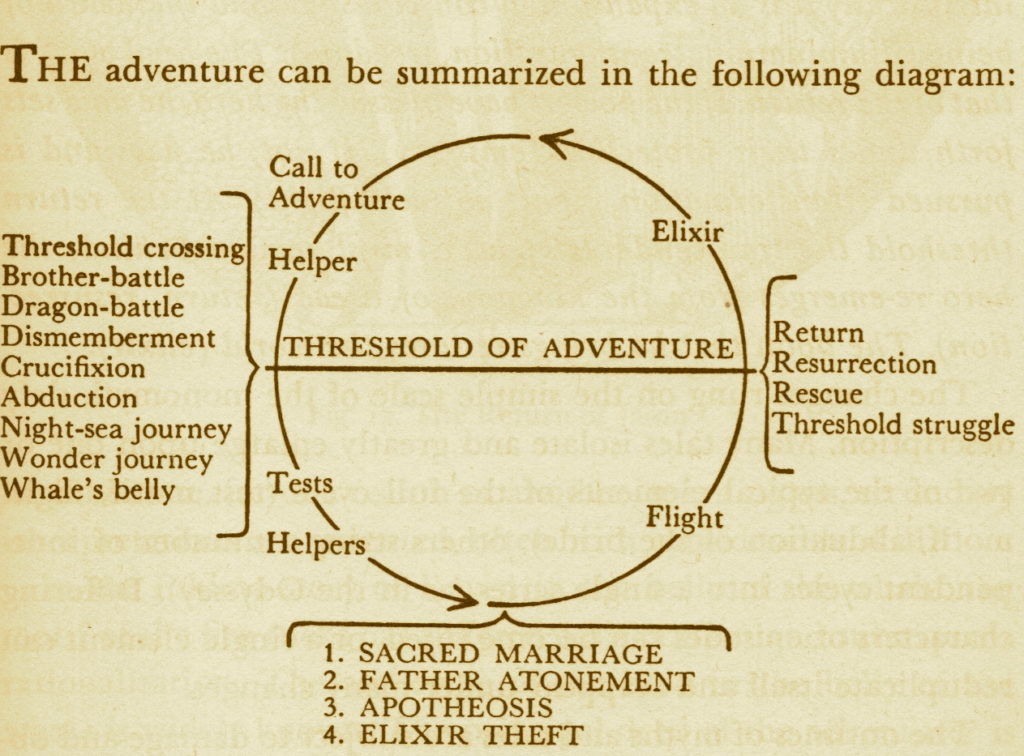
Salvete, readers and history-lovers!
Welcome to the fifth and final part in this blog series on The World of The Stolen Throne.
I hope you have enjoyed these posts about the research, history and myth that inspired the creation of this latest Eagles and Dragons historical fantasy novel. If you missed last week’s post about Tintagel Castle in Cornwall, you can check it out HERE.
As with all other books in the Eagles and Dragons series, The Stolen Throne has elements from ancient Greek and Roman religion and mythology. However, this book also delves into Celtic myth and legend which makes for an interesting addition to the series.
In Part V of The World of The Stolen Throne, we’re going to be taking a brief look at the realm of Annwn, the sort of place it was, and some of the more prominent traditions around it.
If you’ve already read The Stolen Throne, you will know that Annwn plays a large role in the story, but what exactly was this mysterious place that plays such a central and awe-inspiring role in Celtic tradition?
