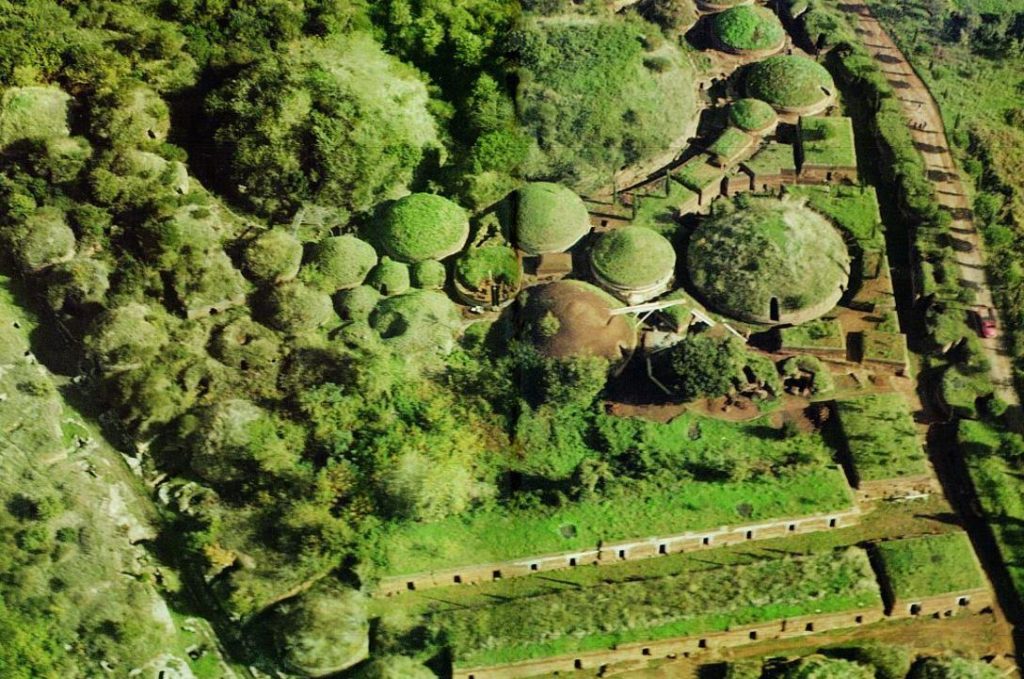
The hill under which the tomb is located is more than fifty meters wide, and was actually discovered by accident in the early 19th century.
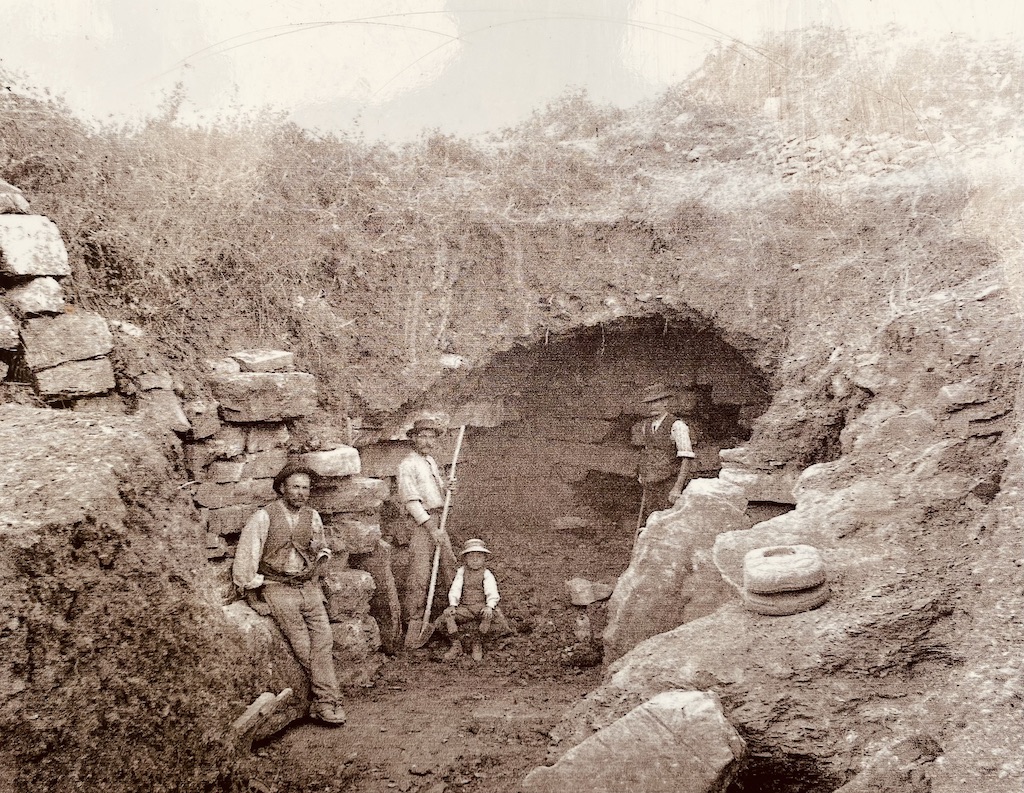

Historic photo of discovery of tomb of Montecalvario (from site interpretation)
What was revealed was an imposing Etruscan funerary monument made up of four chambers aligned with the cardinal directions. Each of the main burial chambers was reached by its own corridor or dromos (Greek for ‘road’) which was flanked by other, small rooms, with the South and West tombs having a more complex, three-chamber layout.
