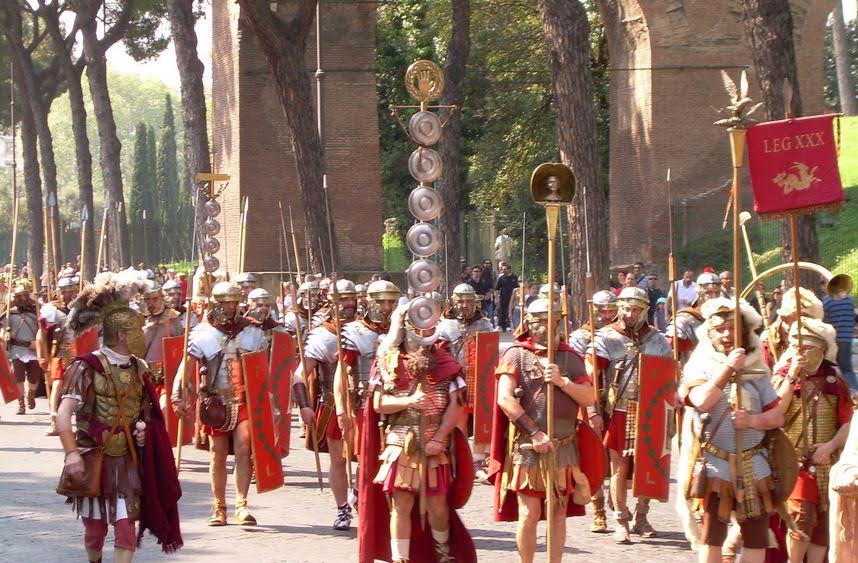
Roman legions
The World of Killing the Hydra – Part V – Desert Legion: The Fortress of Lambaesis – Imagining Saharan Frontier Life
What was it like to live on the very edge of the Roman Empire?
When writing Killing the Hydra, this was something I asked myself many times. What was life like for soldiers, commanders, women, children, and locals under Roman rule? What was it like to be so isolated in a place that, for many, sat on the precipice of the known world?

The Numidian Desert – the Sahara in modern Algeria
In this fifth and final part of The World of Killing the Hydra, we’re going to look at the place where Lucius Metellus Anguis is posted to, and where his family joins him – the legionary base at Lambaesis.
Lambaesis was located in the province of Numidia (modern Algeria), and was the base for the III Augustan legion at the beginning of the third century A.D. when this story takes place. Lambaesis was established by Emperor Hadrian between A.D. 123-129 when the III Augustan legion moved there.
Hadrian toured the Empire and on his visit to Lambaesis, he addressed the troops of this desert legion. Evidence of this address has come down to us in the form of a pillar inscription that was located on the large outdoor parade ground of the base.

Part of the inscription from Lambaesis documenting Hadrian’s address to the troops when he visited there.
The III Augustan legion, however, was older than that. It originated under Pompey the Great in the civil war against Julius Caesar and was eventually moved to North Africa in 30 B.C. by Octavian (who became Augustus) after his victory over Mark Antony.
Eventually, the III Augustan came to be based at Lambaesis, one of only two Roman legions in North Africa, the other being based in Aegyptus.
The III Augustan played an important role in the security and urbanization of North Africa, helping to build roads, aqueducts, fortifications, theatres and more. This work in turn connected towns and cities, facilitated trade, and provided protection for outlying settlements. The work of the army engineers and surveyors brought Roman civilization to this remote frontier.
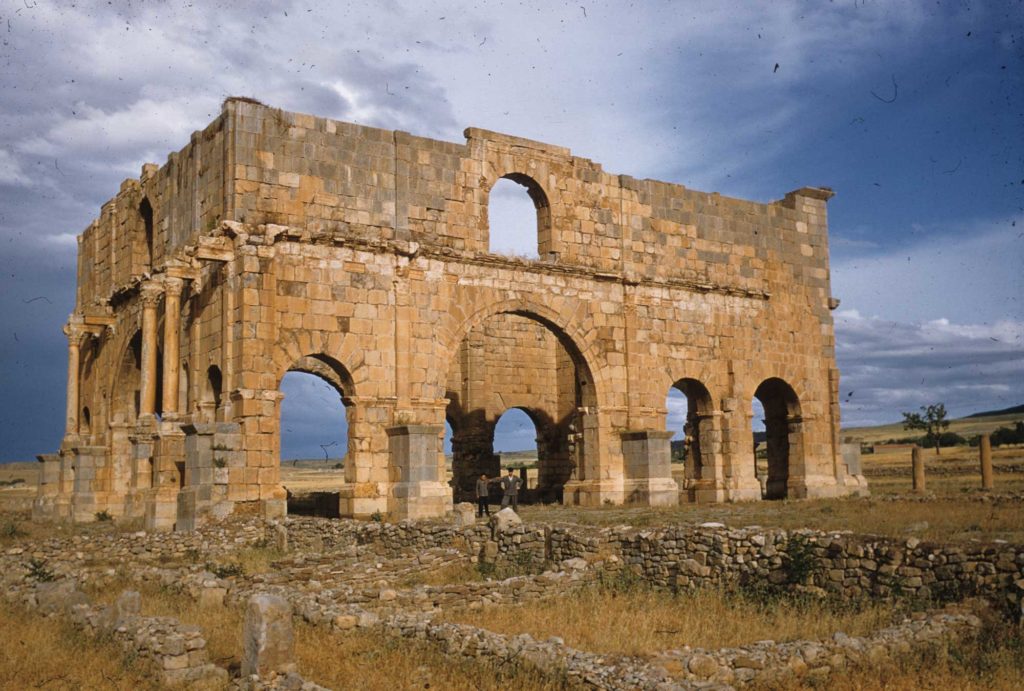

The Praetorium of Lambaesis
The III Augustan was a veteran legion, and of the remains present in that place, apart from the arches of Septimius Severus and Commodus, temples, baths and cemeteries, the principia with its open courtyard is the most stunning of its remains.
This base was on the edge of the deep desert in modern Algeria, backed by the Aures Mountains. At first glance, this seems to have been a lonely windswept place, just as it is today. However, during the Roman period, Lambaesis would have been a busy, thriving place.
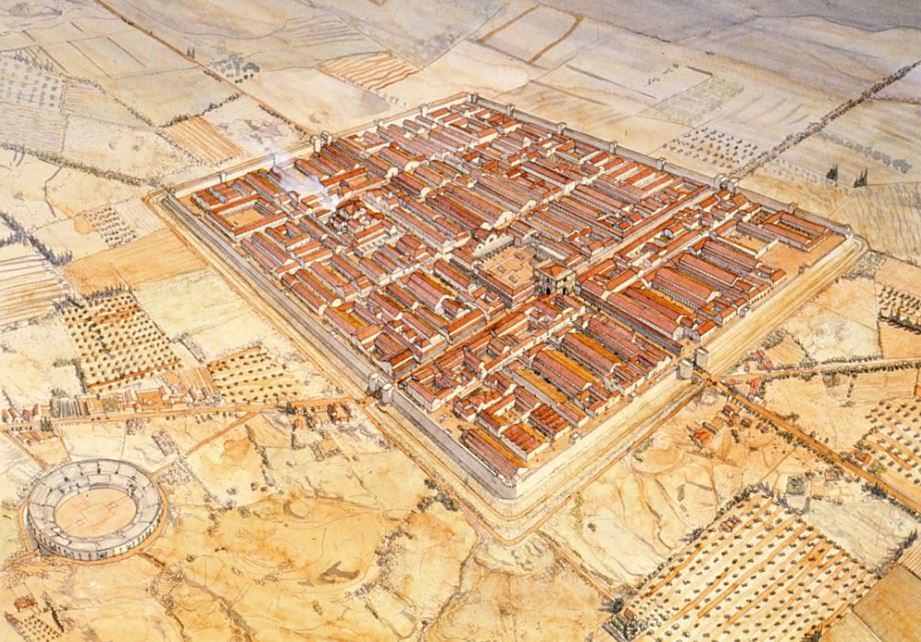

Artist impression of Lambaesis by Jean Claude Golvin
This was not so much an active frontier like that of the Danube or Parthian fronts, but rather a more peaceful place, punctuated with occasional incursions by Garamantians, nomadic Berber tribes and others.
For the most part, the veterans of the III Augustan took part in public building works and improvements, as well as patrols. The men of the legions were a part of society at Lambaesis and the surrounds.
Previously, men of the legions were not permitted to marry, but this law was changed under Septimius Severus, and so many men would have had families living in the vicus outside the base’s walls, or in some instances within the walls.
Add to this the presence of the large, prosperous colonia of Thamugadi, just seventeen miles away, and you have a frontier that was busy, social, and economically vibrant.
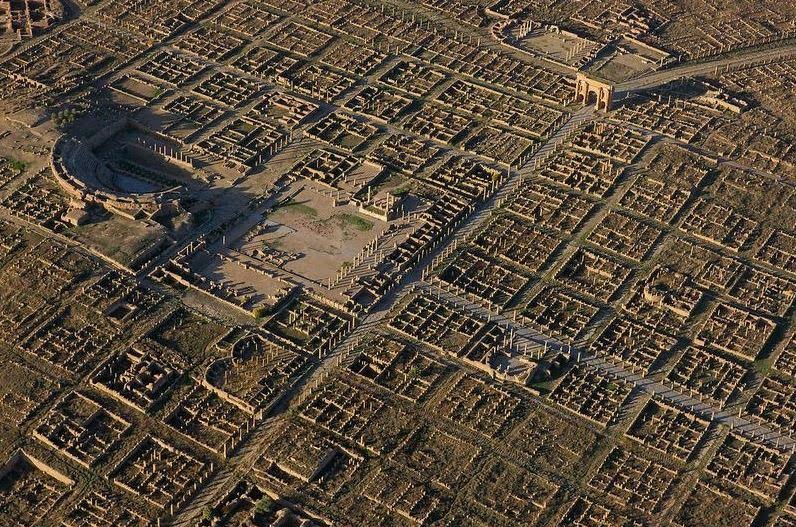

