In this seventh post of The World of Heart of Fire, we are going back to the legend of Pelops and Hippodameia, to a time of gods and heroes.
In the previous post, we looked at boxing in the ancient Olympics and how it differed from today.
In this post we are going to explore the sport of ancient chariot racing, an event that is central to the story of Heart of Fire.

Pelops and Hippodameia racing
The foundation myth of the Olympic Games as it relates to Pelops involves the latter’s chariot race from Olympia to Argos, for the hand of Hippodameia in marriage.
Hippodameia’s father, Oinomaus, was apparenlty quite brutal, and every suitor who came for his daughter’s hand in marriage had to try and beat him in a chariot race across what became known as the Peloponnese, or, the ‘Isle of Pelops’.
Eighteen suitors had raced Oinomaus and been killed by him before Pelops laid down his challenge.
According to the legend, Pelops was trained by Poseidon himself about horses, and given a team of swift-footed horses by the god so that he could succeed in beating Oinomaus.
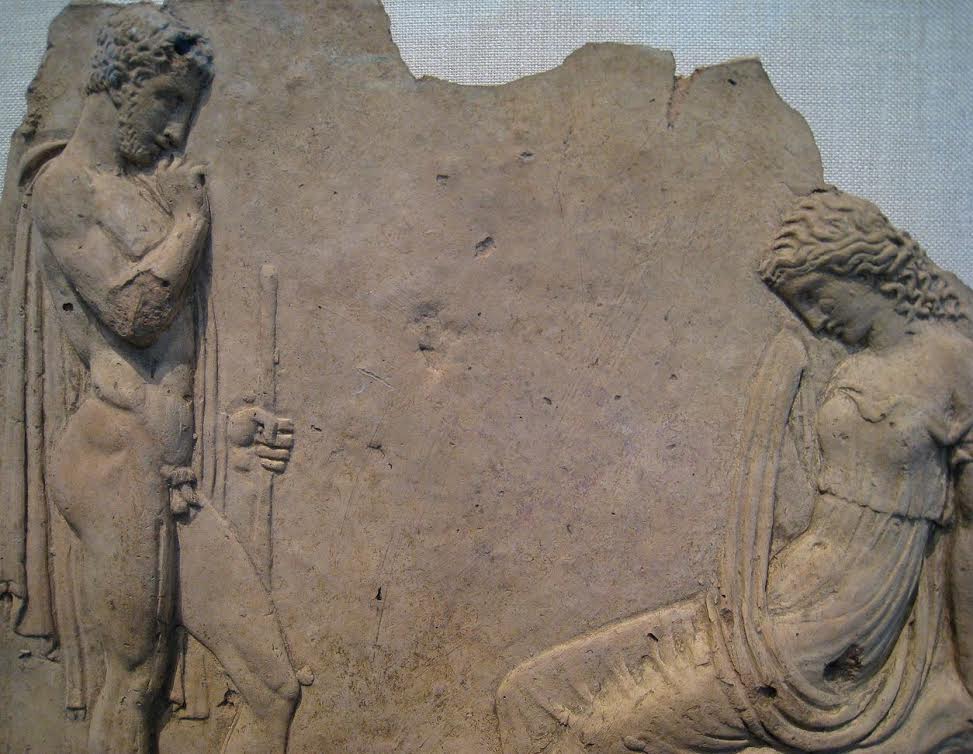
In order to ensure that Oinomaus did not win, Hippodameia also convinced her father’s man, Myrtilus, to replace the wheel pins with wax ones so that Oinomaus’ chariot would crash.