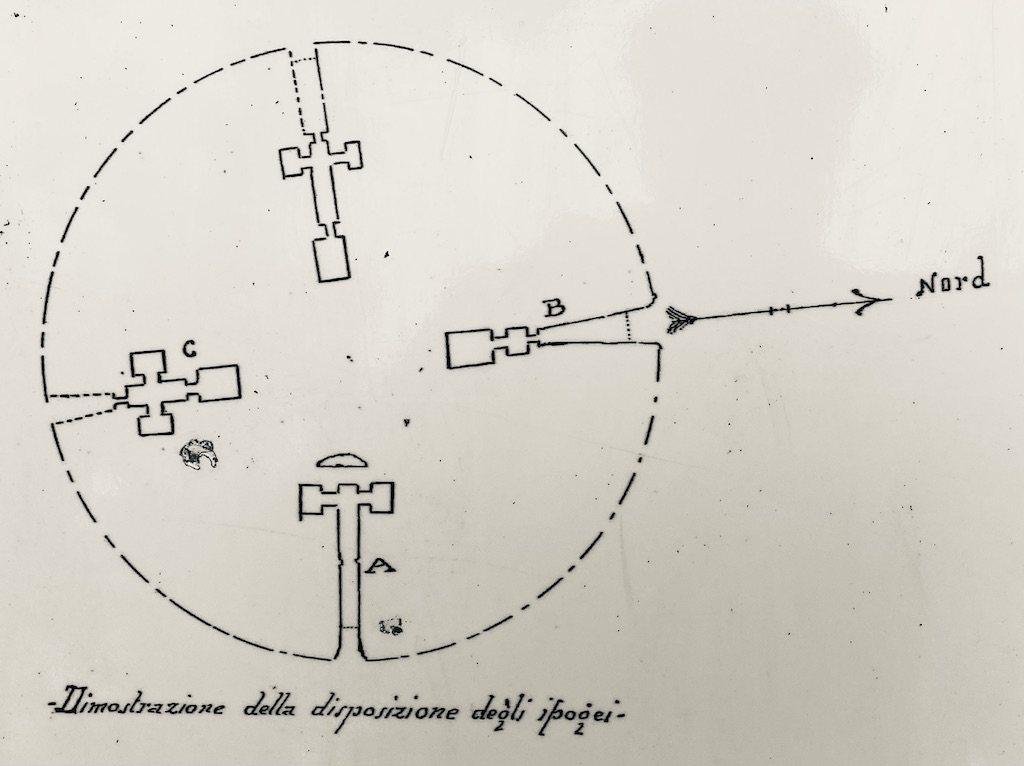
Layout of the tomb of Montecalvario (from site interpretation)
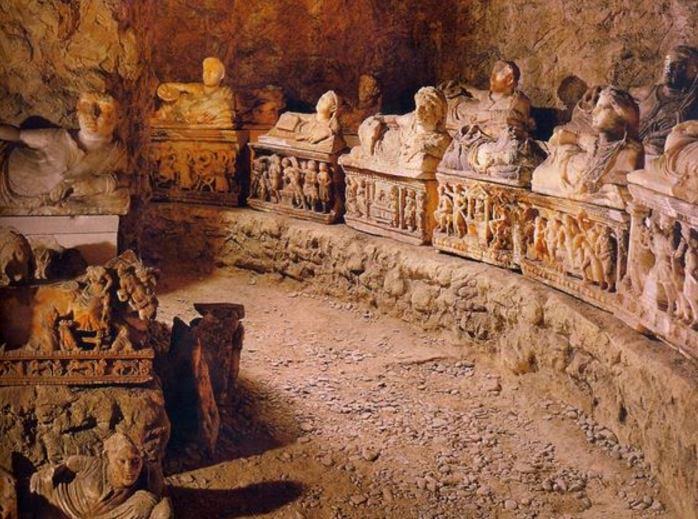
Archaeologists believed the tomb had already been looted by the time it was discovered, but the robbers did not get everything. There were fragments of gold, bronze, iron, bone and ivory scattered about, believed to have been from caskets or urns that had been buried there. In addition, there were the remnants of metal objects, including parts from two chariots and sheets with decorated reliefs on wood panels, also thought to be from the chariots.