Let’s step into this otherworld to find out…

Elysium, or Aeneas Finding His Father at the Elysian Fields (Sebastiaen Vrancx, between 1597 and 1607)
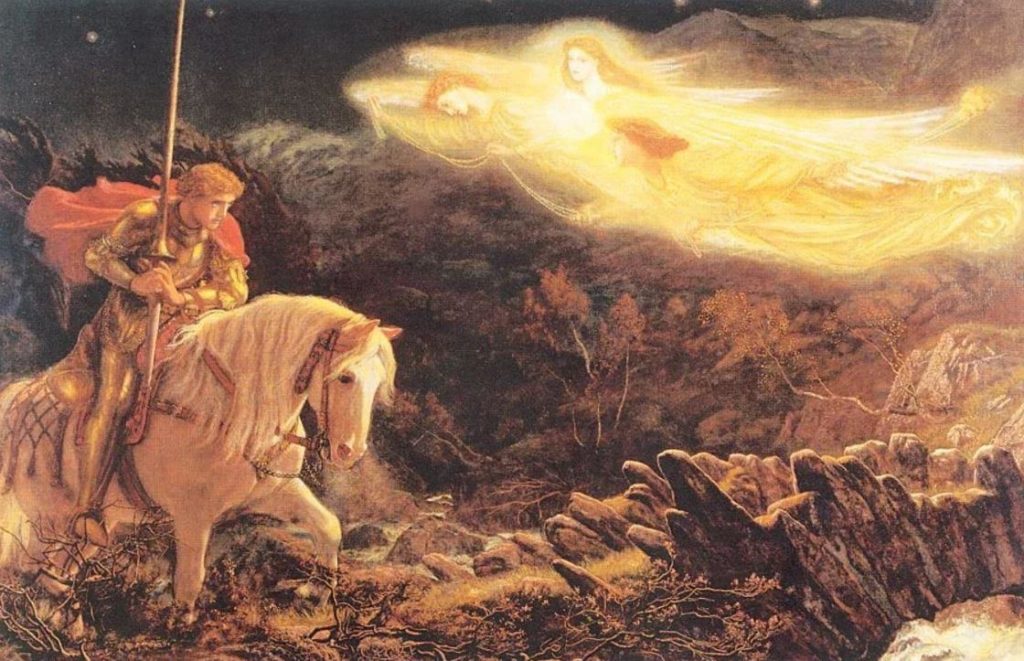
In ancient Celtic mythology and religion, especially Welsh traditions, Annwn (pronounced ‘Ann-win’) is the Otherworld. Annwn is the faery world, a place similar to Elysium in ancient Greek and Roman traditions, or Paradise in Christianity. It is often a place of peace and plenty, there is no death, disease or hunger. It is a land of eternal youth.
In some traditions however, it can be a place of conflict, or a prison to outsiders. It is a land of mystery where all is not as it seems.
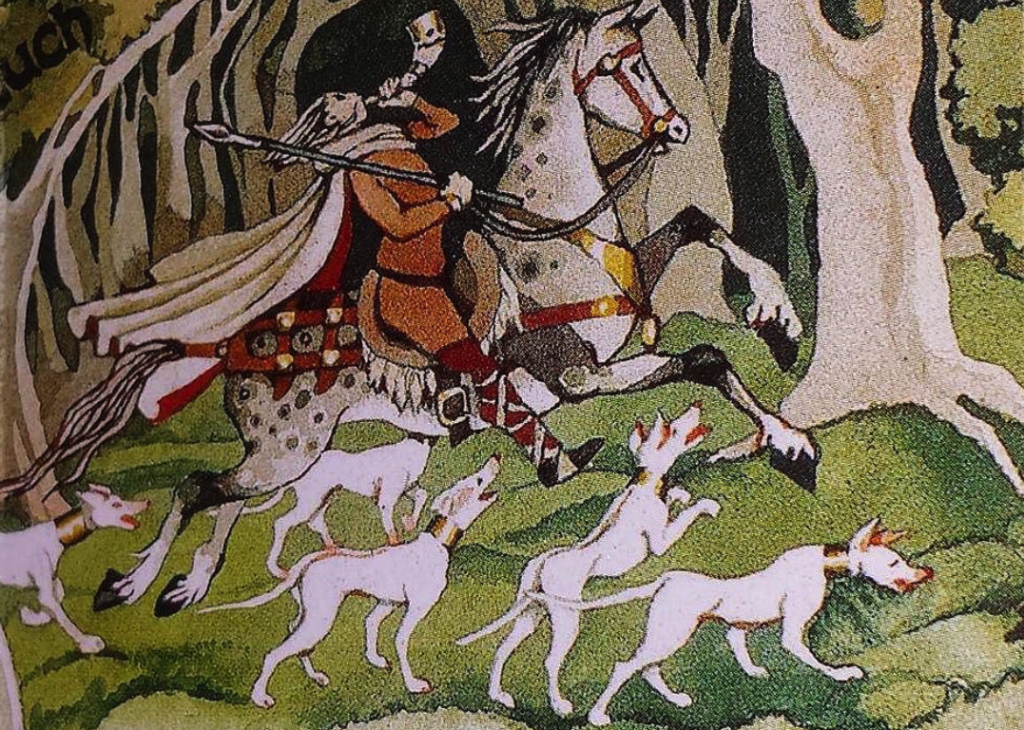

Arawn, Lord of Annwn, with his otherworldly hounds
There are two prominent lords of Annwn in ancient traditions: Arawn, and Gwyn ap Nudd.