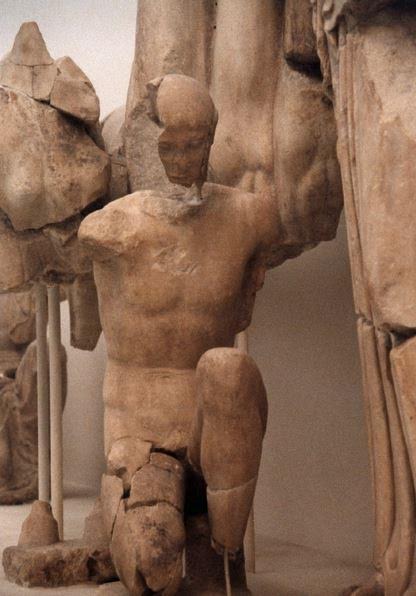

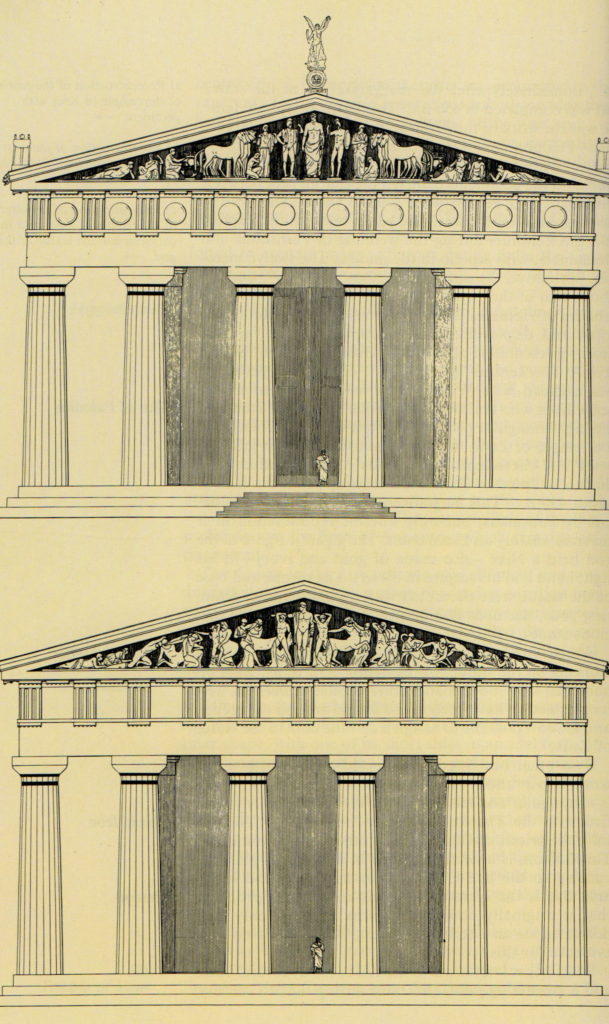
Figure of Mytilus on East Pediment of Temple of Zeus – See him kneeling to switch the pins of Oinomaus’ chariot wheel?
The Theban, epinikion poet, Pindar, describes the contest:
Then he [Pelops] said unto him: ‘Lo now, O Poseidon, if the kind gifts of the Cyprian goddess are anywise pleasant in thine eyes, restrain Oinomaus’ bronze spear, and send me unto Elis upon a chariot exceeding swift, and give the victory to my hands. Thirteen lovers already hath Oinomaus slain, and still delayeth to give his daughter in marriage. Now a great peril allopath not of a coward: and forasmuch as men must die, wherefore should one sit vainly in the dark through a dull and nameless age, and without lot in noble deeds? Not so, but I will dare this strife… (Pindar, Olympian Ode 1)
After Pelops’ victory, it was said that he began the Olympic Games in thanks to Zeus for his win. Another theory is that the Olympics were begun by Pelops as funeral games for the deceased Oinomaus who died in the race, or for Myrtilus, whom Pelops had killed.
Whatever the ‘truth’ about these Olympic beginnings, one thing is certain – Chariot racing and horses had a deep connection to the Games.
As far as we know, the very first event of the Olympic Games was the stade race sprint. As mentioned before, boxing became a part of the Olympic roster in the fourteenth Olympiad.
So when did chariot racing become a part of the Games?
It is generally agreed that chariot racing first made an appearance in the ancient Olympics during the twenty-fifth Olympiad in the year 680 B.C., almost three hundred years before Heart of Fire takes place.