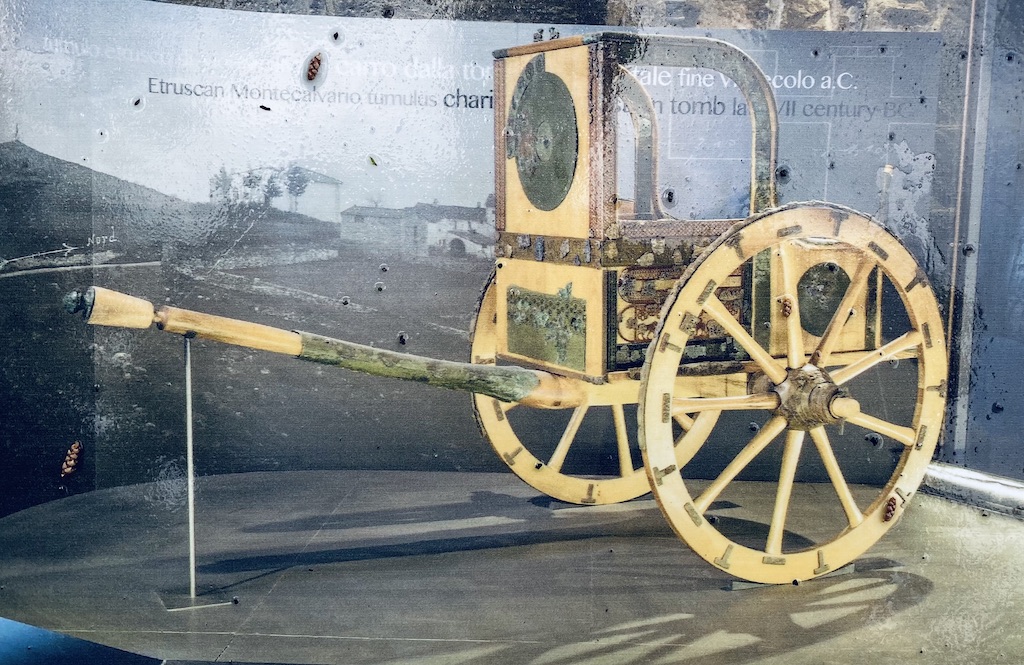

Recreated chariot using finds from the tomb (from site interpretation)
Due to the monumental size of this tomb, and the hint of grave goods that the archaeological finds provide, it is believed that this may have been a princely tomb for members of the ruling families of this region around the seventh and sixth centuries B.C.
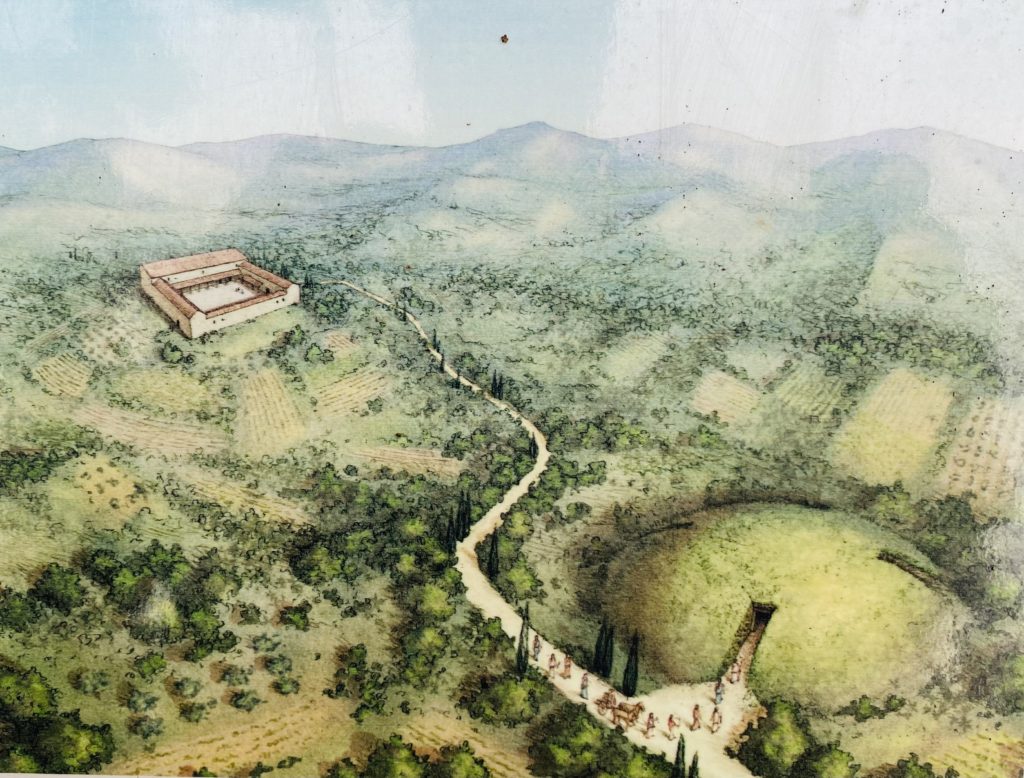

Artist Impression of Tomb of Montecalvario (from site interpretation)
So what was it like to return to this land, this place, after twenty years, after writing about it and imagining it many times over so that it took on a life of its own in my fiction?