Aerial view of the colonia of Thamugadi
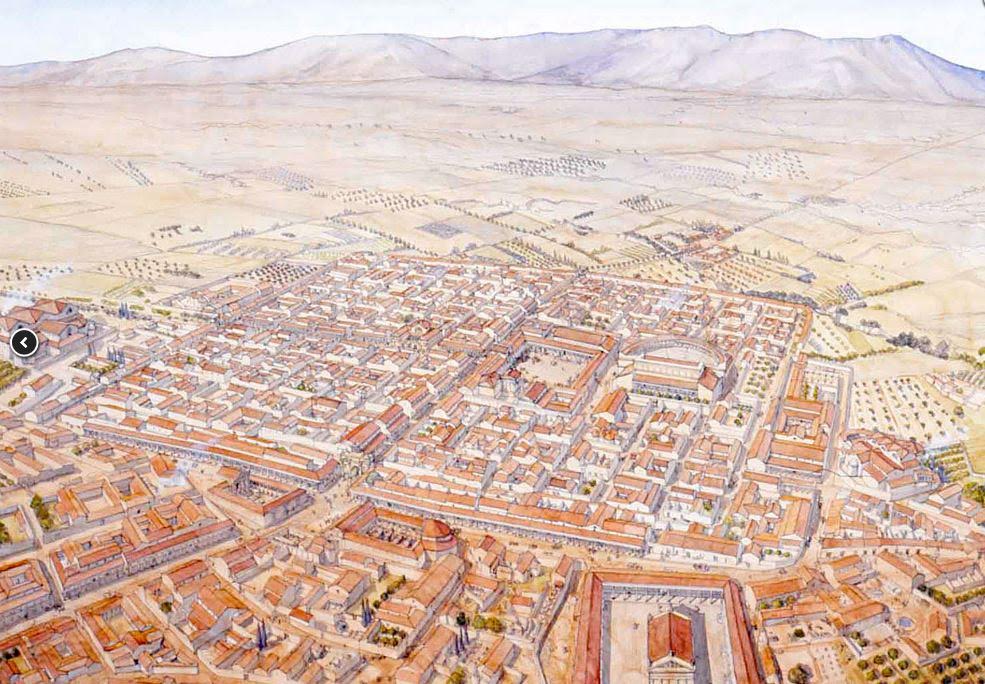
The colonia of Thamugadi was where veterans of the III Augustan legion retired to once their military service was at an end. It was founded by Emperor Trajan in about A.D. 100 under the name of Marciana Traiana Thamugadi. It was a walled settlement, but not fortified, and had a population of about 15,000.
Today, it is made up of some of the most intact and vast ruins of Roman North Africa, including the well-preserved arch of Trajan. It had twelve public baths, theatres, a public library, a basilica and a magnificent temple of Jupiter.
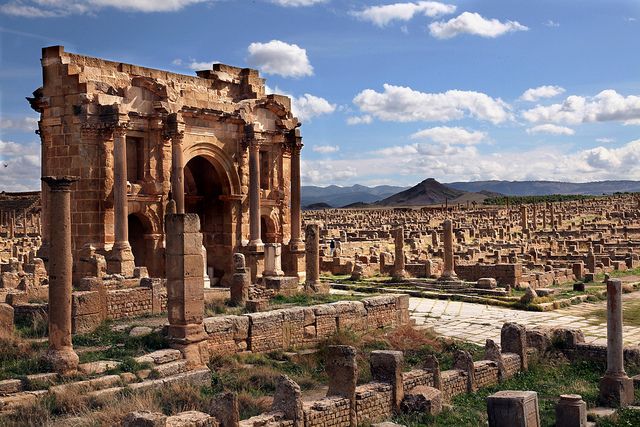

The arch of Trajan in Thamugadi
One imagines that it was lonely for soldiers’ wives and their children, being posted to such a remote location, compared with other parts of the Empire, but with the changed laws regarding marriage for troops, the close proximity of Thamugadi to Lambaesis, and the thriving economy of Roman North Africa at this point in time, it seems like Saharan frontier life may not have been the sort of lonely, wasteland existence that I had in mind when I started my research and writing.
I always try to travel to the places I am writing about, but sometimes that just isn’t possible, or safe. Lambaesis was one of those places.
At the time of my Tunisian research for Children of Apollo and Killing the Hydra, we were told there was a travel ban to Algeria where the remains of both Lambaesis and Thamugadi are located.
Artist impression of Thamugadi by Jean Claude Golvin – this was not a tiny village, but a bustling settlement!
Our 4X4 skirted the military border between the two countries, distant guard towers and barbed wire visible as a long grey line cutting across the North African landscape.
We asked our guide if we could drive into Algeria but he was adamant that it wasn’t possible. “No chance. It is forbidden. They will shoot at us,” he said.
I don’t know if that was true or not, but some things are not worth the risk. After all, we have the internet now and a myriad of resources on-line.
So, we had to settle for pulling our truck over on the gravelly roadside and gazing westward across the guarded border to the Aures Mountains of Algeria and imagining what remnants of Rome lay scattered in that vast expanse.

Mosaic fragment from Lambaesis
The light was dull that day, an iron-grey winter sky, so the feeling of loneliness and desolation was acute. Somewhere out there was the base of the veteran III Augustan legion. There was a colonia for veterans filled with the amenities of Roman civilization.
This was a land where my character was to be posted, along with his family, and the families of his fellow officers and troops. Many would have had family and friends in Thamugadi, done business there, and used the network of roads that really did, in one way or another, lead back to Rome…
It was hard to imagine as I stood there with the dust whipping around us, our guide looking nervously in our direction as if we might attempt something stupid.
The relief on his face when we said “OK. Let’s go.” was darkly comic. It was also real.
But maybe that hints at Saharan frontier life in the Roman Empire?
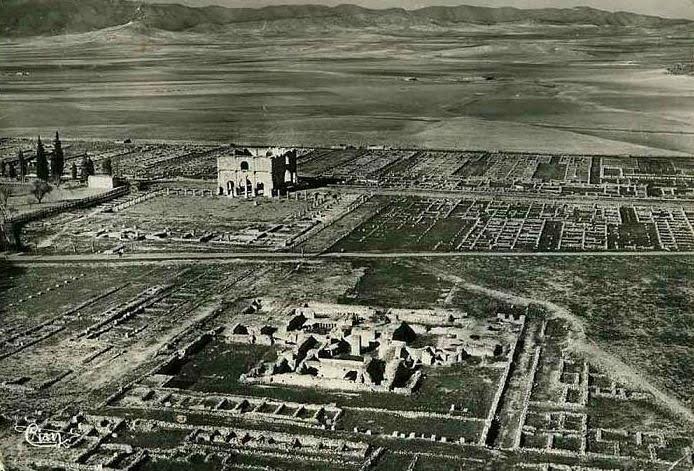

Aerial view of Lambaesis
Despite the fact that this was not one of the most active (militarily) fronts of the Empire, or that Roman civilization was indeed present and thriving in this remote place far from the heart of the Empire, Lambaesis was nevertheless a place of war, a place of danger, a place where one could not let one’s guard down. When war was not being waged, there were still battles to be fought on the political front, and enemies lurking in the shadows.
History has taught us that complacency can lead to trouble, and in the Roman Empire this was a fact of life.
Will Lucius Metellus Anguis come out of it alive? Will he be able to protect his family in that remote corner of the world?
Well, you would have to read the book to find out.
I hope you have enjoyed this series on The World of Killing the Hydra.
Writing this book was a fantastic adventure that took me to places I never expected to reach, but which are endlessly fascinating. If you read it, I do hope you enjoy it.
And if you missed any of the posts in this blog series, you can read the full set of blog posts by CLICKING HERE.
If you have not yet read any of the Eagles and Dragons series books, remember you can always get the first book, A Dragon among the Eagles, for FREE. Just CLICK HERE.
Thank you for reading.
The World of A Dragon among the Eagles – Part IV – Cities Under Siege
One of the great things about reading and writing historical fiction is that one is given the chance to journey to a time and place far away from the modern world.
In this fourth part of The World of A Dragon among the Eagles, we’re going on location to some of the places where the action takes place, some of which, sadly, are still making headlines today.
This won’t be an in-depth look at these ancient cities, for their histories are long and varied, and they each deserve their own a book. Here, we’re just going to take a brief look at their place in this story.
Sites where A Dragon among the Eagles takes place
The first third of A Dragon among the Eagles takes place in Rome, then Athens, and a little at Amphipolis which has gained recent fame for the massive tomb and the excavations there which have been linked to the period of Alexander the Great.
However, we are not going to look at Rome and Athens, as we visit those cities much more in Children of Apollo and Killing the Hydra, the sequels to A Dragon among the Eagles. If you would like to read more about Amphipolis, you can read this BLOG POST HERE.
For this blog, we are mainly concerned with the cities where Lucius Metellus Anguis, our protagonist, gets his first taste of war with the Legions.
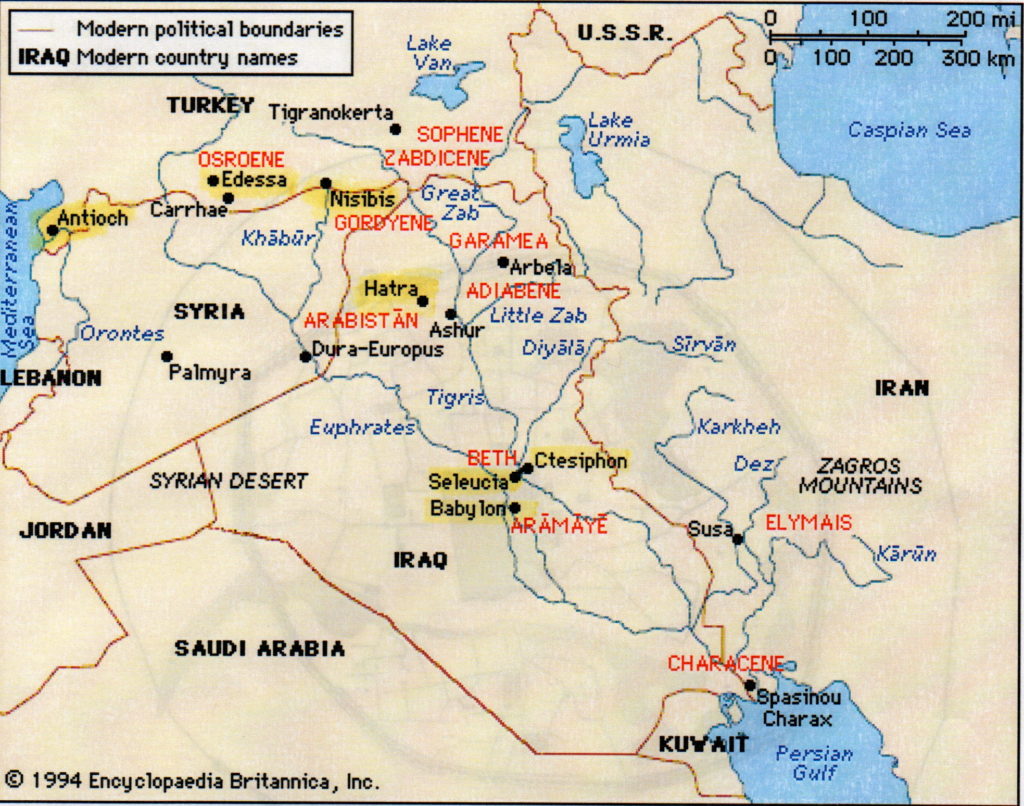
Mesopotamia is said to be the cradle of civilization, a land of alternating fertility and desert where the first cities were built, and empires made. It also was, and is, a land of war, a land of terrible beauty.