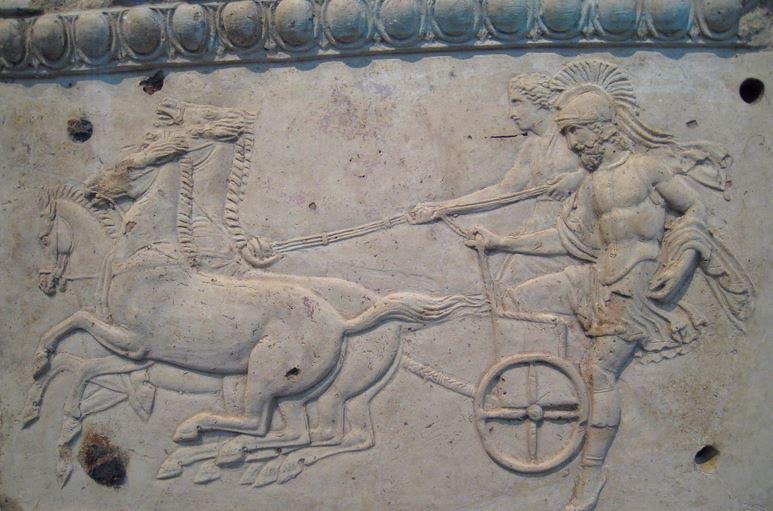
Olympic Chariot Race – The Most Popular Event of the Games
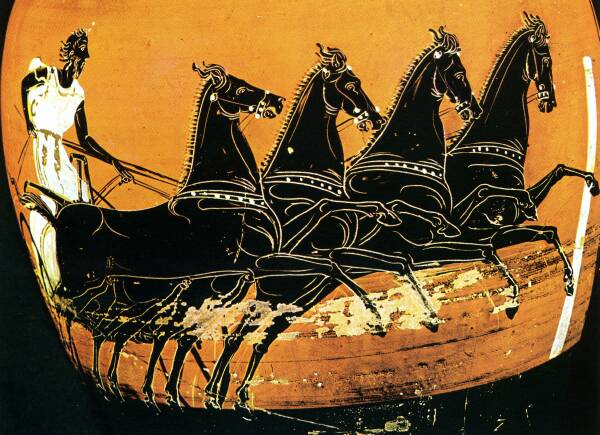
In the ancient Olympics, there were two types of chariot race that took place in the hippodrome of Olympia – the synoris (two-horse chariot race), and the tethrippon (the four-horse chariot race).
In Heart of Fire, we are concerned with the tethrippon race, which was the marquee event of the ancient games.
However, this was not like the chariot racing you’ve seen in the movies. Forget about Ben Hur, and the massive chariots that were pulled around the track in that classic movie.
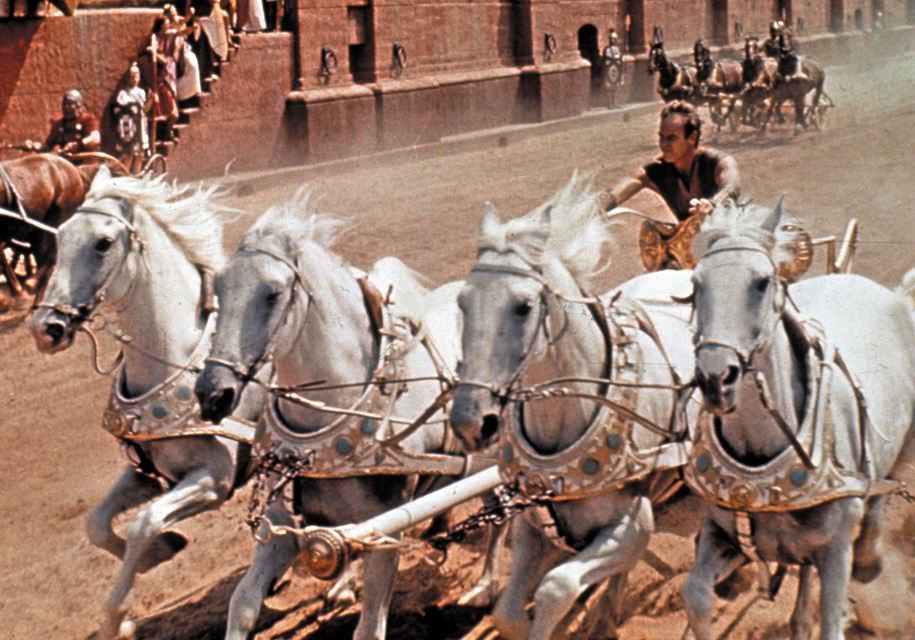

The Chariot Race scene from the movie Ben Hur
Ancient Olympic chariots were meant for speed. They were basically a small platform on wheels, with a skinny rail, and yoked to the horse team of two or four.
Ancient chariots were small, light, and fast, and driving them required a lot of skill. It wasn’t just about controlling the horses. A charioteer had to know his team well, to determine their strengths and weaknesses, where they could pull ahead of the pack, and how to keep them out of danger without giving ground.
In ancient chariot racing, the drivers did not compete naked like the rest of the Olympic athletes. Rather, they wore a long, Ionic chiton called a xystis which was belted high with leather straps criss-crossing over the back and chest so as to prevent the garment from ballooning out at speed and slowing the team down.

