What was it like to live on the very edge of the Roman Empire?
When writing Killing the Hydra, this was something I asked myself many times. What was life like for soldiers, commanders, women, children, and locals under Roman rule? What was it like to be so isolated in a place that, for many, sat on the precipice of the known world?

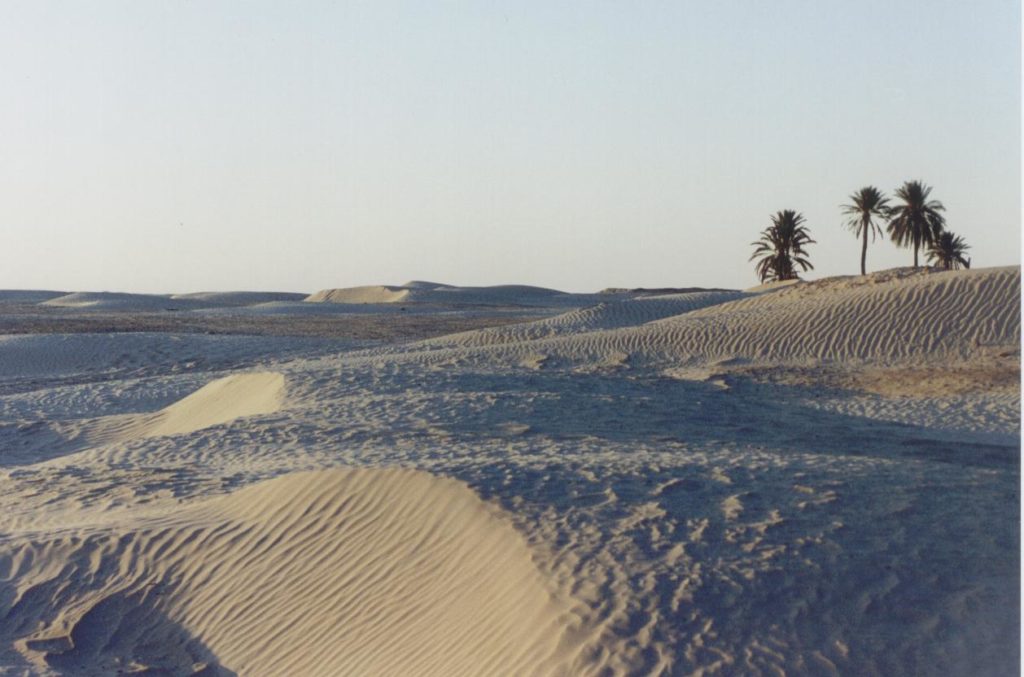
The Numidian Desert – the Sahara in modern Algeria
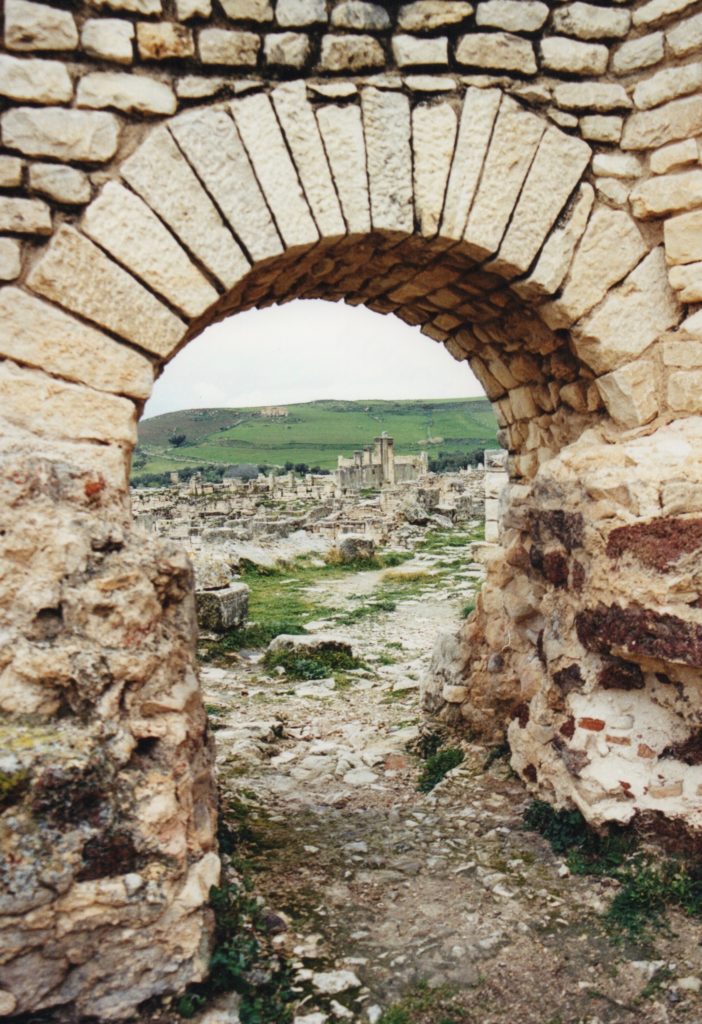
In this fifth and final part of The World of Killing the Hydra, we’re going to look at the place where Lucius Metellus Anguis is posted to, and where his family joins him – the legionary base at Lambaesis.