And he [Pwyll] beheld a glade in the wood forming a level plain, and as his dogs came to the edge of the glade, he saw a stag before the other dogs. And lo, as it reached the middle of the glade, the dogs that followed the stag overtook it and brought it down. Then looked he at the colour of the dogs, staying not to look at the stag, and of all the hounds that he had seen in the world, he had never seen any that were like unto these. For their hair was of brilliant shining white, and their ears were red; and as the whiteness of their bodies shone, so did the redness of their ears glisten. And he came toward the dogs, and drove away those that had brought down the stag, and set his own dogs upon it.
And while he was setting on his dogs, he saw a horseman coming towards him upon a large light-grey steed, with a hunting horn round his neck, and glad in garments of grey woollen in the fashion of a hunting garb. And the horseman drew near and spoke unto him… ‘A crowned King am I in the land whence I come’… ‘Arawn, a King of Annwn am I’…
(Pwyll Lord of Dyfed, The Mabinogion; trans. Lady Charlotte Guest)
Arawn, Lord of Annwn, appears in the first branch of the Welsh Mabinogi, Pwyll, Lord of Dyfed.
Of the four branches, Pwyll, Lord of Dyfed is my absolute favourite. I have never tired of reading it since I first studied it in university. Not only is it full of magic, love, battles, monsters, and tales of honour and betrayal, but it’s also a perfect illustration of Celtic archetypes (you can read more about Celtic literary archetypes HERE.) Here is the story in brief:
Pwyll, a mortal man, is a lord of Dyfed who comes into contact with Arawn, a lord of Annwn, the Celtic Otherworld. The two become friends and switch places for a year so that Pwyll can help Arawn defeat a foe in his own world. Pwyll succeeds and becomes ‘Head of Annwn’. While he is away, Arawn rules justly and fairly in his place, and Pwyll’s subjects ask him to continue the good rule upon his return, which he does.
One of the purposes of the Mabinogi tales was to serve as teaching texts for Welsh princes, and the tale of Pwyll is a good example, for Arawn is an ideal lord whose actions instruct Pwyll in ideal rule.

Artist impression of Gwynn ap Nudd at the hunt
As Lord of Annwn, Gwyn ap Nudd, is different from Arawn. He is a darker figure in Celtic myth and legend who appears later in Arthurian traditions. He is the Faery King and Lord of Annwn. He is an Underworld god. However, he does not always remain in Annwn.
The time of year during which The Stolen Throne takes place is Samhain, the ancient Celtic new year, and what we know today as ‘Halloween’. Some of the ancient traditions around Samhain – a very sacred time of year – was the burning of bonfires to keep evil spirits at bay, the harvesting of hazelnuts and of apples, both fruits of the Otherworld. One fascinating tradition was apparently to peel apples and toss the peels over the shoulder or into a fire as offerings.
Samhain was a time when the veil between worlds was at its thinnest, and where strange things happened at borders or thresholds, those in-between places of the world. Fairies were believed to be abroad, taking captives before going to their winter barrows with them.