Trooper in modern Iraq
For millennia, successive civilizations have fought over this rich land, a land from which Alexander the Great had decided to rule his massive empire.
In A Dragon among the Eagles, Lucius Metellus Anguis’ legion arrives at the port of Antioch where Emperor Severus has assembled over thirty legions on the plains east of the city.
Antioch, which was then located in Syria, now lies in modern Turkey, near the city of Antyaka. It was founded in the fourth century B.C. by one of Alexander’s successor-generals, Seleucus I Nicator, the founder of the Seleucid Empire.
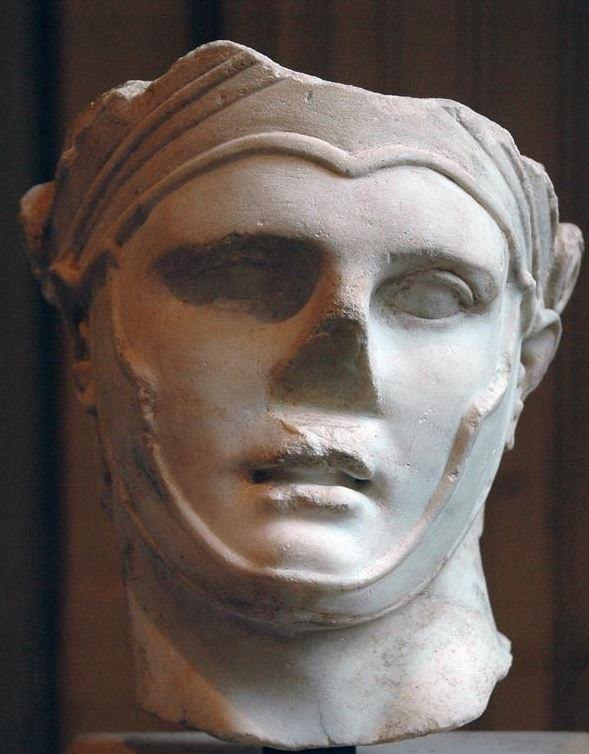

Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus named this city after his son, Antiochus, a name that would be taken by later kings of that dynasty.
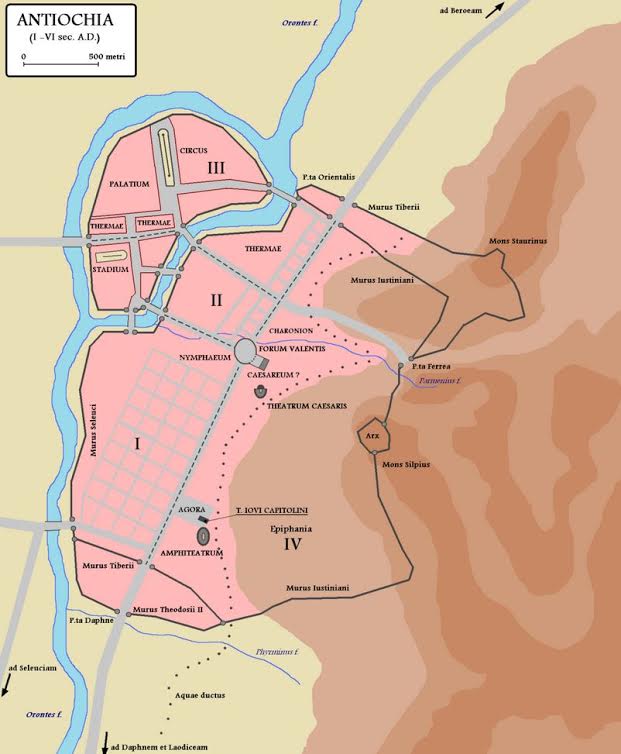
Antioch was called the ‘Rome of the East’, and for good reason. It was rich, mostly due to its location along the Silk Road. Indeed, Antioch was a sort of gateway between the Mediterranean and the East, with many goods, especially spices, travelling through it. It is located on the Orontes river, and overlooked by Mt. Silpius.
Antioch in the Roman Empire
In the book, we catch a glimpse of this Ancient Greek city that was greatly enhanced by the Romans who saw much value in it. Actually, most of the development in Antioch took place during the period of Roman occupation. Enhancements included aqueducts, numerous baths, stoas, palaces and gardens for visiting emperors, and perhaps most impressive of all, a hippodrome for chariot racing that was 490 meters long and based on the Circus Maximus in Rome.
Antioch, during the late second century A.D., rivalled both Rome and Alexandria. It was a place of luxury and civility that was in stark contrast to the world of war where the legions were headed.
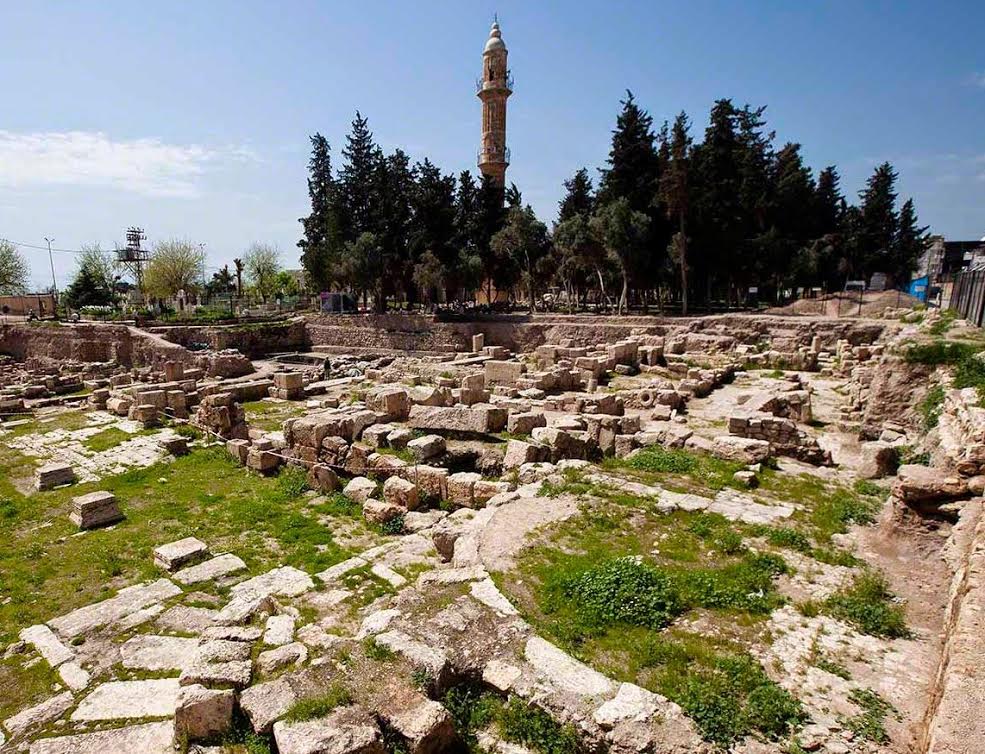