The Charioteer of Delphi
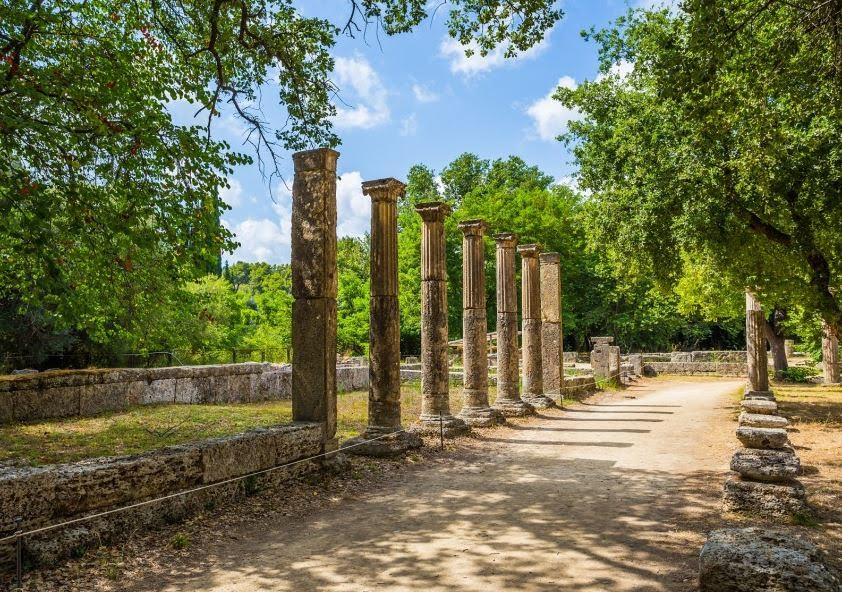
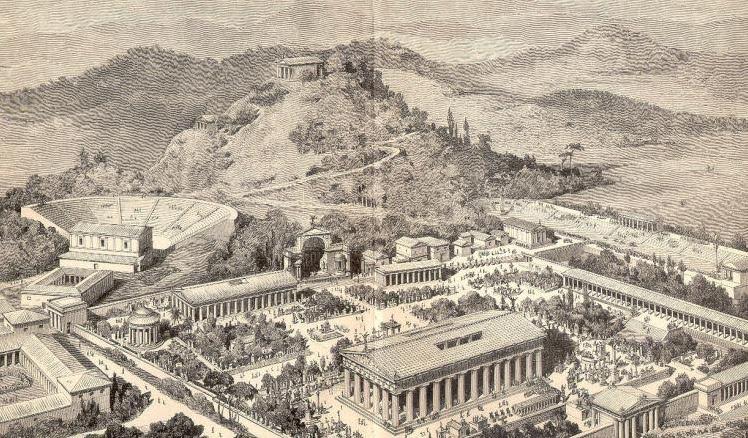
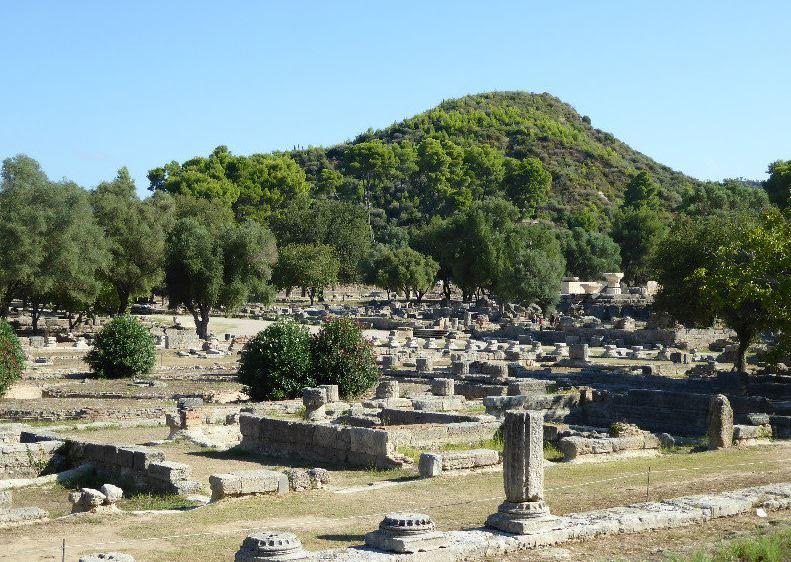
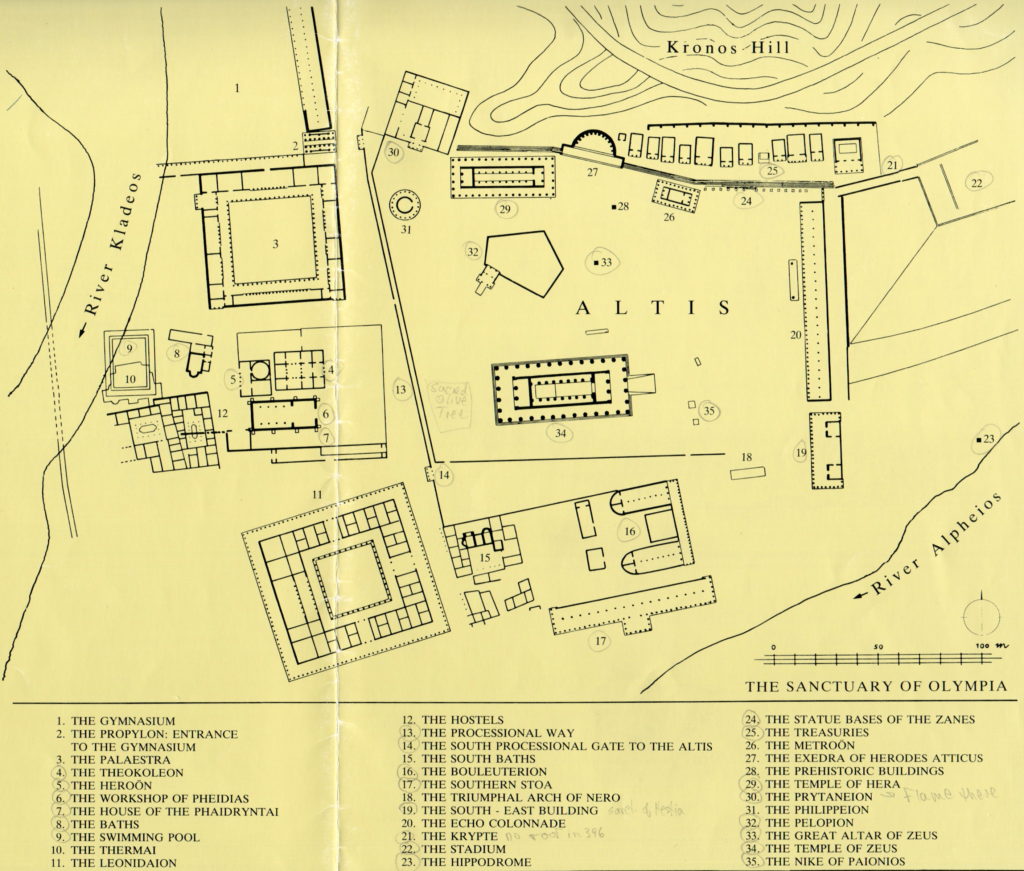