It was like walking through a dream.
We had set out early that morning from our agriturismo accommodation south of Siena (under which was an Etruscan tomb!) to drive over the forested hills to the soaring Etruscan fortress town of Volterra, to the southwest of San Gimignano. It was a long, beautiful drive over winding roads across the Tuscan landscape, but the view from Volterra’s heights were well worth it.
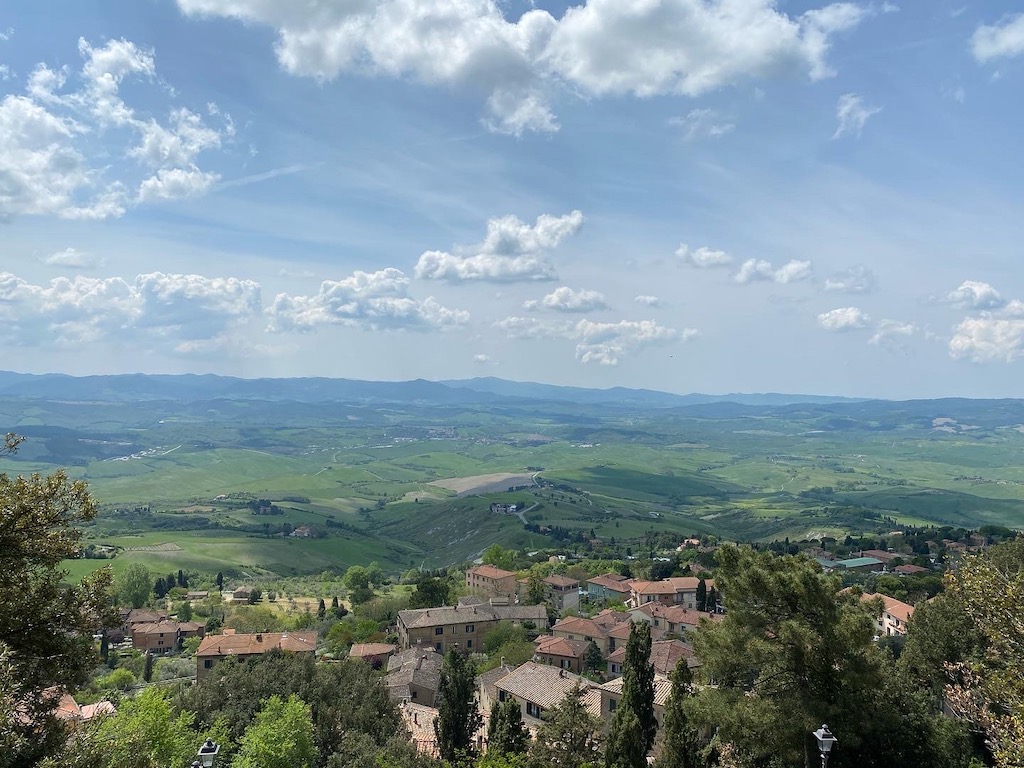

View from the heights of the Etruscan fortress of Volterra
If you ever go to Tuscany, do so in the Spring when the weather is not too hot and the landscape is supremely green and dotted with myriad brilliant poppies bobbing their delicate heads. It is a world bursting with life when Springtime asserts itself for a few weeks before the world turns dry and brown.
From Volterra, we set out on the winding road through the Chianti region, that rich and fertile land over which Florence and Siena fought so viciously during the Middle Ages.
When one thinks of Tuscany, it is difficult not to think of rolling, grassy hills, of lanes and roads dotted with sentry cypresses, but when you come to the Chianti Classico region, you are met with an often steep and mountainous terrain covered in forests where boar and deer roam, and between the hills are smaller valleys in which ancient vines are grown alongside groves of olive.