Some ruins of Nisibis today
In writing A Dragon among the Eagles, I have followed the itinerary presented to us by Cassius Dio, the main source for this period in Rome’s history and the Severan dynasty. So, the order in which we are looking at these locales is roughly the order in which Severus’ legions are supposed to have attacked them.
The first real battle in the book, and the first time our main character experiences battle, is at the desert city of Nisibis.
At the time, Nisibis was under Roman control. However, that control was about to break according to Dio, as the Romans inside were just holding onto it. This is due mainly to the leadership of the Roman general, Maecius Laetus, whom we meet in the story.
Laetus managed to hold the defences of Nisibis until Severus’ legions showed up, and was hailed as a hero for it.
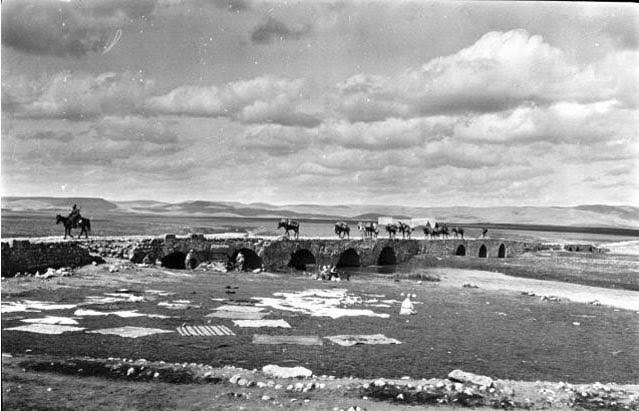

Nisibin Bridge – Gertrude Bell’s caravan crossing bridge.
Nisibis was situated along the road from Assyria to Syria, and was always an important centre for trade. This was the only spot where travellers could cross the river Mygdonius, which means ‘fruit river’ in Aramaic. Today it is located on the edge of modern Turkey.
Early in its history, Nisibis was an Aramaen settlement, then part of the Assyrian Empire, before coming under the control of the Babylonians. In 332 B.C. Alexander the Great, and then throughout the Roman-Parthian wars, it was captured and re-captured, over and over.
Such is the fate of strategically placed settlements, especially when they are located along the Silk Road.
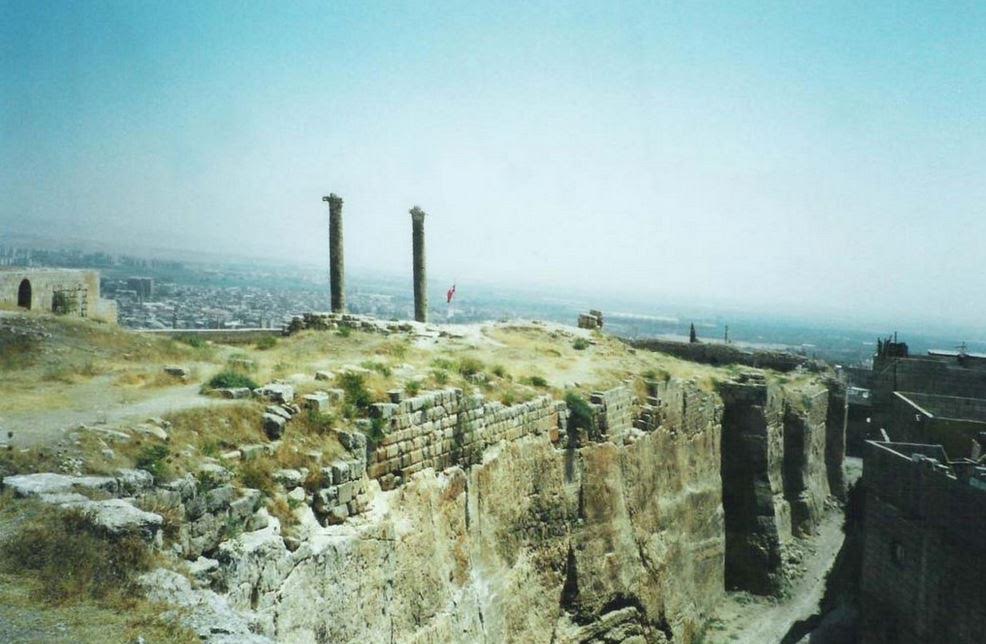

Ruins of Edessa
From the bloody fighting in Nisibis, Severus’ forces then moved into the Kingdom of Osrhoene and the upper Mesopotamian city of Edessa, located in modern Turkey.
Edessa was originally an ancient Assyrian city that was later built up by the Seleucids.
Edessa’s independence came to an end in the 160s A.D. when Marcus Aurelius’ co-emperor, Lucius Verus, occupied northern Mesopotamia during one of the Roman-Parthian wars.
From that point on, Osrhoene was forced to remain loyal to Rome, but things changed when the civil war broke out between Severus, Pescennius Niger, and Clodius Albinus. Osrhoene threw their support behind Niger, who was then governor of Syria.
When Severus came out the victor in the civil war, it was inevitable that Edessa and Osrhoene would have to face the drums of war.
Edessa was where King Abgar of Osrhoene, who was sympathetic to the Parthians, was holed up as Severus’ legions advanced.

King Abgar of Osrhoene and Commodus
One has to wonder what King Abgar was thinking as Severus approached this ancient city. Whatever it was, and whatever he said to the Roman Emperor when he arrived, it must have been acceptable, for Abgar was permitted to keep his throne as a client king of the Empire.
There was a siege, but it seems that with King Abgar accepting Rome’s overlordship, and Severus’ need to move south, this is why the Osrhoenes escaped any large scale retribution.
In a way, it was not so for Lucius Metellus Anguis, for whom Edessa proves to be a harsh and enlightening experience.
At this time, Septimius Severus had his sights set on southern Mesopotamia and the great cities of Seleucia, Babylon, and the Parthian capital of Ctesiphon.
Ancient Babylon
The legions made their way south, directly for Seleucia-on-Tigris.
Seleucia, as the name suggests, was built by the Seleucus I Nicator in 305 B.C. as the capital of his empire. It was located sixty kilometers north of Babylon, and just across the Tigris River, on the west bank, from Ctesiphon. Today, Seleucia is located in modern Iraq, thirty kilometers south of Baghdad, and in its day, it was a major city in Mesopotamia.
It was a great Hellenistic city in the third and second centuries B.C., with a rich mixture of Greco-Mesopotamian architecture, and walls enclosing a full 1,400 acres as well as a population of 60,000 people.
When the Parthians took Seleucia, the capital was moved across the river to Ctesiphon and, though the city remained in use and inhabited, it went into a slow decline.
During the Roman-Parthian wars, Seleucia was burned by Trajan, rebuilt by Hadrian, and then destroyed again. Like a battered boxer with heart, it kept rising from the ground until there was no more will to keep it alive.
By the time Severus’ legions were marching on Seleucia, the Parthians had abandoned it completely, giving the Romans a foothold on the Tigris River, opposite their capital.

Seleucia on Tigris c.1927
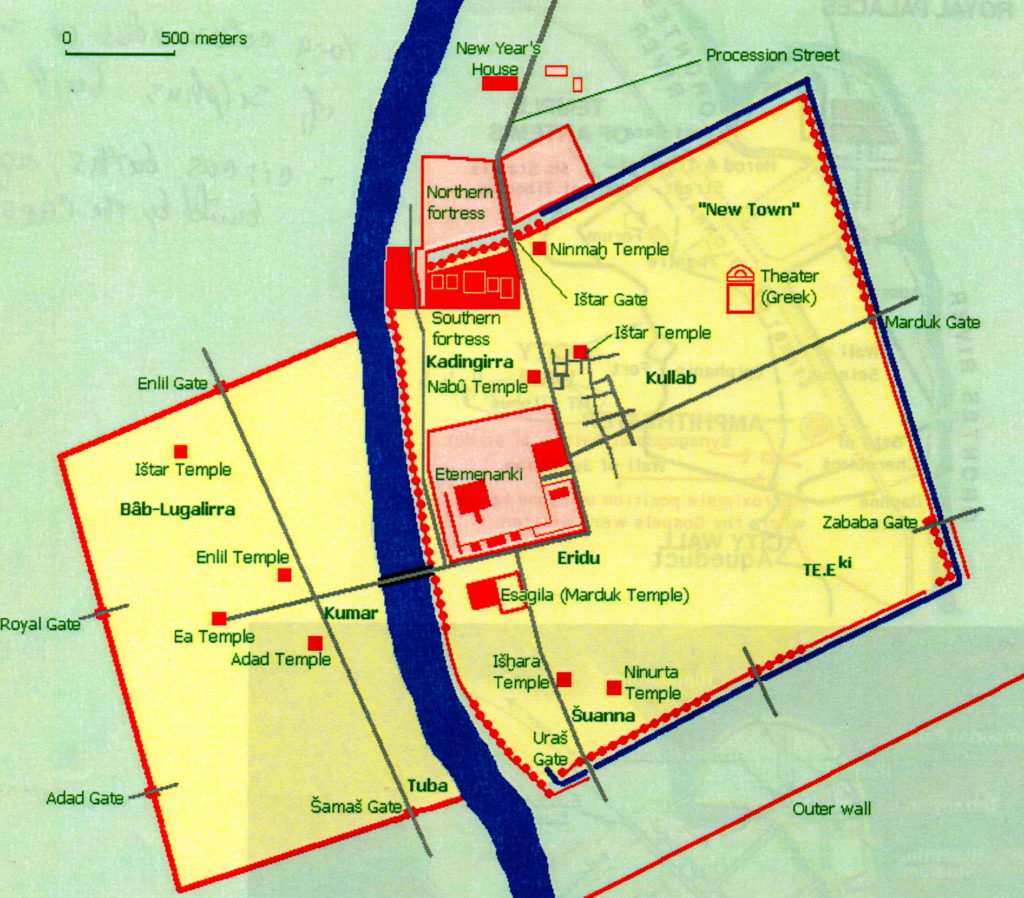
Ctesiphon would have to wait, however, for there was another magnificent and symbolic prize within Severus’ grasp at that time – Babylon.
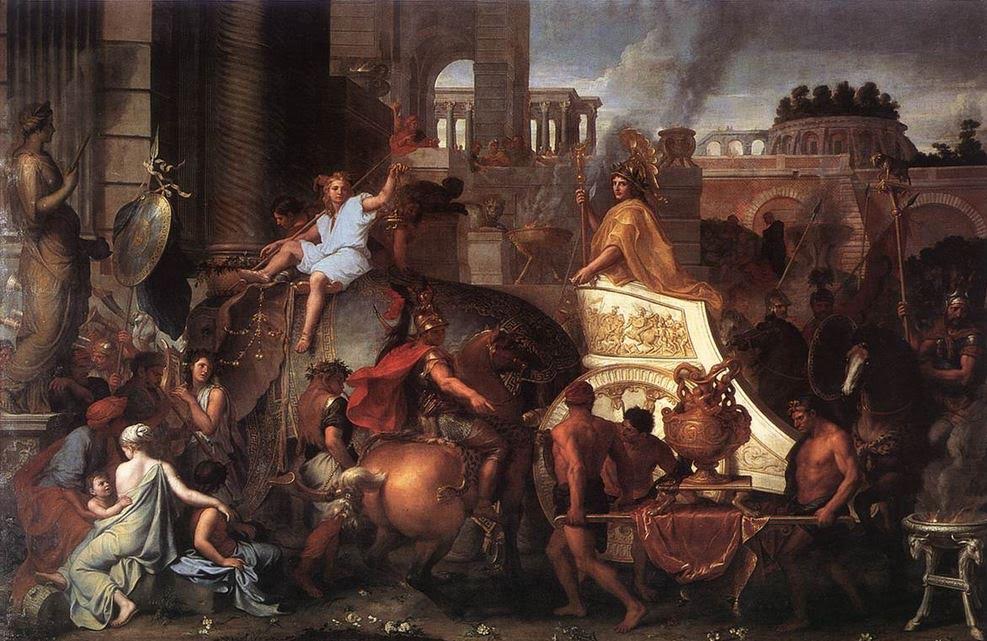