Lambaesis was located in the province of Numidia (modern Algeria), and was the base for the III Augustan legion at the beginning of the third century A.D. when this story takes place. Lambaesis was established by Emperor Hadrian between A.D. 123-129 when the III Augustan legion moved there.
Hadrian toured the Empire and on his visit to Lambaesis, he addressed the troops of this desert legion. Evidence of this address has come down to us in the form of a pillar inscription that was located on the large outdoor parade ground of the base.

Part of the inscription from Lambaesis documenting Hadrian’s address to the troops when he visited there.
The III Augustan legion, however, was older than that. It originated under Pompey the Great in the civil war against Julius Caesar and was eventually moved to North Africa in 30 B.C. by Octavian (who became Augustus) after his victory over Mark Antony.
Eventually, the III Augustan came to be based at Lambaesis, one of only two Roman legions in North Africa, the other being based in Aegyptus.
The III Augustan played an important role in the security and urbanization of North Africa, helping to build roads, aqueducts, fortifications, theatres and more. This work in turn connected towns and cities, facilitated trade, and provided protection for outlying settlements. The work of the army engineers and surveyors brought Roman civilization to this remote frontier.
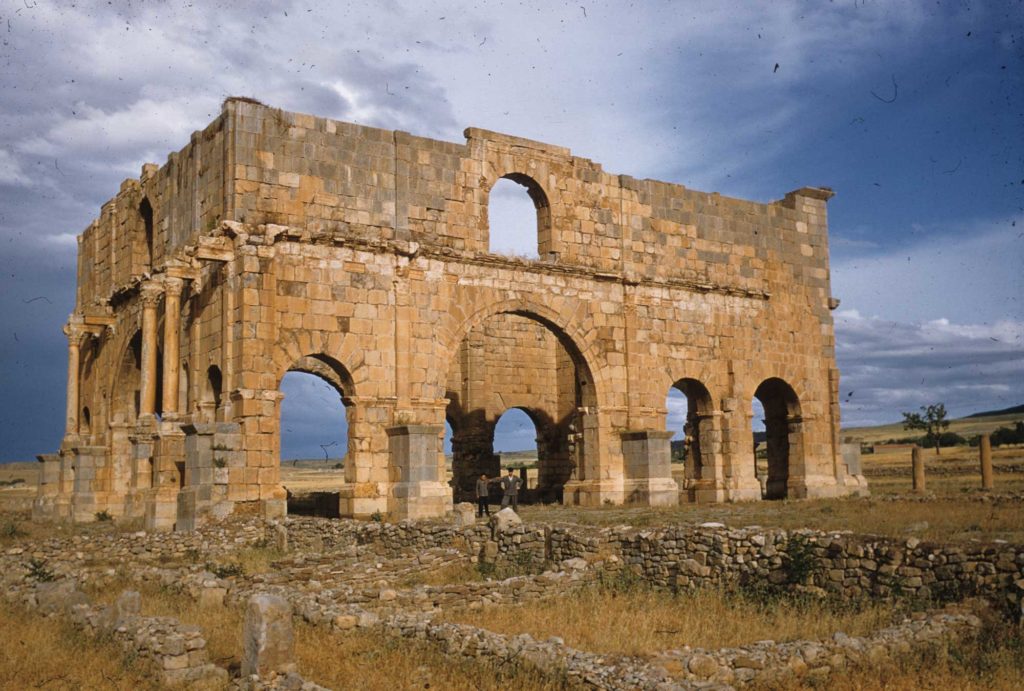

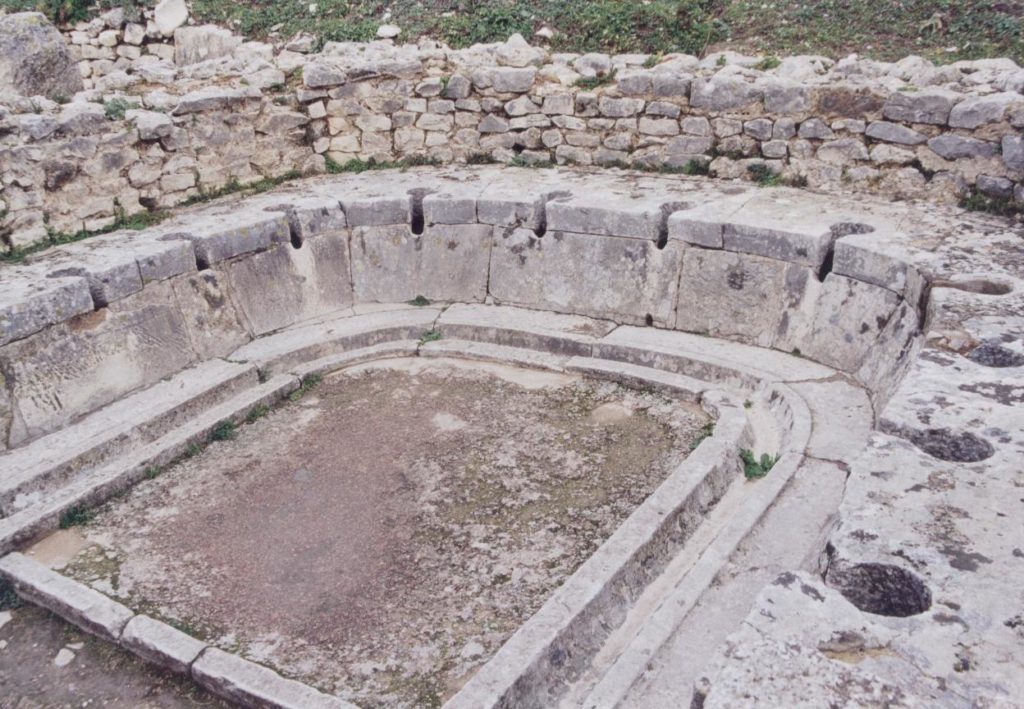
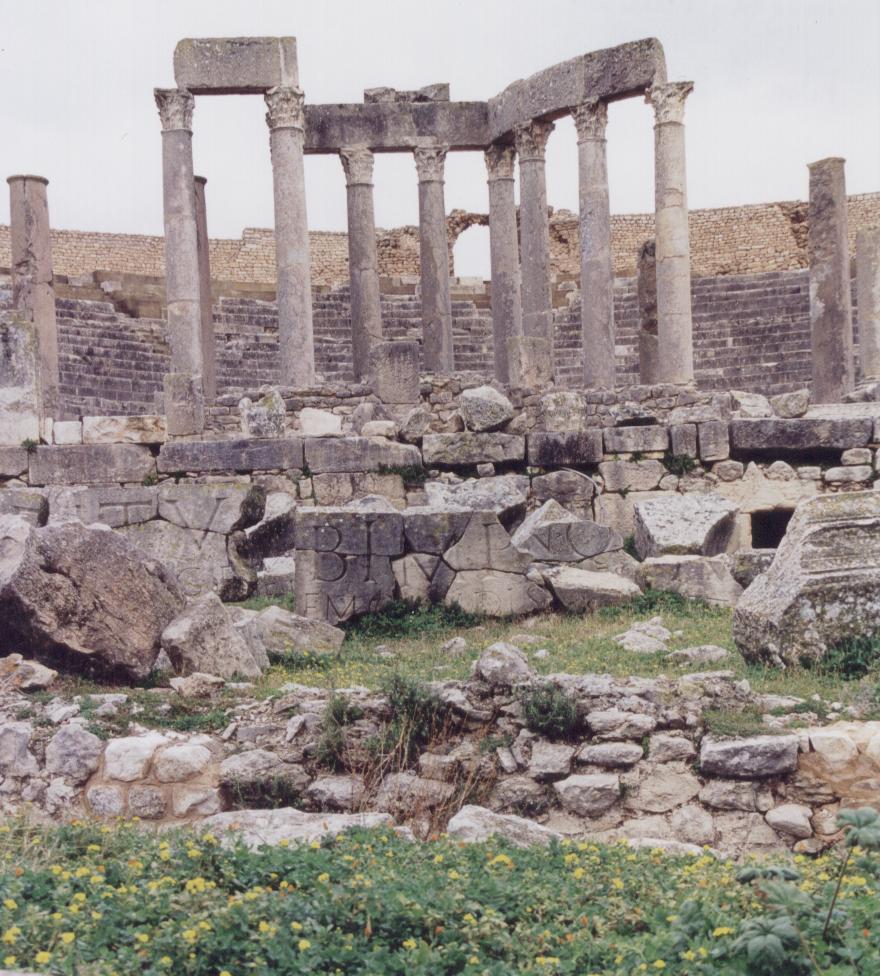
The Praetorium of Lambaesis
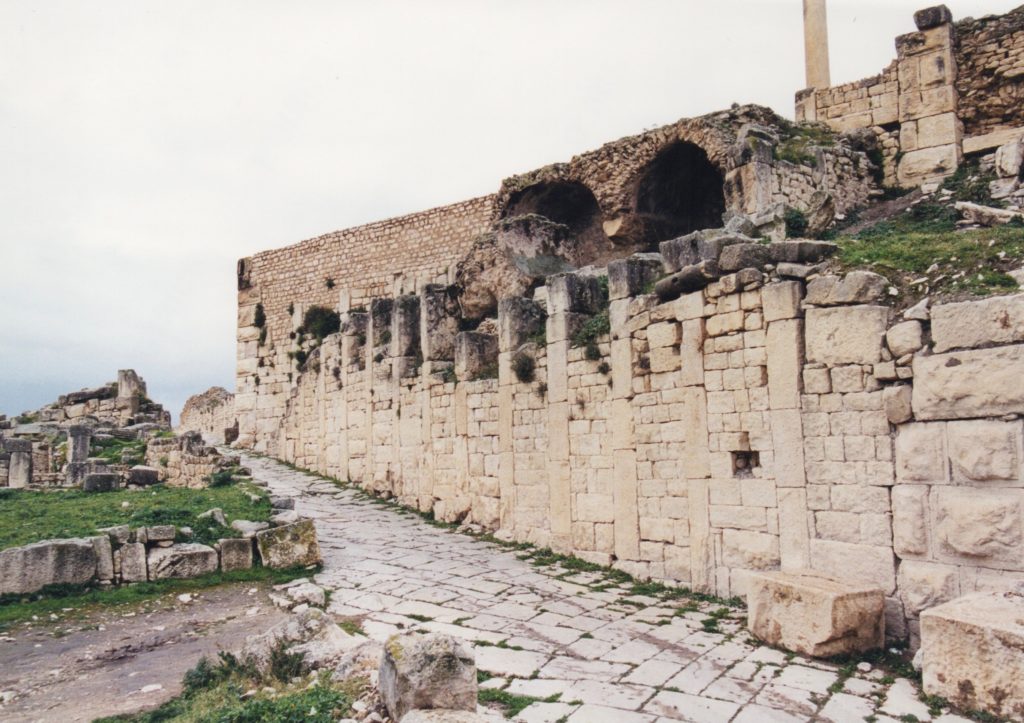
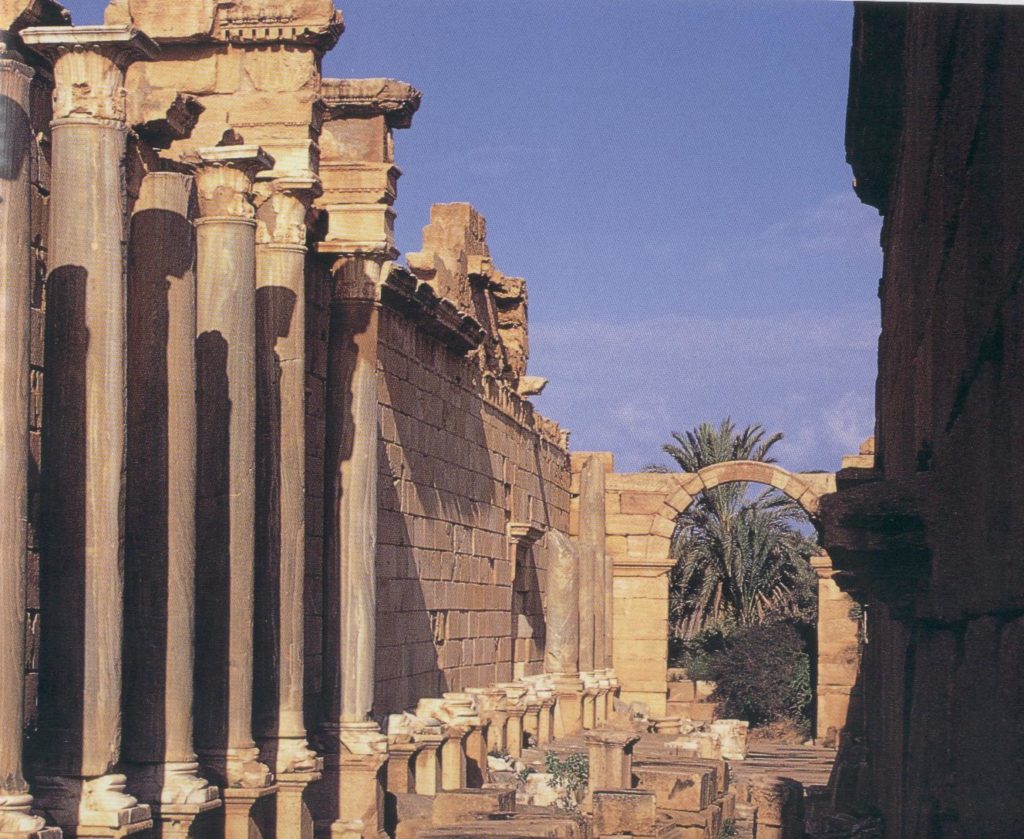
The III Augustan was a veteran legion, and of the remains present in that place, apart from the arches of Septimius Severus and Commodus, temples, baths and cemeteries, the principia with its open courtyard is the most stunning of its remains.