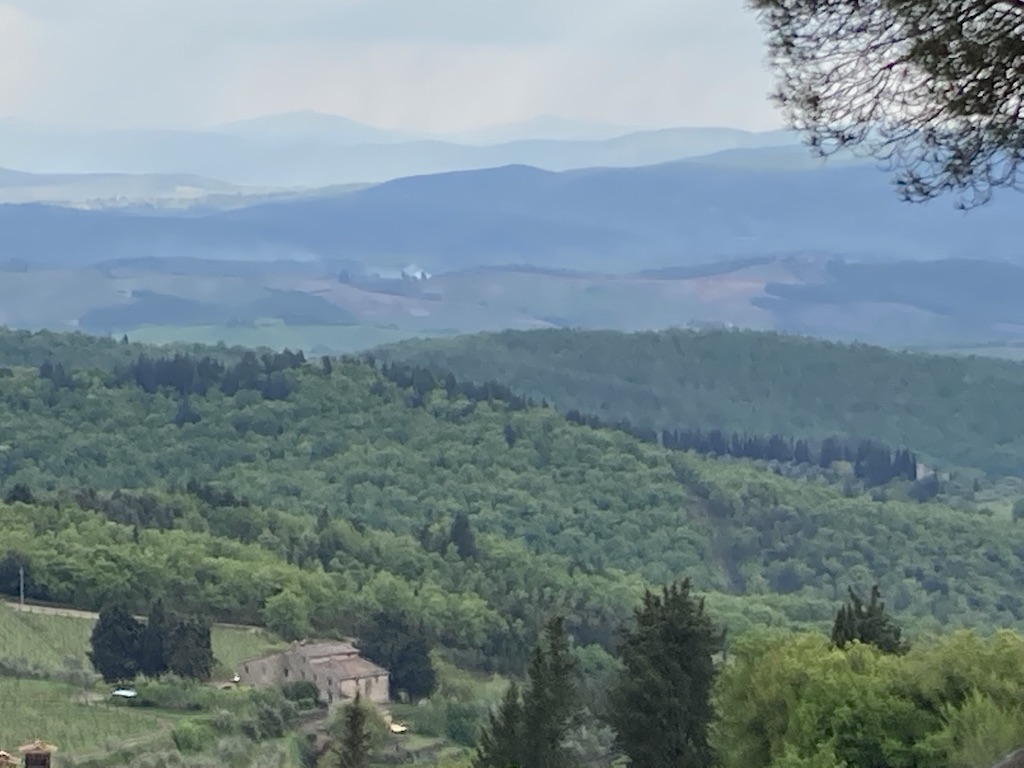

A view of the Chianti hills
I had forgotten how thickly-forested Tuscany could be, and I was happy to be reminded as we drove past the many-towered settlement of San Gimignano in search of Castellina in Chianti and the tomb that had been such an inspiration years before.
As we drove into the Chianti Classico region in search of the tomb, the sky turned dark and a storm threatened us with black clouds and flashes of angry lightning in every direction.
It was quite a change from the hot and sunny heights of Volterra.
From the fortress town of Monteriggioni, we headed northwest through the storm to Castellina in Chianti, passing the headquarters of wineries whose names were warm and familiar to us, even in Canada.
At last, with a pause in the rain, we arrived in Castellina in Chianti, searching for signs to the tomb that seemed to elude even our car’s GPS and Siri herself.
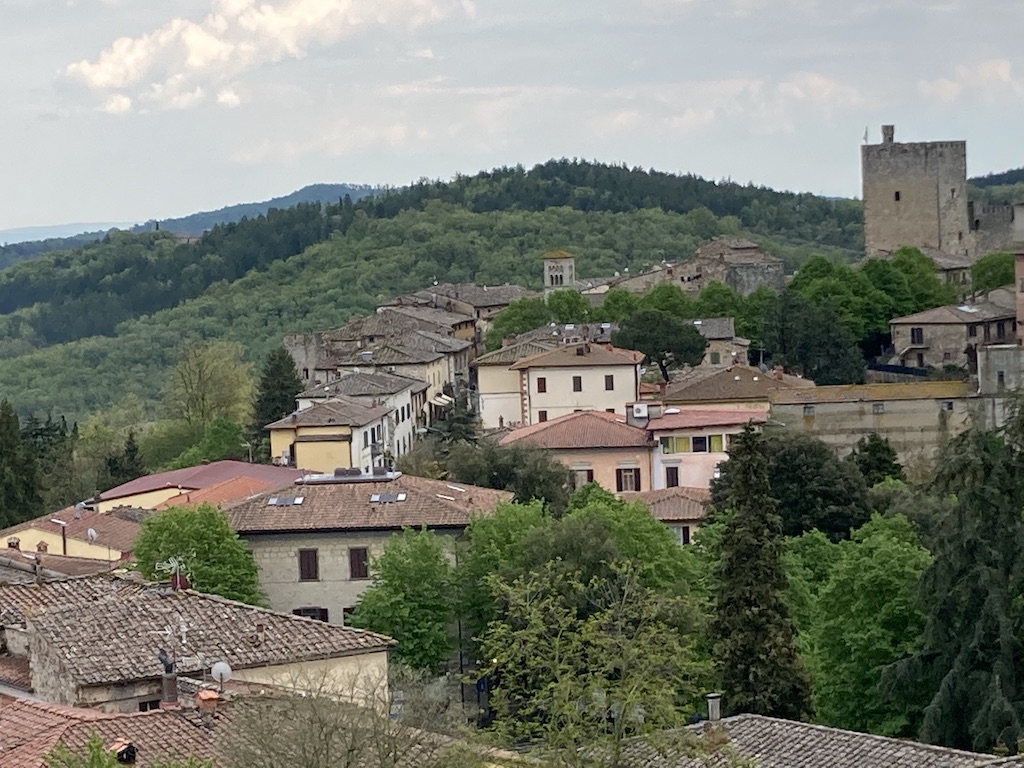

Castellina in Chianti with the Medieval tower to the right.