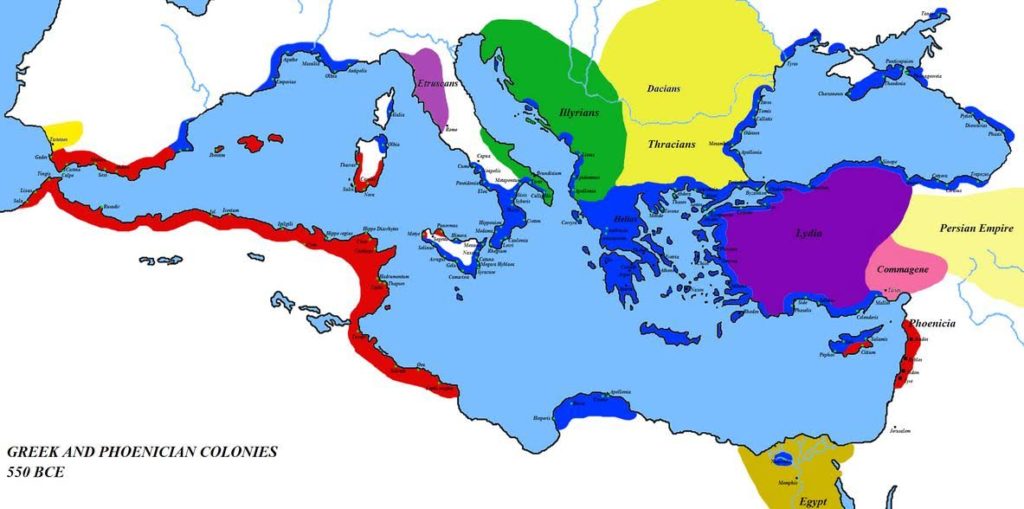
The hippodrome at Olympia, which lies somewhere at the southeast corner of the sanctuary, was about four stades long (780 meters), and one stade, four plethra wide (320 meters).