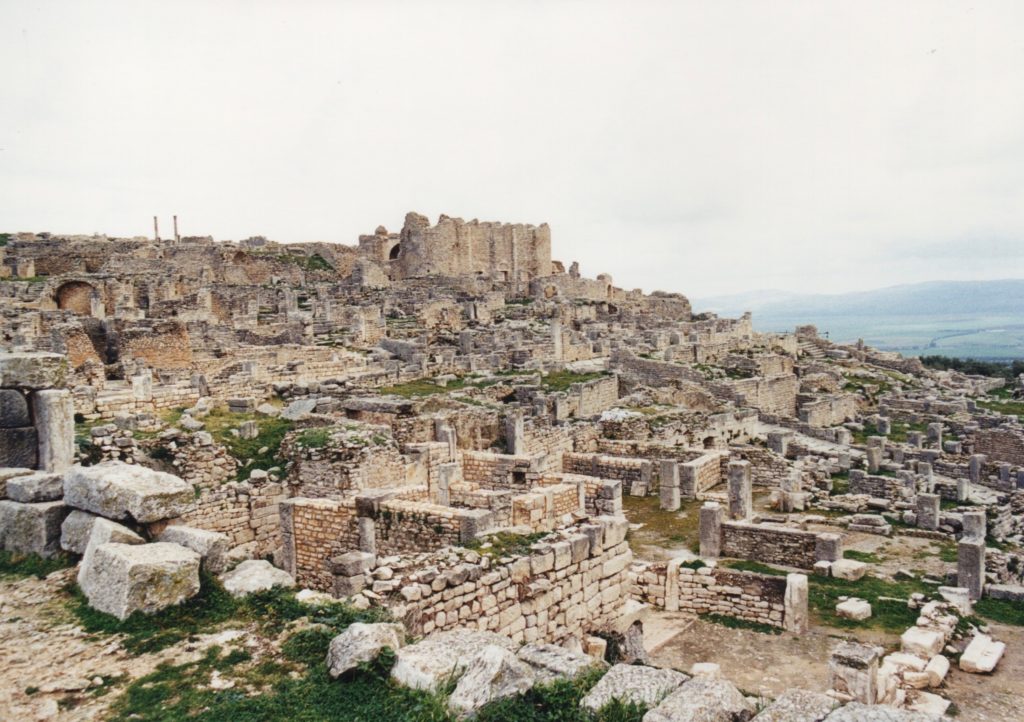
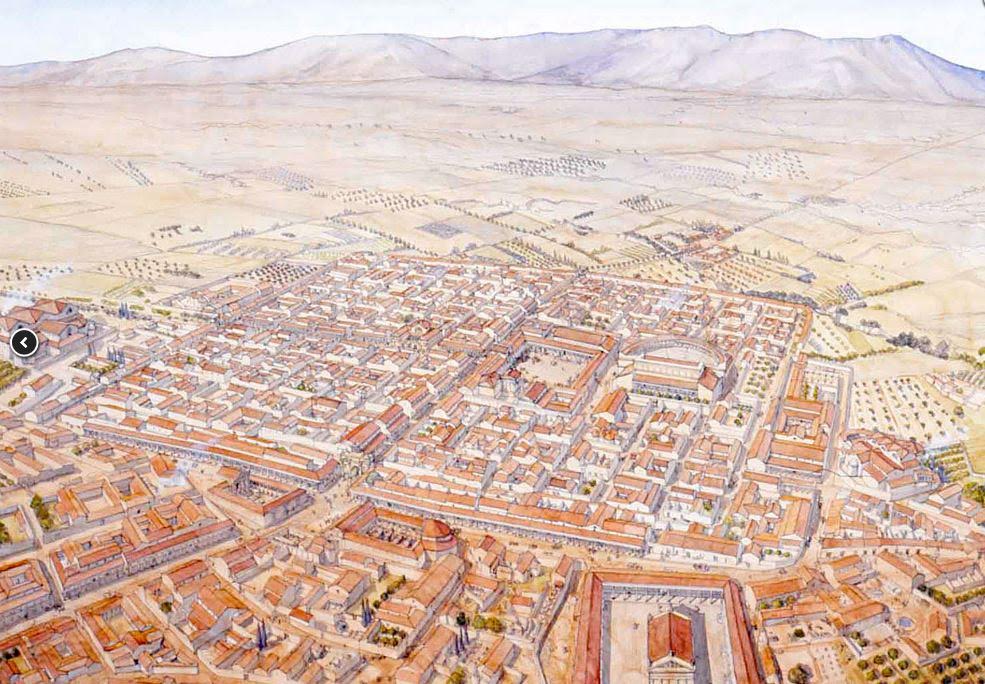
This base was on the edge of the deep desert in modern Algeria, backed by the Aures Mountains. At first glance, this seems to have been a lonely windswept place, just as it is today. However, during the Roman period, Lambaesis would have been a busy, thriving place.
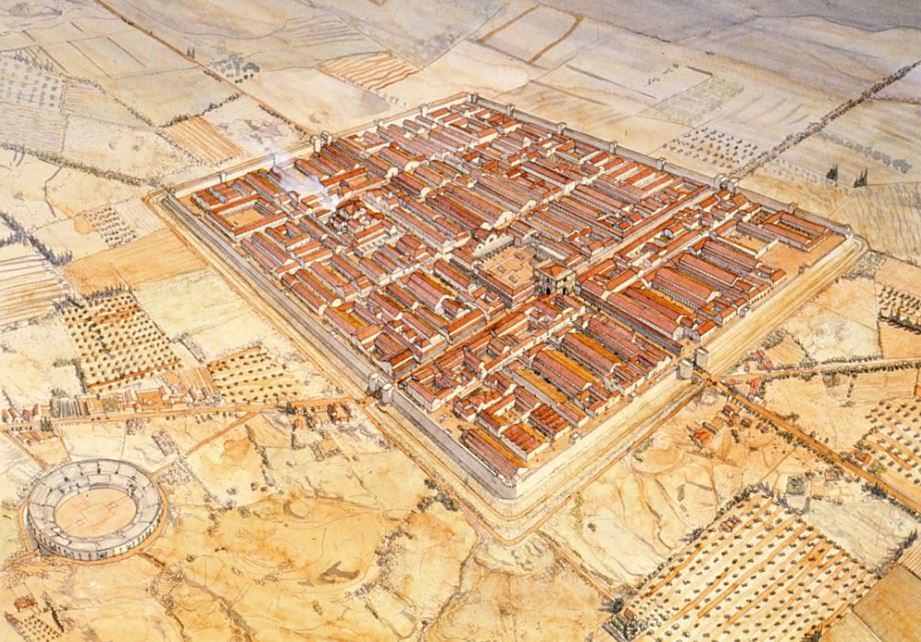

Artist impression of Lambaesis by Jean Claude Golvin
This was not so much an active frontier like that of the Danube or Parthian fronts, but rather a more peaceful place, punctuated with occasional incursions by Garamantians, nomadic Berber tribes and others.
For the most part, the veterans of the III Augustan took part in public building works and improvements, as well as patrols. The men of the legions were a part of society at Lambaesis and the surrounds.
Previously, men of the legions were not permitted to marry, but this law was changed under Septimius Severus, and so many men would have had families living in the vicus outside the base’s walls, or in some instances within the walls.
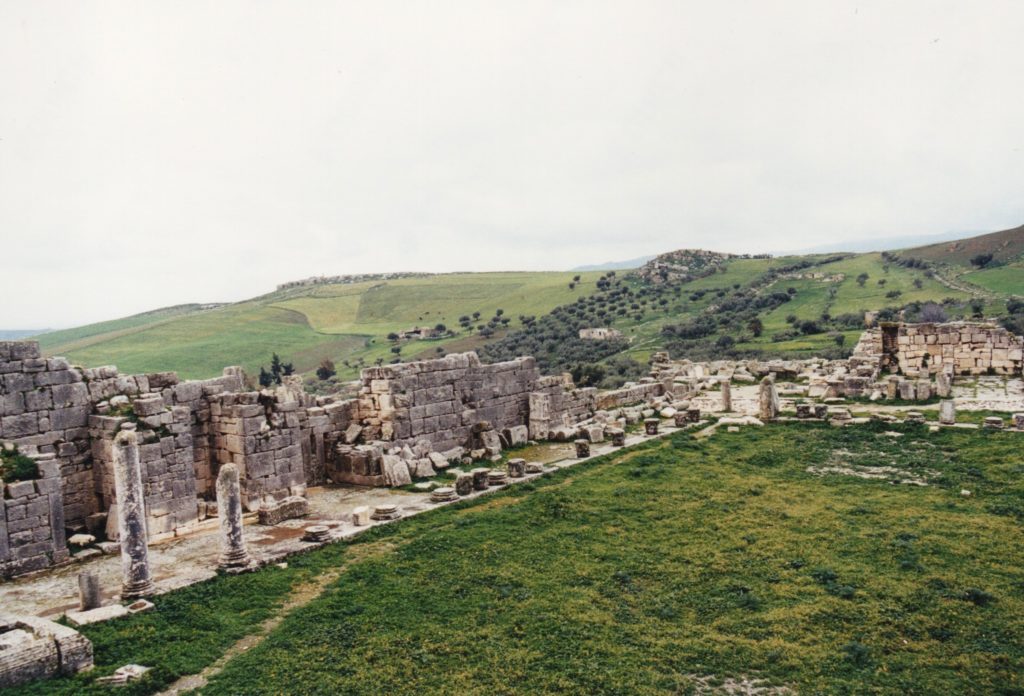
Add to this the presence of the large, prosperous colonia of Thamugadi, just seventeen miles away, and you have a frontier that was busy, social, and economically vibrant.
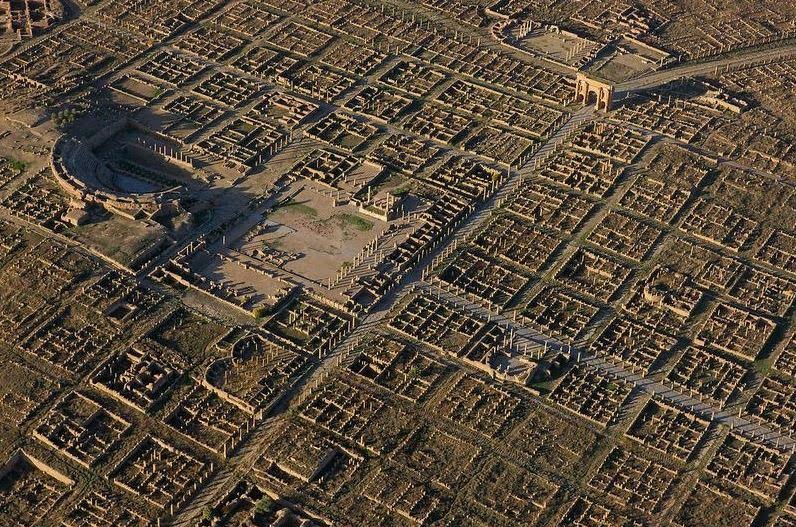

Aerial view of the colonia of Thamugadi
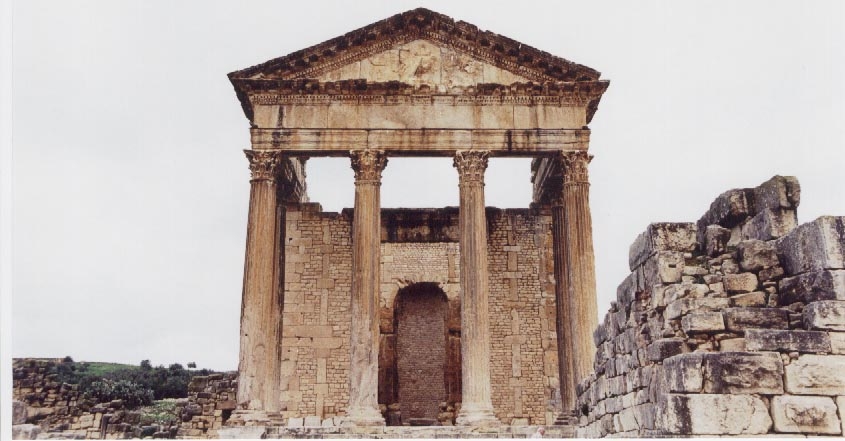
The colonia of Thamugadi was where veterans of the III Augustan legion retired to once their military service was at an end. It was founded by Emperor Trajan in about A.D. 100 under the name of Marciana Traiana Thamugadi. It was a walled settlement, but not fortified, and had a population of about 15,000.
Today, it is made up of some of the most intact and vast ruins of Roman North Africa, including the well-preserved arch of Trajan. It had twelve public baths, theatres, a public library, a basilica and a magnificent temple of Jupiter.
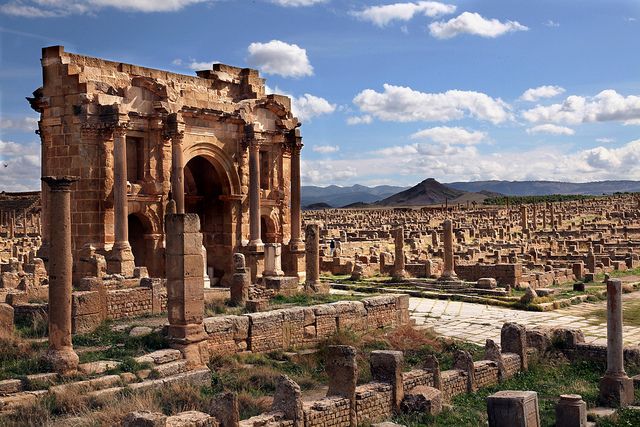

The arch of Trajan in Thamugadi
One imagines that it was lonely for soldiers’ wives and their children, being posted to such a remote location, compared with other parts of the Empire, but with the changed laws regarding marriage for troops, the close proximity of Thamugadi to Lambaesis, and the thriving economy of Roman North Africa at this point in time, it seems like Saharan frontier life may not have been the sort of lonely, wasteland existence that I had in mind when I started my research and writing.
I always try to travel to the places I am writing about, but sometimes that just isn’t possible, or safe. Lambaesis was one of those places.
At the time of my Tunisian research for Children of Apollo and Killing the Hydra, we were told there was a travel ban to Algeria where the remains of both Lambaesis and Thamugadi are located.
Artist impression of Thamugadi by Jean Claude Golvin – this was not a tiny village, but a bustling settlement!
Our 4X4 skirted the military border between the two countries, distant guard towers and barbed wire visible as a long grey line cutting across the North African landscape.
We asked our guide if we could drive into Algeria but he was adamant that it wasn’t possible. “No chance. It is forbidden. They will shoot at us,” he said.
I don’t know if that was true or not, but some things are not worth the risk. After all, we have the internet now and a myriad of resources on-line.
So, we had to settle for pulling our truck over on the gravelly roadside and gazing westward across the guarded border to the Aures Mountains of Algeria and imagining what remnants of Rome lay scattered in that vast expanse.

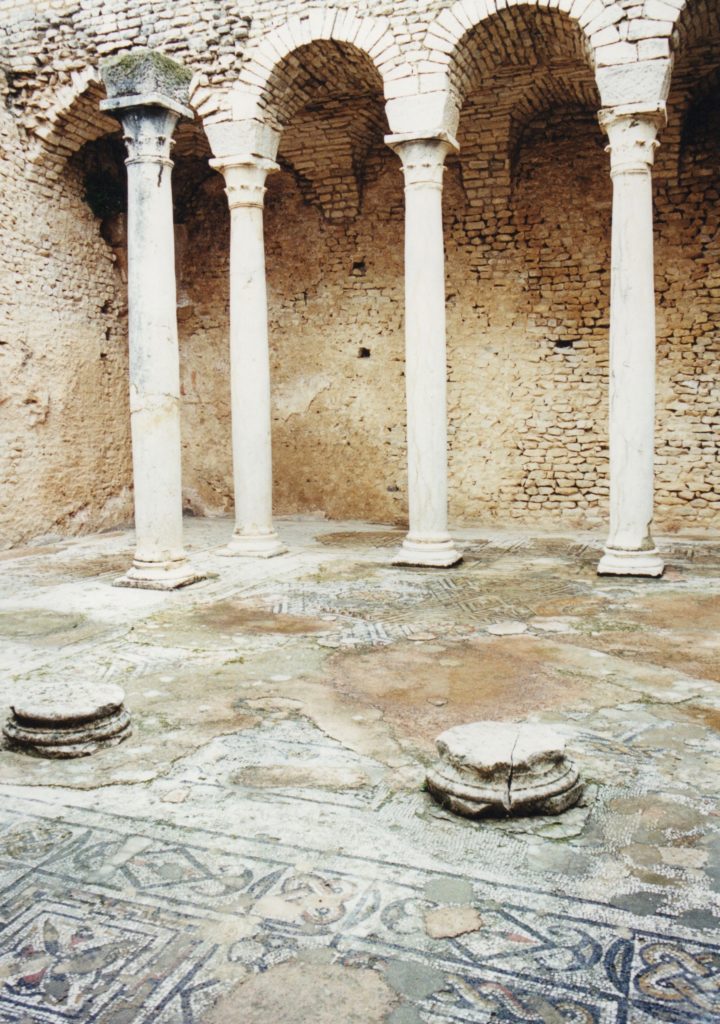
Mosaic fragment from Lambaesis
The light was dull that day, an iron-grey winter sky, so the feeling of loneliness and desolation was acute. Somewhere out there was the base of the veteran III Augustan legion. There was a colonia for veterans filled with the amenities of Roman civilization.
This was a land where my character was to be posted, along with his family, and the families of his fellow officers and troops. Many would have had family and friends in Thamugadi, done business there, and used the network of roads that really did, in one way or another, lead back to Rome…
It was hard to imagine as I stood there with the dust whipping around us, our guide looking nervously in our direction as if we might attempt something stupid.
The relief on his face when we said “OK. Let’s go.” was darkly comic. It was also real.
But maybe that hints at Saharan frontier life in the Roman Empire?
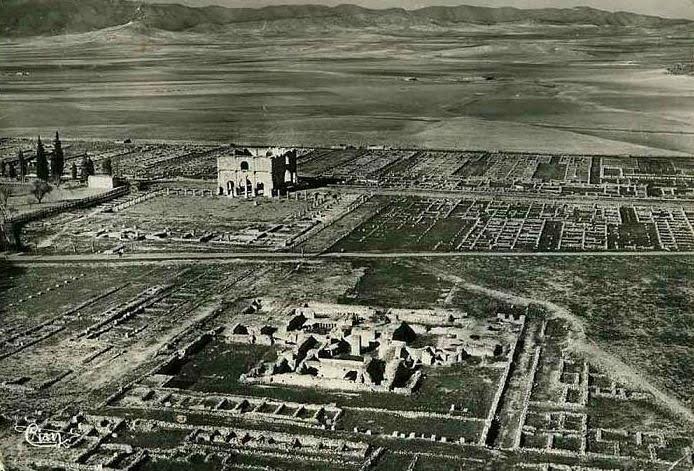

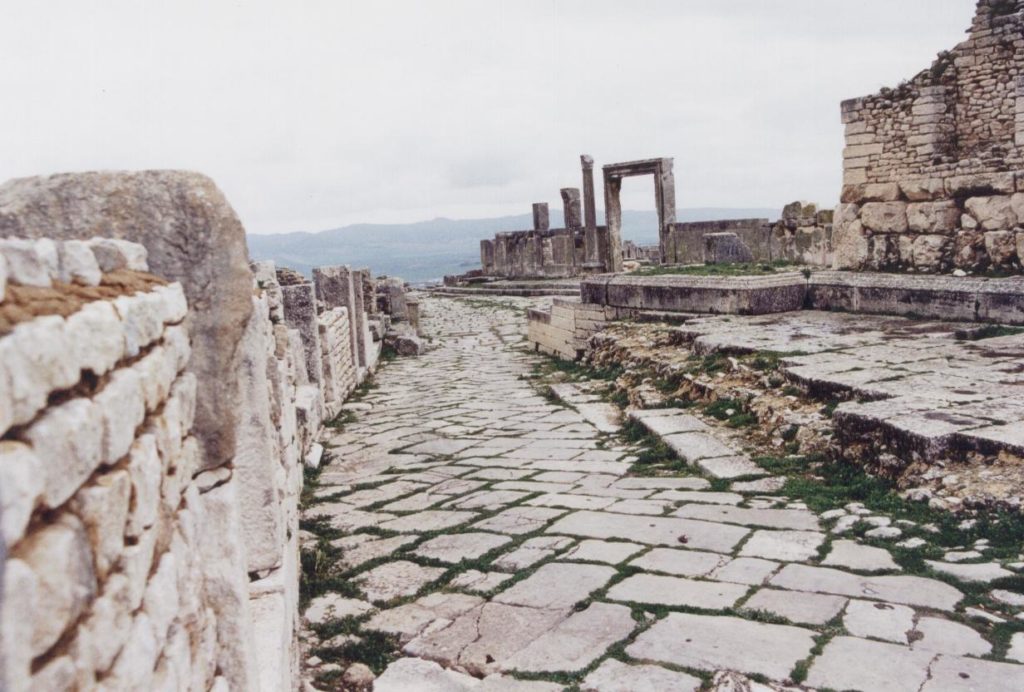
Aerial view of Lambaesis