After taking the wrong road, and having to turn back, we finally arrived at the small parking lot for the tomb of Montecalvario, located on a hill opposite the small 14th century castle from which the town gets its name.
There was no one else around when we parked and began the short walk up the road to the tomb’s entrance. The sky was still dark in places, and a chorus of thunder continued to rumble in the background.
I felt strange walking up the path to the tomb, almost like my character, Lucius Metellus Anguis, when he returns to the family estate after many years away.
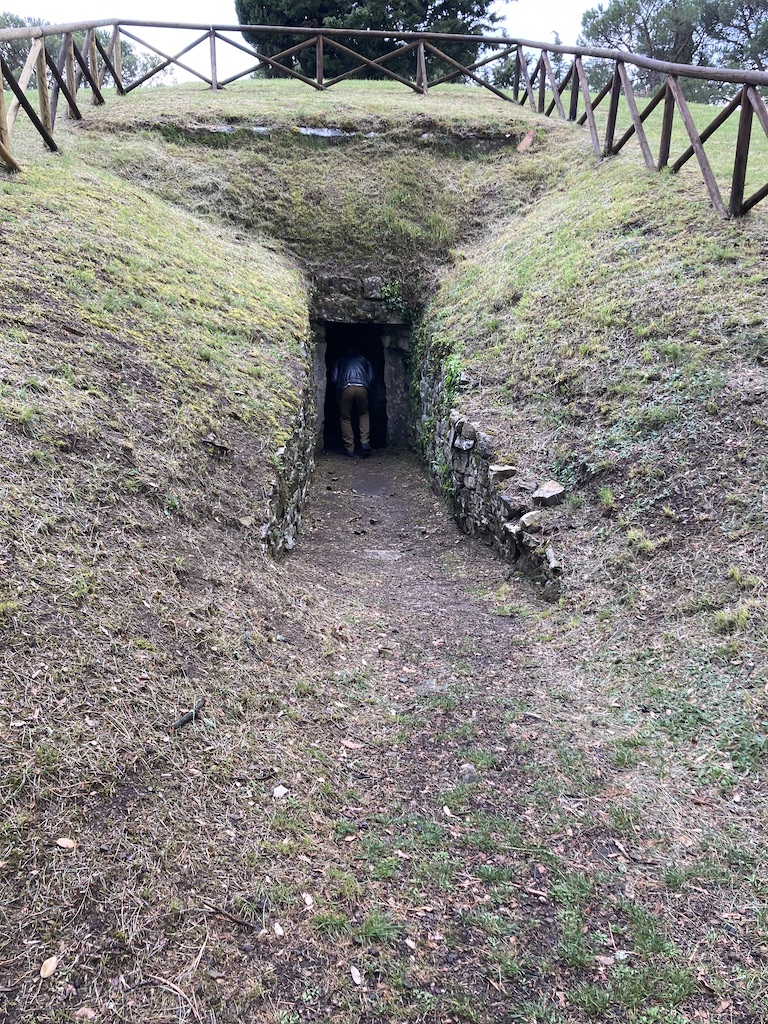

Watch out for snakes! Adam heading into the tomb…
Make no mistake… This Tuscan experience is far different from the Renaissance grandeur of Florence. In the countryside, you step back in time. Beyond the occasional passing car on the road below, all I could hear was the distant thunder, the crunch of my boots on the path, birdsong and the beating of my heart.
As I did years before, I wondered again about the people who had built this tomb high on a hill, about the rituals they might have performed for the dead. If you block out the sound of cars, you can almost hear weeping or prayers to the gods on the air.
I spent more time exploring and documenting the tomb of Montecalvario this time. I headed farther into the tomb than I had dared previously, trying to ignore the fact that snakes could have been hiding within (there weren’t any that I could see, thankfully!).