When visiting Olympia the stadium seems big, but you can imagine how it would have been dwarfed in size by the hippodrome.

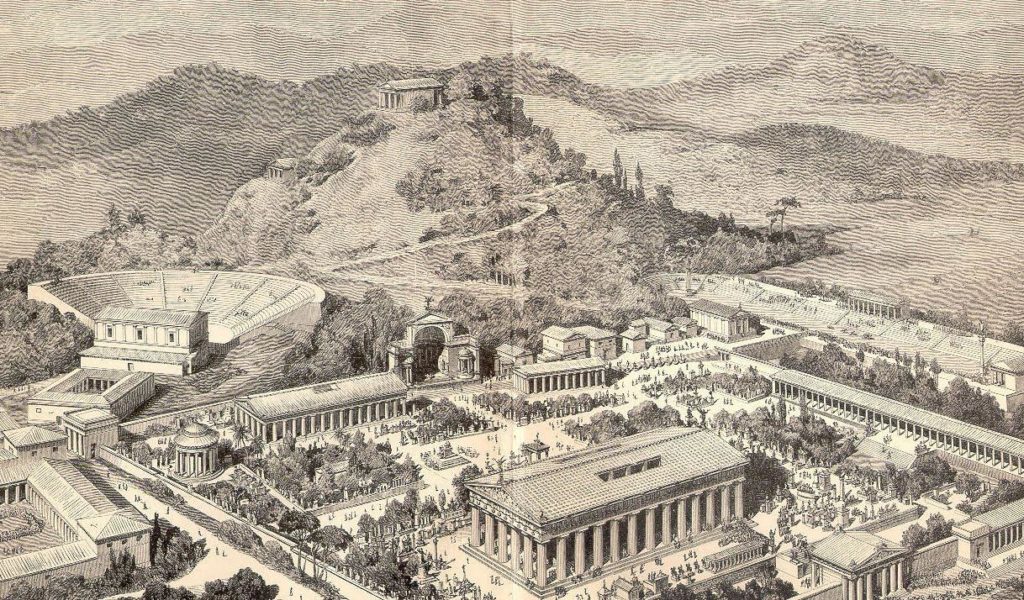
Artist impression of the Olympic Hippodrome and Hyspleges
Once again, the ancient writer, Pausanias, gives us a description:
When you have passed beyond the stadium, at the point where the umpires sit, is a place set apart for the horse-races, and also the starting-place for the horses. The starting-place is in the shape of the prow of a ship, and its prow is turned towards the course. At the point where the prow adjoins the porch of Agnaptus it broadens and a bronze dolphin on a rod has been made at the very point of the ram.
Each side of the starting-place is more than four hundred feet in length, and in the sides are built stalls. These stalls are assigned by lot to those who enter for the races. Before the chariots or race-horses is stretched a cord as a barrier. An altar of unburnt brick, plastered on the outside, is made at every Festival as near as possible to the center of the prow, and a bronze eagle stands on the altar with his wings stretched out to the fullest extent. The man appointed to start the racing sets in motion the mechanism in the altar, and then the eagle has been made to jump upwards, so as to become visible to the spectators, while the dolphin falls to the ground.
First on either side the barriers are withdrawn by the porch of Agnaptus, and the horses standing thereby run off first. As they run they reach those to whom the second station has been allotted, and then are withdrawn the barriers at the second station. The same thing happens to all the horses in turn, until at the ram of the prow they are all abreast. After this it is left to the charioteers to display their skill and the horses their speed.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece, 6.20)
The hippodrome could accommodate over one-hundred thousand spectators along its embankments, and one can imagine the roar of the crowd combined with the pounding of hooves of twenty to forty chariot teams. It would have been spectacular!
The Hellanodikai, the judges, sat on the West side of the hippodrome, and, as ever, there were sacrifices before the race. As the marquee event of the Games, there was a lot of ceremony around this event.
Once the charioteers brought their teams into the hippodrome, a sacrifice was performed at an altar on the track. Then the teams made a slow circuit of the track so that the spectators could see them and hear their names, and those of their cities, announced.
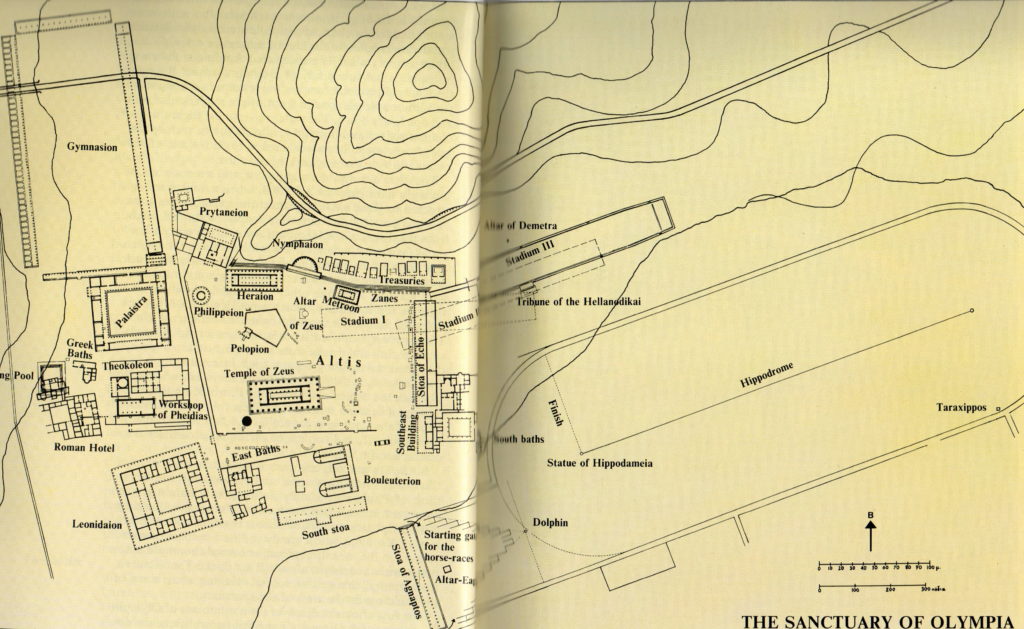
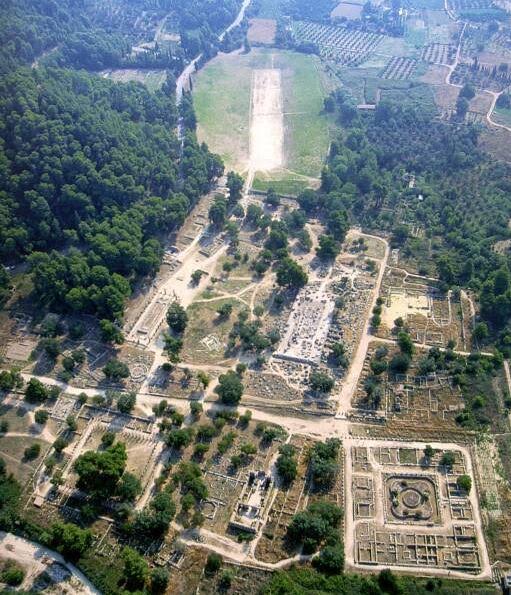
Olympia map showing hippodrome
When the introductory circuit was complete, each team lined up in his appointed starting gate, or hysplex, which was overlooked by a statue of Hippodameia high above them.
What is fascinating is that the ancient Greeks had engineered the starting gates (hyspleges) so that each team shot off the line at the same time, but in order to do this, they staggered the positions so that the teams at the rear were released first and all reached the lead team just as their rope dropped. This was a great piece of ancient ingenuity!
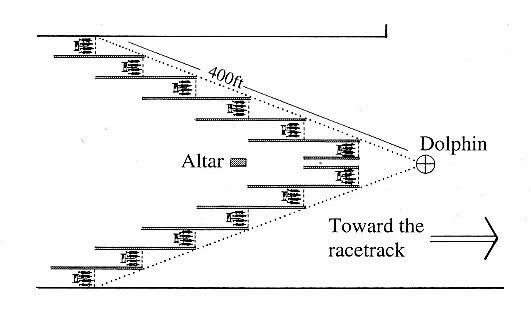
The Olympic starting gates, or ‘hyspleges’
The Tethrippon, or the four-horse race, involved twelve laps of the massive course. The deadliest parts of the hippodrome course were the nyssa, the turns where so many accidents tended to happen.
One of the turns in particular at Olympia was especially dangerous because it was said to be haunted by an evil spirit, some say the wicked shade of Oinomaus, the cruel father of Hippodameia who had killed so many of her suitors. This turn was called the Taraxippos, which literally means ‘horse-frightener’.
The race-course has one side longer than the other, and on the longer side, which is a bank, there stands, at the passage through the bank, Taraxippus, the terror of the horses. It has the shape of a round altar, and as they run along the horses are seized, as soon as they reach this point, by a great fear without any apparent reason. The fear leads to disorder; the chariots generally crash and the charioteers are injured.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece 6.20)
After each lap of the course, one of twelve suspended bronze dolphins tipped over or dropped to indicate the completion of that lap, allowing the drivers and the spectators to see where they were in the race.
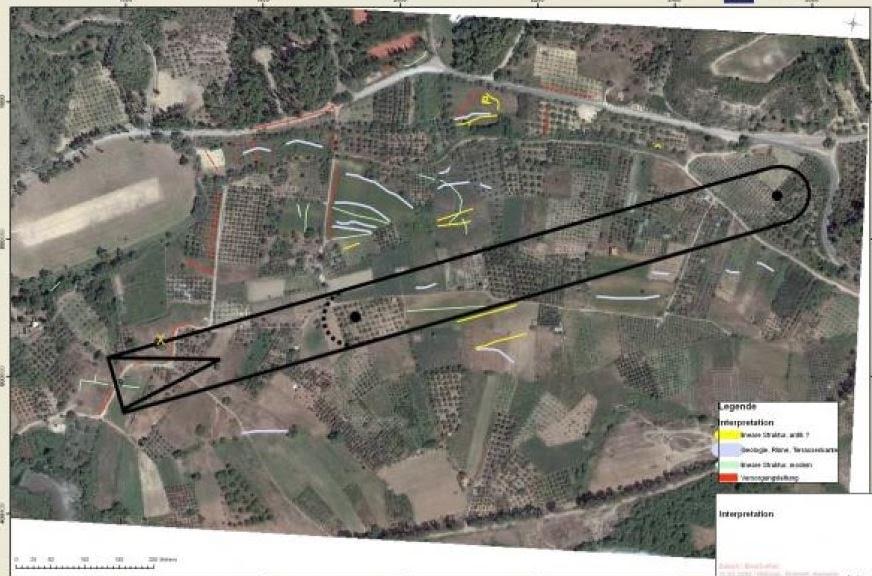
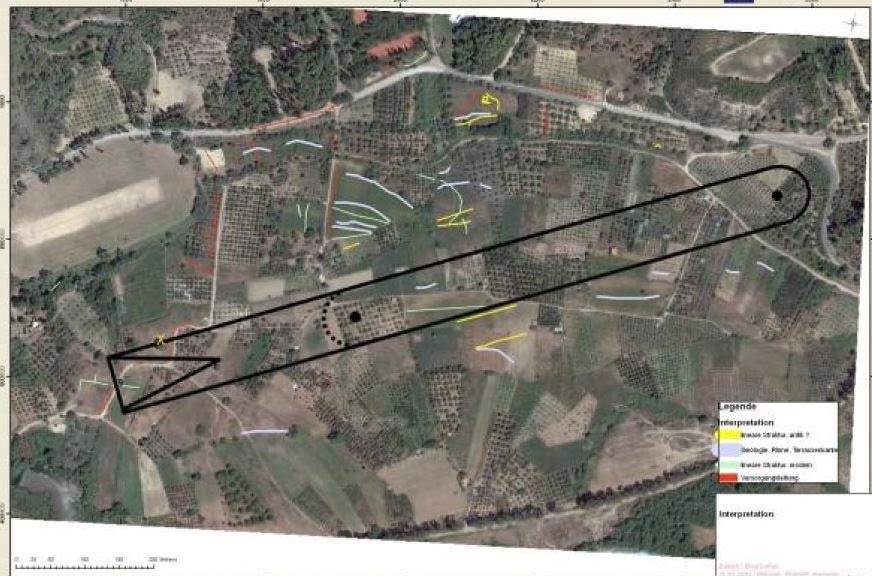
Olympia’s Hippodrome shown in supposed location
The climactic scene of Heart of Fire, and one of the most fun and challenging for me to write, was the chariot race of the 396 B.C. Olympiad.
This was a games that went down in Olympic, and Ancient Greek, history.
In the next post, we’ll find out why the 396 B.C. Olympics were so important, and how one person managed to change the face of sport forever.
Thank you for reading!
Now that the 2016 Olympic Games are underway, the very best of luck to all the athletes in their competitions… May Nike smile on you!