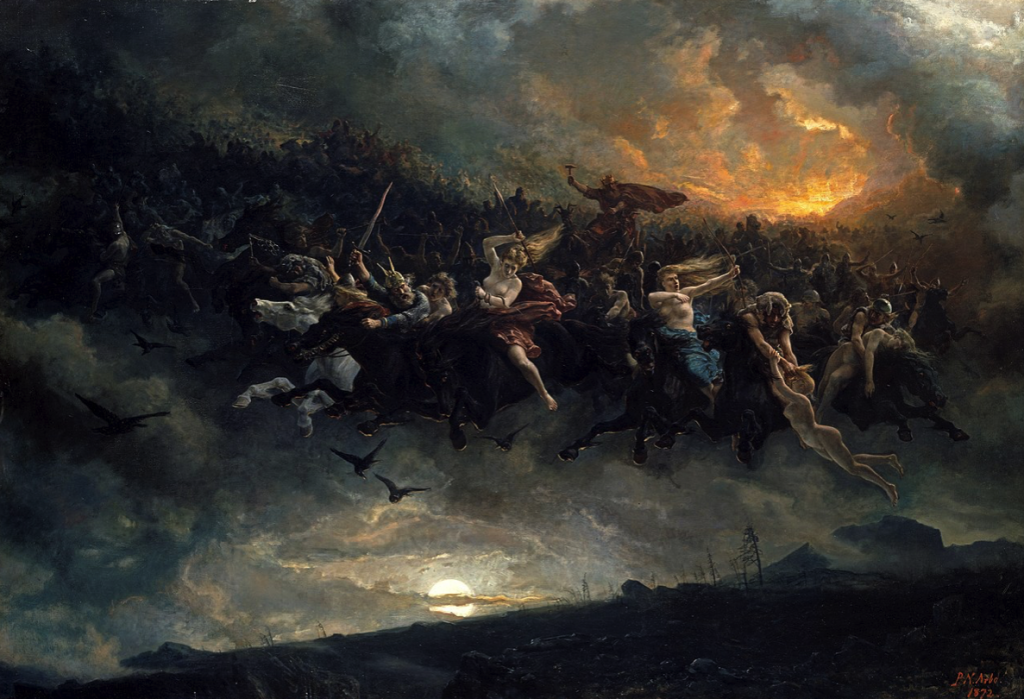

The Wild Hunt (1872) by Peter Nicolai Arbo
Gwyn ap Nudd was also believed to be abroad at Samhain as the doors of Annwn opened and he led the Wild Hunt across the land, terrifying the living with the sound of otherworldly hunting horns and the baying of his hounds.
There were several gates to Annwn, one of them being Glastonbury Tor, which we have looked at in a previous blog series. Forests also served as liminal spaces where one could go from the mortal to the immortal realm. However, it was not only the souls of the dead, or magical beings who could pass through these gates.
In the ancient traditions, though Annwn was the Otherworld or faery realm, it was possible for mortals to travel there in certain circumstances, and then return to the mortal world again, if they were lucky. The tale of Pwyll is the obvious example, but there are others.

The Book of Taliesin (Wikimedia Commons)
In Arthurian romance, there is a tradition of the wicked Melwas imprisoning Guinevere on Glastonbury Tor. Arthur rides to the rescue, attacks Melwas and saves Guinevere. This particular story mirrors an episode in Culhwch and Olwen, one part of the Welsh Mabinogi, in which Gwythyr ap Greidawl attempts to save Creiddylad, daughter of Lludd, whom he is supposed to marry, from Gwyn ap Nudd himself.
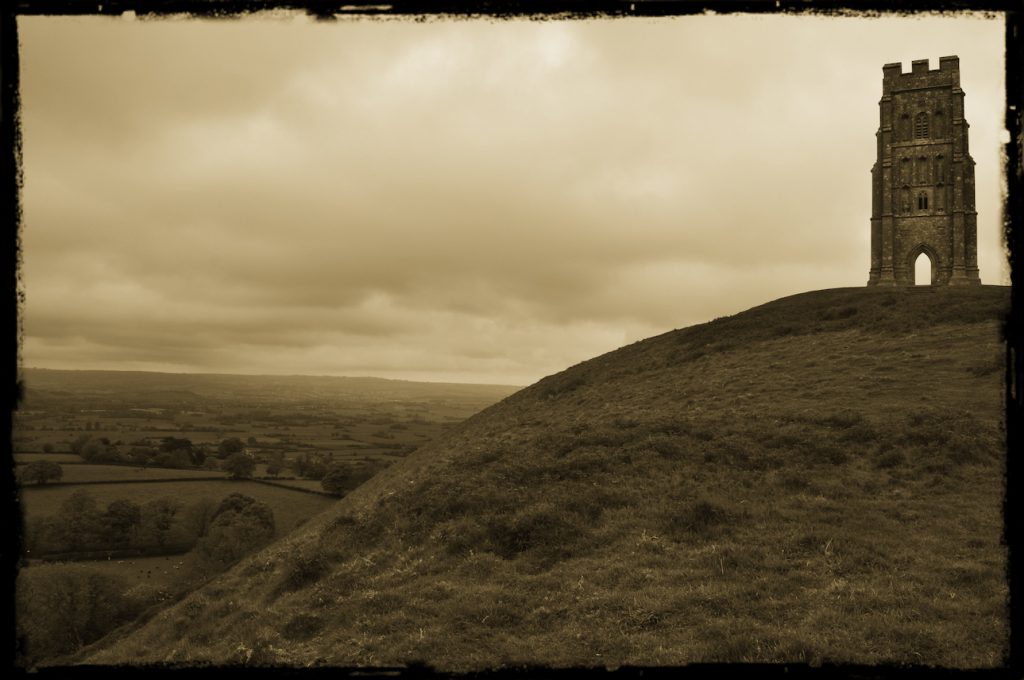

Glastonbury Tor – Gateway to Annwn
Another even more fascinating Arthurian connection can be found in a pre-Christian version of the ‘Quest of the Holy Grail’, called the ‘Spoils of Annwn’ which was found in the ‘Book of Taliesin’. In this tale, Arthur and his companions enter Annwn to bring back a magical cauldron of plenty.
… And before the door of hell
lamps burned.
And when we went with Arthur,
brilliant difficulty,
except seven
none rose up
from the Fortress of Mead-Drunkenness…
… Beyond the Glass Fortress they did
not see
the valour of Arthur.
Six thousand men
stood upon the wall.
It was difficult
to speak
with their sentinel.
Three fulness of Prydwen [Arthur’s ship]
went with Arthur.
Except seven
none rose up
from the Fortress of Guts…
(excerpt from The Spoils of Annwn, the Book of Taliesin; trans. Sarah Higley)
This is a fascinating and mysterious poem (you can read the full translation HERE). The debated location of the castle Arthur and his men lay siege to aside, we see here again that a voyage into Annwn is not one of peace or plenty, but of strife. There is a war between the worlds, no doubt encouraged by later Christian writers of Arthurian romance.

The Cauldron (E. Wallcousins, 1912)
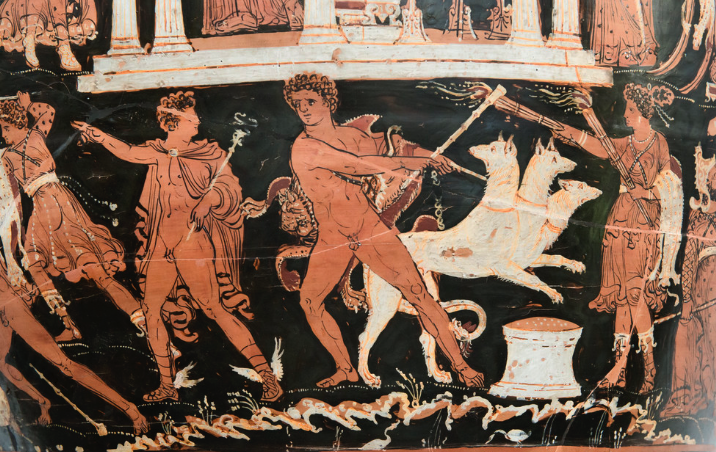
There is an ancient tradition of heroes making a journey to the Otherworld or Underworld. It wasn’t just Herakles and Odysseus who did so. Pwyll and Arthur too journeyed there, and others. The tradition of mortals crossing into another realm for some feat of strength or adventure, or even a painful experience, is longstanding.
It is also supremely fascinating to write about.

Herakles captures Cerberus in the Underworld, wtih Hermes guiding him