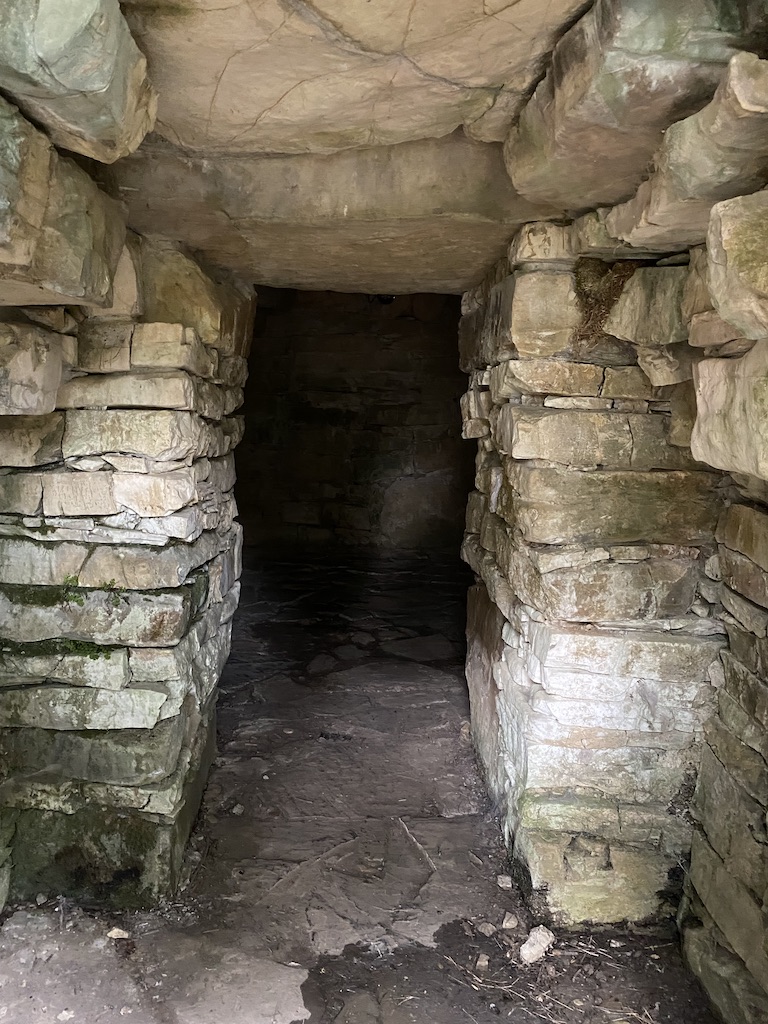

One of the inner chambers
While in the tomb, I was reminded of the fiction I have created around this place, and it came to life in my mind as though it had all really occurred there.
That was, admittedly, a very strange feeling, and one that made me somewhat melancholy. But such is the way of things when you visit realms of the dead. There is a sadness, a thick nostalgia in the air, and I felt both of those acutely as I roamed about the Metellus family tomb of my books.
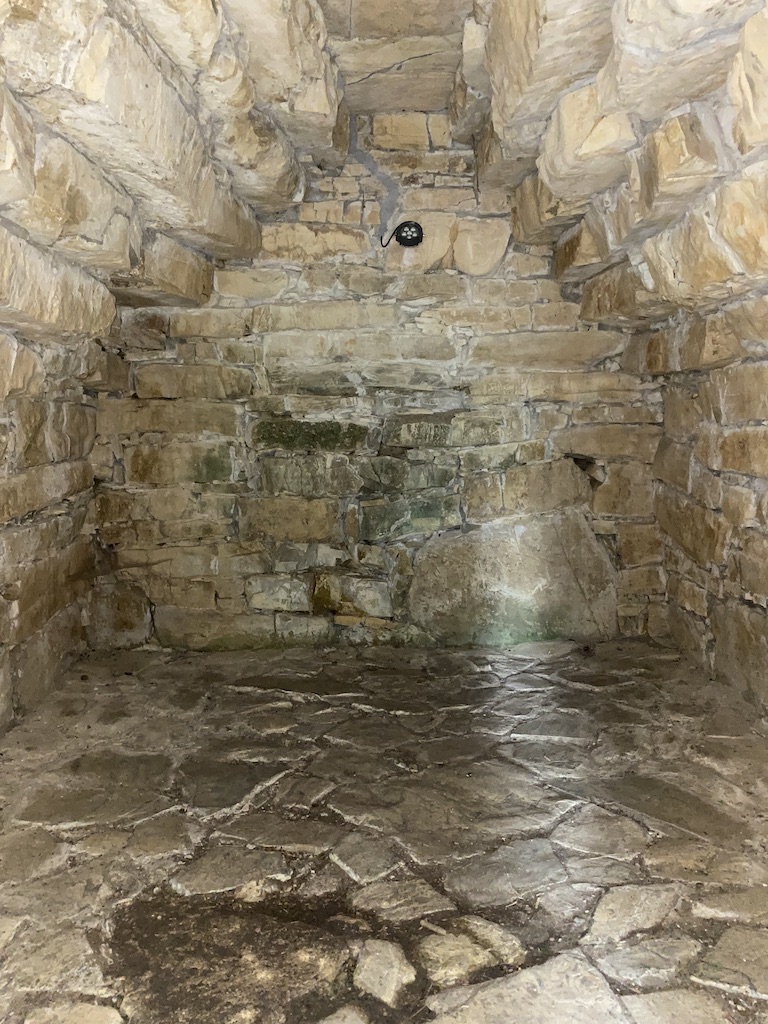

The largest of the inner chambers
After absorbing the site, and taking all of the pictures and video I had planned on taking, it was time to leave that cypress-crowned tumulus.