Alexander entering Babylon (Charles Le Brun)
I find that when I utter the name of Babylon, I get chills. Think about it, this is one of the most famous of ancient cities! This was the place that welcomed Alexander the Great with open arms and triumph, the place from which he had decided to rule his titanic empire, and the place where he died.
Babylon was located on the fertile plain between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Actually, part of it was built over the Euphrates.
The original settlement of Babylon is said to date to about 2300 B.C when it was part of the Semitic Akkadian Empire. It was fought over and rebuilt, and in about 1830 B.C. it became the seat of the first Babylonian dynasty.
From about 1770 B.C. to 1670 B.C. Babylon was the largest city in the world with a population of over 200,000.
Perhaps the most famous period in Babylon’s long and ancient history is during what is known as the Neo-Babylonian Empire (626-539 B.C.), and especially the reign of King Nebuchadnezzar II (605-562 B.C.)

Then Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Nebuchadnezzar was a great builder, and it was he who made Babylon one of the most beautiful cities of the ancient world, home to one of the Seven Wonders.
He built the famed Hanging Gardens of Babylon for his Median wife who missed the lushness of her homeland, and he also constructed the giant ziggurat of Etemenanki beside the temple of Marduk.
Babylon at this time must have been a sort of paradise on earth with the ziggurat as the doorway to the heavens. The walls of the city too, were so big that it was said that two chariots could pass each other as they drove along the top of the walls.
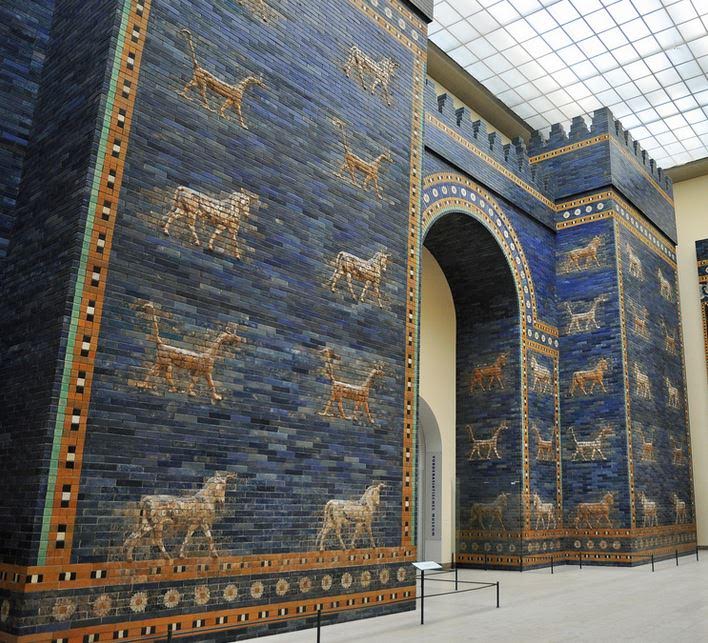

Ishtar Gate of Babylon at Pergamon Museum Berlin
When the Seleucids came onto the scene and Babylon’s power and beauty faded into history, the population was moved to Seleucia, one supposes to bolster the economy of the great new capital envisioned by Seleucus I.
There was a lot of history at Babylon, and it’s not improbable that all the Romans who marched through there thought of Alexander as they approached, including Severus.
But Babylon was a very different place when the legions marched on it late in A.D. 198.
Just as Seleucia had been abandoned, so too was Babylon. And so, with barely a drop of blood being shed, the Romans walked into this ancient city of faded glory in stern silence, their prize almost too easily won.
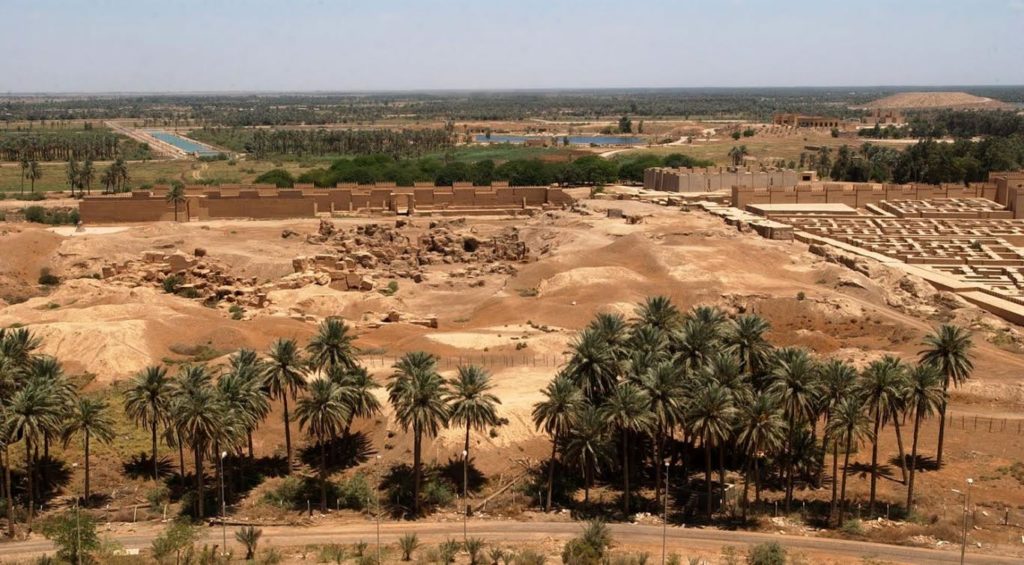

Ruins of Babylon (Wikimedia Commons)
It was time for the real battle.
With Seleucia and Babylon basically given over to Rome and Severus’ legions, the forces of Rome and Parthia converged on the capital of Ctesiphon.
This time, the Parthians were waiting.
Ctesiphon, compared to the other cities we have seen, was a relatively new settlement on the east bank of the Tigris River, facing Seleucia. It was built around 120 B.C. on the site of a military camp built by Mithridtes I of Parthia. At one point in time, it merged with Seleucia to form a major metropolis straddling the river.
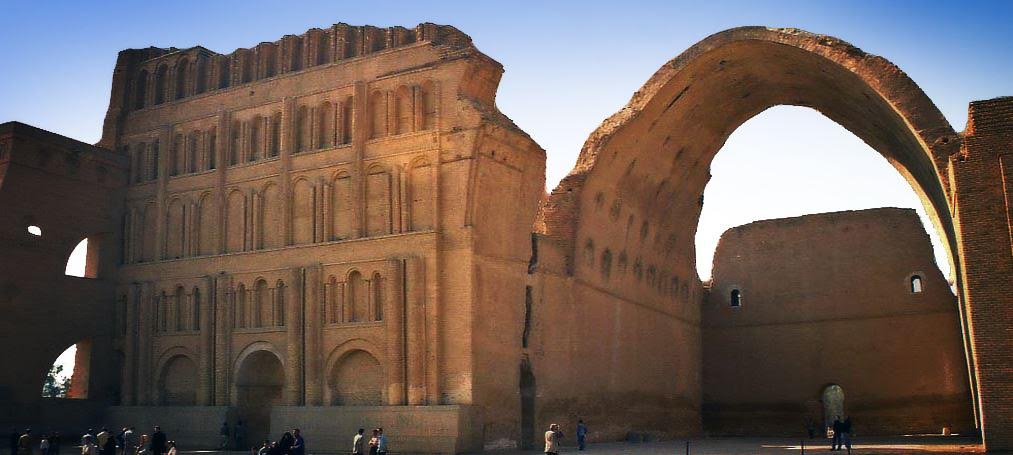

Ctesiphon’s ruins today, including the great audience hall.
During the Roman-Parthian wars, Ctesiphon did not have an easy time of it. It was captured by Rome five times in its history, the last time by Septimius Severus who burned it to the ground and enslaved much of the population.
The Greek geographer, Strabo, describes the foundation of Ctesiphon here:
In ancient times Babylon was the metropolis of Assyria; but now Seleucia is the metropolis, I mean the Seleucia on the Tigris, as it is called. Nearby is situated a village called Ctesiphon, a large village. This village the kings of the Parthians were wont to make their winter residence, thus sparing the Seleucians, in order that the Seleucians might not be oppressed by having the Scythian folk or soldiery quartered amongst them. Because of the Parthian power, therefore, Ctesiphon is a city rather than a village; its size is such that it lodges a great number of people, and it has been equipped with buildings by the Parthians themselves; and it has been provided by the Parthians with wares for sale and with the arts that are pleasing to the Parthians; for the Parthian kings are accustomed to spend the winter there because of the salubrity of the air, but they summer at Ecbatana and in Hyrcania because of the prevalence of their ancient renown.
Being built by the Parthians, Ctesiphon, unlike Seleucia, Babylon, or the other places we have discussed, was a Parthian invention. Probably the greatest structure of this capital was the great, vaulted audience chamber, or hall, which seems to be all that remains today. In truth, there is very little information on other structures within Ctesiphon itself.
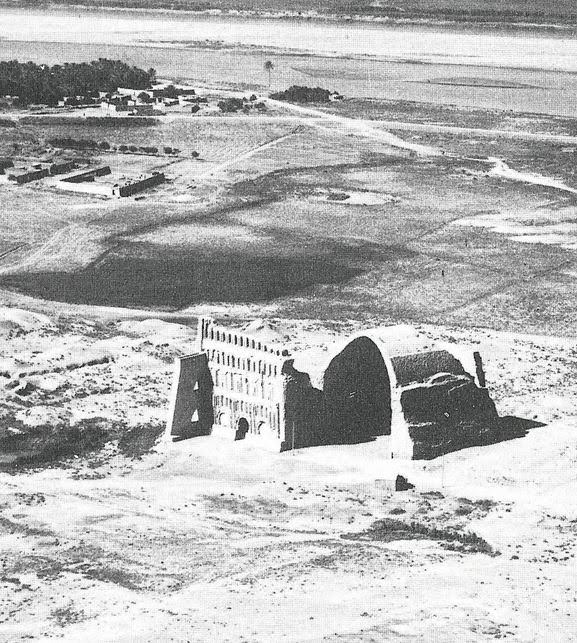

Ctesiphon from the air
The final sack of Ctesiphon by Severus’ legions in A.D. 197 was a brutal affair, and one that ended that city and provided the death blow to the Parthian Empire.
In A Dragon among the Eagles, the Roman attack on Ctesiphon is one of the major battle scenes which I had envisioned a long time ago. Imagine, almost thirty legions lined up on the other side of the river with the entire force of Parthian horse archers and heavy cataphracts awaiting them.
The Romans had to cross the river, gain a beachhead, and then push forward. In the end, Rome prevailed, but at great cost to the troops.
One would have thought that with the sacking of the Parthian capital, all would be finished, but there was another score for Rome to settle, another city to take – the desert city of Hatra.
As I write this, I have a pang of sadness, for while I was researching and writing about Hatra and the Roman siege there, extremist groups in the Middle East were in the process of the wonton destruction of this ancient heritage site. Writing this part of the book was indeed an odd experience.
Hatra is located in modern Iraq, about 290 kilometers north of Baghdad, on the Mesopotamian desert, far from either the Tigris or Euphrates. It was built by the Seleucids, those Hellenistic giants we’ve heard so much about, around the third century B.C.
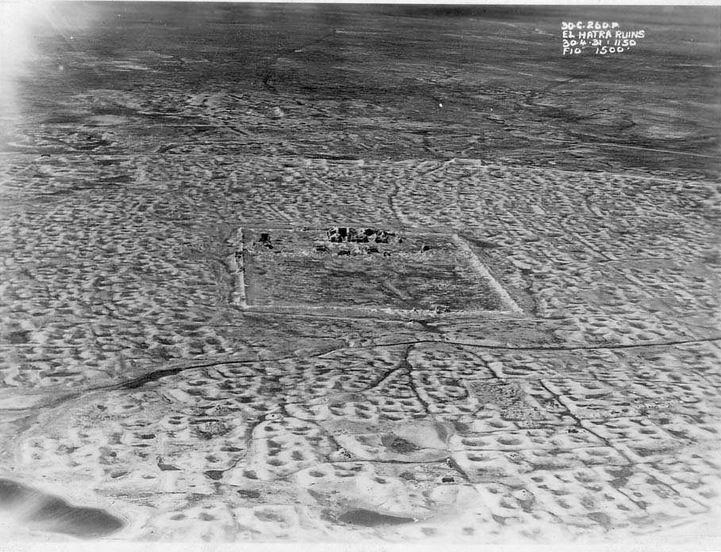

Hatra old survey aerial photo
It flourished under the Pathians too as a center of religion and trade during the first and second centuries A.D. What is fascinating about Hatra is the harmony and religious fusion it represented. This remote desert city was a place where Greek, Mesopotamian, Canaanite, Aramean, and Arabian religions lived peacefully side-by-side. And for 1,400 years it was protected and preserved by Islamic regimes, until it was destroyed in 2015.
It was the best-preserved Parthian city in existence.
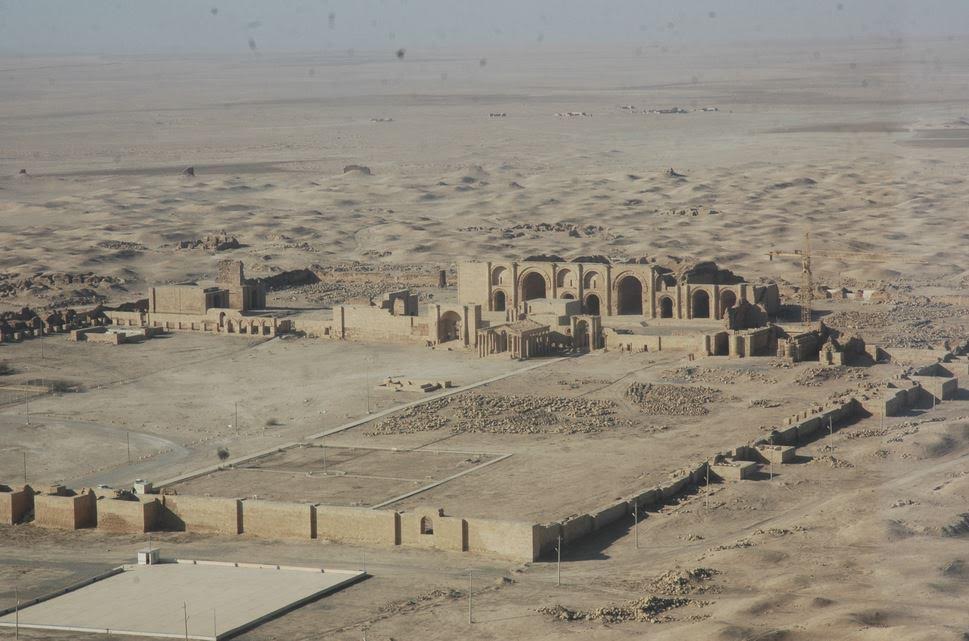

Hatra before the 2015 destruction
When Septimius Severus turned his attention on Hatra after the fall of Ctesiphon, it was with a goal of doing what no other Roman, even Trajan, had been able to do.
It was personal too, for Hatra and its ruler, Abdsamiya, had supported Pescennius Niger against Severus in the civil war.
But there were a few reasons Hatra had withstood Roman sieges, including the two attempted by Severus in his Parthian campaign.
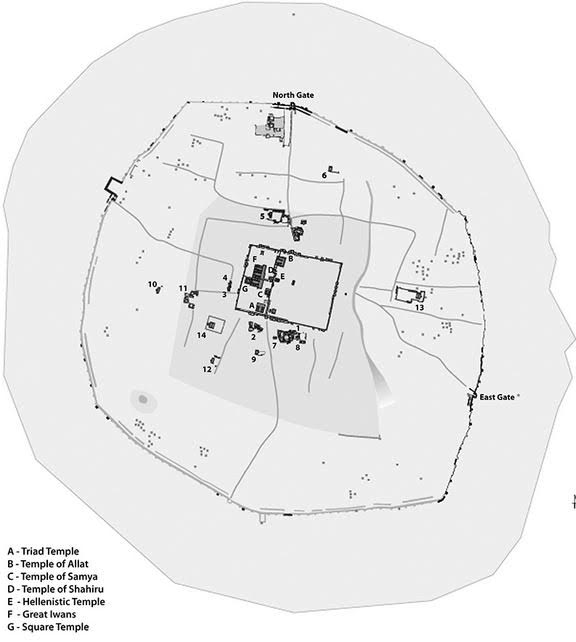
First of all, Hatra was remote, stranded out in the desert with its own water source within the walls, but none without. The nearest water was over forty miles in any direction. A legion could only march a maximum of twenty-five miles in one day. So, thirst for those laying siege was a big factor.
Then there were the walls – two of them. Hatra was protected by immense, circular, inner and outer walls, the diameter of which was 2 kilometers, or 1.2 miles. Along these massive walls were 160 towers, making this island fortress of the sand seas no easy target.
Hatra Map (with temples labelled)
At Hatra’s heart were the sacred buildings of the gods of various religions, gods whom many believed protected the city from attack.
The temples within Hatra covered a total of 1.2 hectares, and that area was dominated by the Great Temple of Bel which was about 30 meters high.
Hatra withstood two major attacks by Roman emperors, Trajan and Severus. Every time, Hatra’s walls, and her gods, turned Rome back.
Cassius Dio describes Severus’ last siege of Hatra:
He himself made another expedition against Hatra, having first got ready a large store of food and prepared many siege engines; for he felt it was disgraceful, now that the other places had been subdued, that this one alone, lying there in their midst, should continue to resist. But he lost a vast amount of money, all his engines, except those built by Priscus, as I have stated above, and many soldiers besides…
When the walls were breached, Severus gave the Hatrans time to consider surrender, as he respected the religious importance of the place, especially the temple of the Sun God. But the Hatrans were stubborn, and the troops were fed up:
Thus Heaven, that saved the city, first caused Severus to recall the soldiers when they could have entered the place, and in turn caused the soldiers to hinder him from capturing it when he later wished to do so [threat of mutiny].
Once again, Hatra resisted being conquered by Rome, making it the only place Severus’ legions were not able to take.
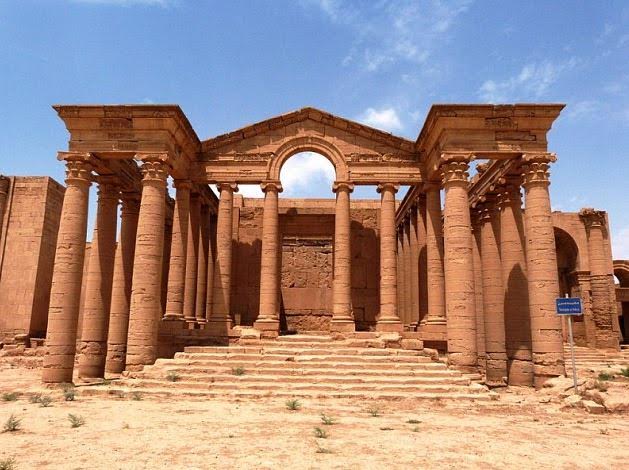

One of Hatra’s many magnificent temples
It is sad that, in light of the events of 2015, it seems Hatra’s gods finally deserted it.
To see more of Hatra before its destruction, CLICK HERE to watch the UNESCO video.
I hope you’ve enjoyed this march with the legions! In the next post, we’ll be going somewhere more civilized – the City of Alexander the Great!
This past week has been a good one for A Dragon among the Eagles, for in the UK it became an Amazon #1 Bestseller in three categories, including Historical Fantasy. It is also climbing in the Amazon US charts too, so thank you to everyone for supporting the book!
For those of you who prefer to read paperbacks, A Dragon among the Eagles is now available in trade paperback format from either Amazon or Create Space.
And as ever, thank you for reading.
The World of A Dragon among the Eagles – Part II – The Imperial Roman Legion
The world in which A Dragon among the Eagles takes place, and with which the main characters are concerned, is also the world of the Roman legion.
Indeed, the imperial Roman legion figures largely in the entire Eagles and Dragon series, and so, I thought it good to do a brief introduction of the make-up of the legion at the time the book begins in A.D. 197.
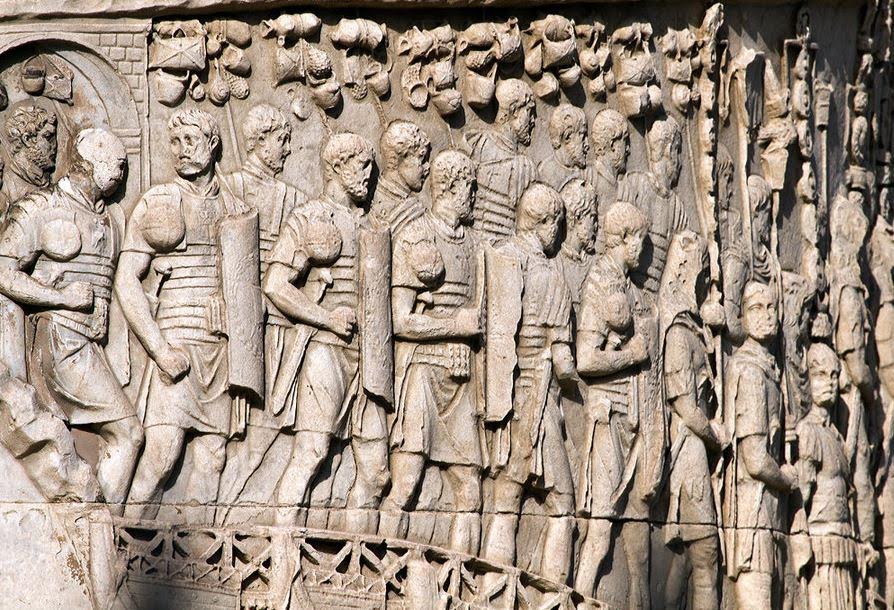

Roman legionaries on Trajan’s column
At this time in the history of the Roman Empire, the Roman legion is a well-oiled machine. It, and its troops, had been perfected after centuries of warfare, of trial and error, victory and defeat.
This army, the army of the Principate, is quite different from that of the Republic. It used to be that Roman legionaries were required to meet minimum requirements of possession and wealth in order to qualify for service in the ranks.

Republican Roman troops (illustration by Angus McBride)
This all changed in 107 B.C when Caius Marius was elected consul and sent to Numidia to continue the war there. However, Marius was denied the right to raise new legions in Africa, permitted only to take volunteers with him.
Of course, Marius took advantage of this, and in a move no other had taken, he appealed to the poorest classes of citizens who became known as the capite censi.
These ‘head count’ citizens were enthusiastic about joining the legions and the new opportunity for a livelihood that it presented them with. They became the backbone of the Roman Legion, and from that time onward the link between military service and property was done away with. They need only have been citizens.
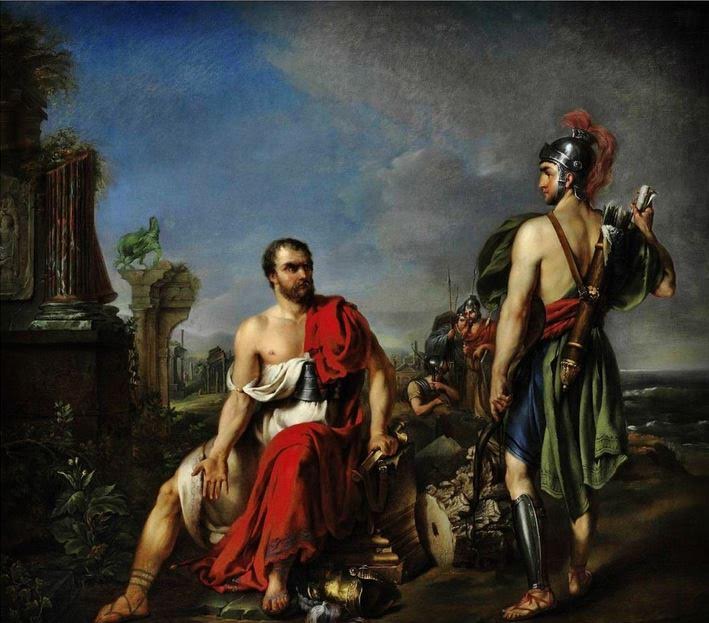

Gaius Marius among the ruins of Carthage (Joseph Verner 18th century)
Marius made many reforms to the Roman army which I won’t go into here, however, his move contributed to the creation of a permanent, full-time citizen army, a self-sufficient fighting force of well-trained men with standard-issue equipment, food and lodging. They carried everything they needed on the march on their own backs, including weapons, spikes for palisades, pots, pans, and pick-axes for digging fortifications.

Marius’ Mules – Re-enactors marching in full kit
Because of all the kit they carried in the field, they became known as ‘Marius’ Mules’.
The average kit for a rank-and-file soldier in the imperial legions included hobnail sandals known as caligae, a standard tunic, a leather belt or cingulum, a lorica segmentata which was a breast plate made up of individual iron strips, a helmet, cloak, gladius (short sword), pugio (dagger), a pilum (javelin), and a scutum (shield).

Re-enactor in Roman Legionary outfit
In A Dragon among the Eagles, there is mention of the various ranks and units that make up the legion, so I think it a good idea to cover the basics now.
The smallest unit of men in the imperial legion was a contubernium which consisted of eight men who shared a tent, or barrack room. These men marched, fought, lived, and cooked together.
Then there was the century. This is probably the most well-known unit of men. It consisted of 10 contubernia, and was run by a centurion with a standard bearer and an optio beneath him.
The centurion was usually a career soldier, and a harsh task-master. He wore different armour that was chain mail, usually with a harness decorated with phalerae, decorative discs that represented awards he had been given. The crest of a centurion’s helmet was horizontal, and he carried a short wooden staff called a vinerod, which gave him the right to strike his citizen soldiers in the interests of discipline.

Re-enactor dressed as a Centurion (Wikimedia Commons)
There are stories about a particular centurion in the imperial legions whose nick-name was ‘give me another’ because he was constantly breaking his vinerod over the backs of his men!
Centuries of eighty men were the most flexible military units in the legion. They numbered enough to go on patrol, or building duty, and could manoeuvre effectively in battle.
Now, the next unit of the legion was the cohort.
The imperial cohort was made up of 480 men, and consisted of six centuries let by an Equestrian tribune. The first cohort of a legion, however, was led by a Patrician tribune.

Officers of the Imperial Roman Legions (illustration by Ron Embleton)
Finally, there were ten cohorts in a legion which brought the average number of troops in the imperial legion to 5000.
The commander or general of an entire legion was known as the legatus legionis, or legate commander. This person was usually a senator, just like the patrician tribune who was his second-in-command. The third person of overall authority in the legion was the camp prefect, or praefectus castrorum. The latter was often a career soldier, perhaps a former centurion who had been promoted, and was responsible for much of the legion’s administration and logistics.
There were many other minor positions within the legions such as duplicarii, men who received double pay for skills such as engineering, or the building of siege equipment, as well as benificari, those who were aides to the legate or other officers, and who were excused for intense labour such as the digging of ditches and erecting palisades.
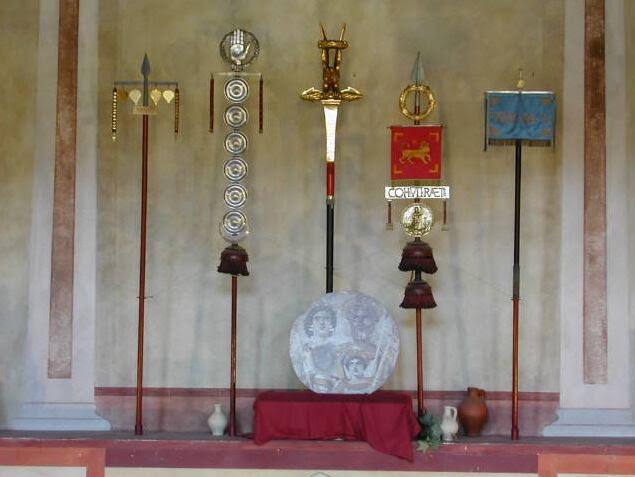

Roman legionary standards with an image of Emperor Severus and his family
We must not forget the standard bearers who made up the imperial legion. These included the vexillarius, the person who carried the vexillum standard of each unit, the signifer, the soldier who carried a century’s standard and wore a wolf or other pelt over his helmet. There was the cornicen, the trooper who carried the cornu, the round horn used to rally the troops and give commands, as well as the imaginifer of the legion, the trooper whose task it was to carry the image of the emperor before the legion.
Probably the most important standard bearer was the aquilifer, the man whose solemn duty it was to carry the legion’s golden eagle, the aquila, into battle. This man was to protect the legion’s eagle at all cost, for it was the ultimate disgrace for a legion to lose its aquila to an enemy.
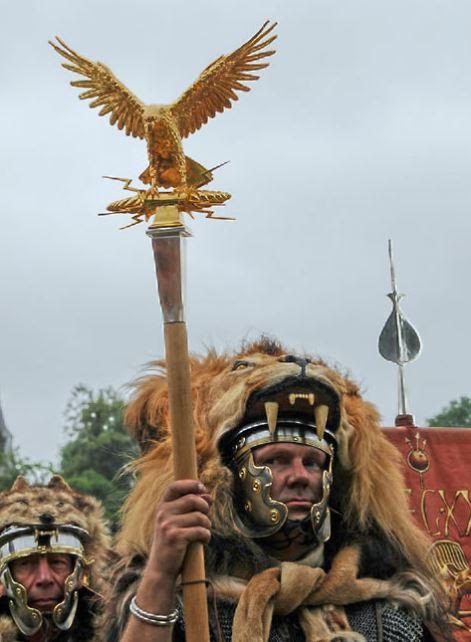

Re-enactor dressed as an Aquilifer
Along with the 5000 regular troops that made up an imperial legion, there were often alae, or auxiliary units, attached to the legion. These were usually units of 120 cavalrymen who acted as scouts and supported the legion on the march. They were often made up of foreign troops who had been brought into the Roman ranks such as Sarmatians, Numidians, or Scythians to name a few.
Ala units might also consist of skirmishers such as Cretan or Balearic slingers, but most often they were cavalry.
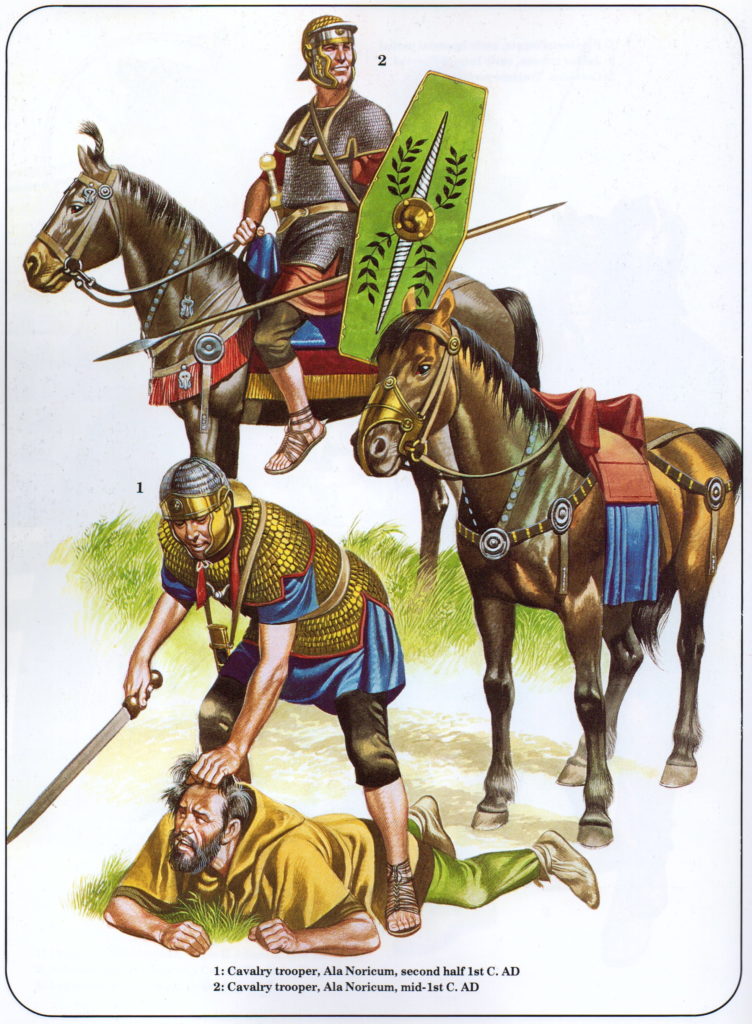

Auxiliary Cavalry troops (illustration by Ron Embleton)
The imperial Roman legion was one of the most effective fighting units of the ancient world, and it is no wonder that the Empire covered so much of the known world by the time in which A Dragon among the Eagles takes place.
Disciplina, the goddess personification of discipline, was something that was taken very seriously. If a soldier obeyed her and remembered his training, he would survive the direst of circumstances.

Roman coin showing stardard bearers and the world ‘Disciplina’ – second century A.D.
When the legions marched in the field, every night they dug in, every trooper going to his assigned space to dig ditches, pile up ramparts, and raise the palisade around the entire camp.
Tent and command centre, the Principia and Praetorium, tribunes’ tents, stables etc. were always in the same position, the streets set out in the same grid every time. So, whatever happened, a Roman soldier knew where he was, and what he had to do.
Every morning, when they would break camp, they would take down the work of the previous evening, which they had done after a twenty mile march, so that the enemy could not make use of their fortifications.
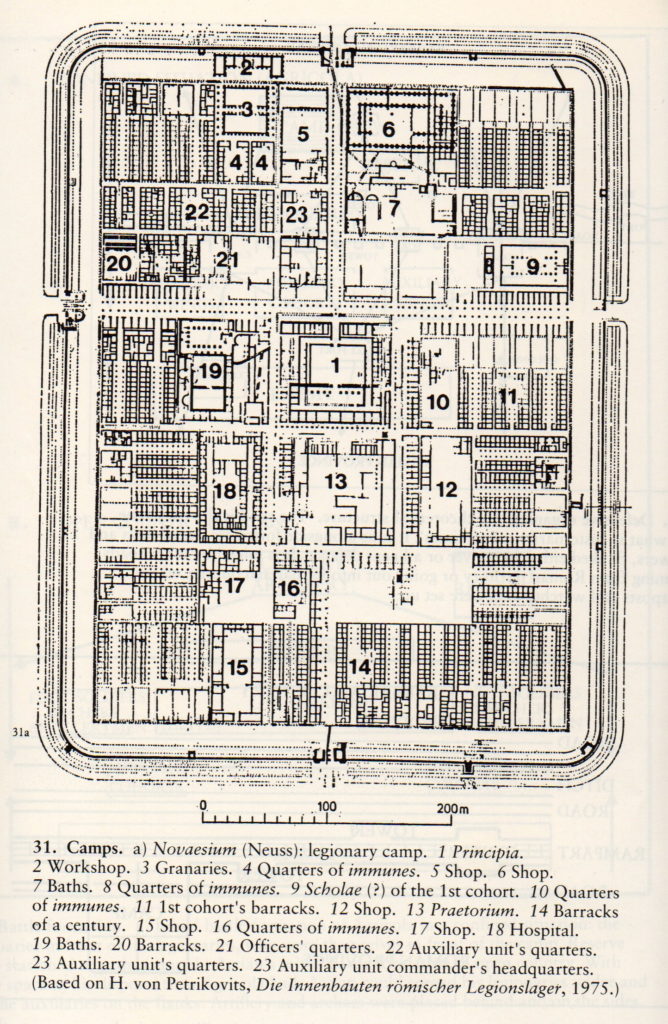
Plan of a typical legionary fortress (from The Imperial Roman Army by Yann Le Bohec)
It was hard work, but the imperial legion gave opportunity to the poorer classes of Roman citizens and allowed them to make something of themselves, if not at least be clothed and fed at the state’s expense.
In return, the men of the legions bled for Rome as they extended her borders into the world.
A Dragon among the Eagles takes place during the Severan invasion of the Parthian Empire, one of the biggest thorns in Rome’s side for over two hundred years.
In A.D. 197, Septimius Severus set out with one of the largest invasion forces in Rome’s history, made up of a titanic 33 legions.
The stage was set for one of the greatest military campaigns in Rome’s history.
In the next post, we’ll look at this powerful enemy and the tactics they used in battle against the legions.
Until then, check out this great video that illustrates the make-up of the Roman legion.
Thank you for reading!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wCBNxJYvNsY