I walked back down the long path with an occasional backward glance over my shoulder as if bidding farewell to a friend I did not know if I would see again.
Then, it was out of site, and the sky cleared a little over the Tuscan hills as we got back in our modern chariot to wend our way through that ancient land to Radda, our next stop along the way.
It was good to revisit the tomb of Montecalvario after so many years and, despite the myriad joys of our wondrous, ten-day Tuscan interlude, reconnecting with this inspiring place was certainly one of the highlights.
Thank you for reading.
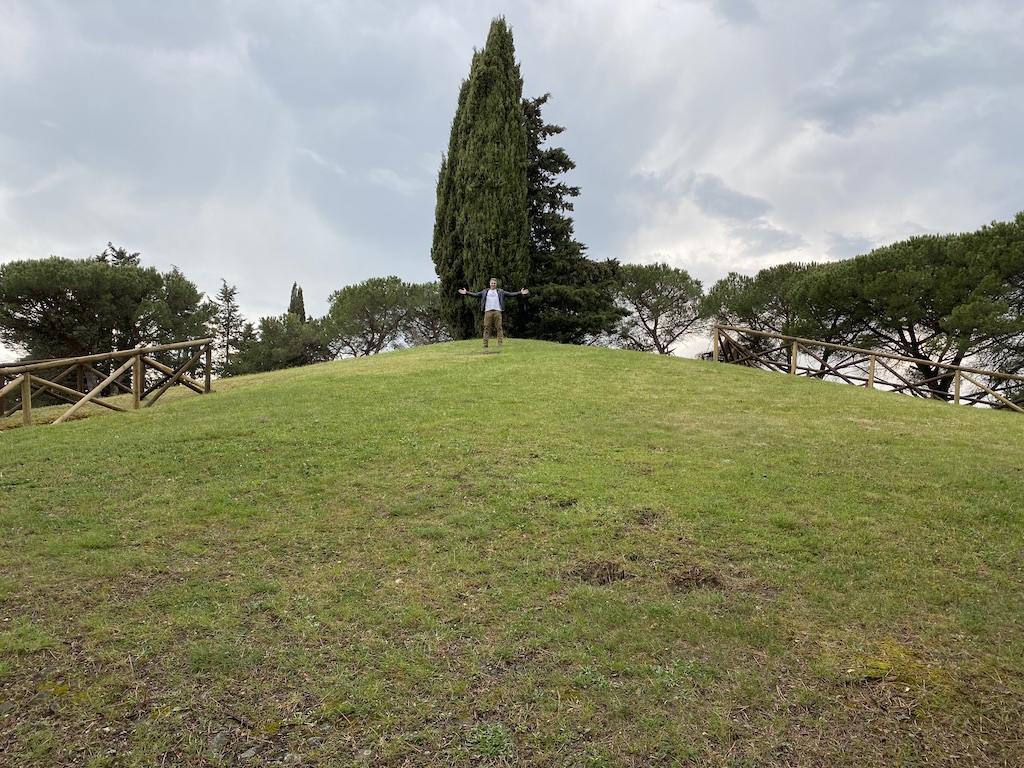

Standing at the top of the tomb.
If you enjoyed this post, you will definitely want to check out the mini-documentary I filmed at this archaeological site of Montecalvario. Just click the YouTube video below on the Eagles and Dragons Publishing YouTube channel to watch it.
For those of you who are interested in starting the #1 best selling Eagles and Dragons historical fantasy series, you can get the first prequel novel, The Dragon: Genesis, for FREE by clicking HERE. The tomb of Montecalvario figures largely in the book.
We hope you enjoy the book and the video, The Etruscan Tomb of Montecalvario: A Short Tour below: