Zenobia Neil
Love is a Monster – A Guest post by Zenobia Neil
Greetings readers and romantics,
Seeing as this is the week of Valentine’s Day, we are going to spice things up a bit with something different.
I’d like to extend a big welcome to my fellow author, Zenobia Neil, who is going to shed some light on the darker side of Love in the ancient world.
This isn’t about red roses and chocolates, though those are quite nice.
As Zenobia will show us, Love can indeed be a monster…

Hale, Edward Matthew; Psyche at the Throne of Venus; Russell-Cotes Art Gallery & Museum; http://www.artuk.org/artworks/psyche-at-the-throne-of-venus-58520
In the modern western world, we tend to think of Cupid as a cherubic angel and that being in love is a wonderful feeling. But in the ancient world, Cupid had a complicated past. Said by some to be one of the oldest gods and by others to be a child of Venus, Eros, who would become the Roman Cupid, was many things. But one thing he was not was romantic.
Like many traditional societies, the Romans arranged marriages to benefit the extended family and make alliances. Only the Romans took it a step further, sometimes forcing couples to get divorced in order to create a better alliance. Falling in love was not seen as a wonderful emotion, but instead a loss of power and control—a terrible thing to happen to a Roman man. Yet, ironically, we get the root of the word romance from the Romans. These ideas intrigued me as I wrote Psyche Unbound, an erotic retelling of the classic story of Cupid and Psyche.
The original tale of Cupid and Psyche was recorded in The Golden Ass by Lucius Apuleius, which is the only existing fully intact Roman novel. The Golden Ass tells an incredible first person story about Lucius, a Roman from Africa who is interested in magic. Attempting to become a bird, he gets turned into an ass, which is only the beginning of his misery. Before he can get turned back into a man, he is taken by robbers. As the robbers’ stolen property, he overhears an old slave woman recount the story of Cupid and Psyche to an abducted virgin to help calm her.
A mythical princess in a city by the sea, Psyche is said to be more beautiful than Venus. If you know anything about the Greek gods, you know this is an unforgivable crime. Psyche herself does not boast of her beauty, yet she is the one to pay the price.
In Ancient Greece and Rome, a girl’s marriage was symbolic of the death of her childhood. She was leaving her father’s home for her husband’s, a man usually much, much older who would have almost complete control of her life.
In my novel, Psyche Unbound, I highlighted this idea by having Psyche be sacrificed to a monster. In the original story, she was taken to a mountain top to be married to a creature “feared by Jupiter.”
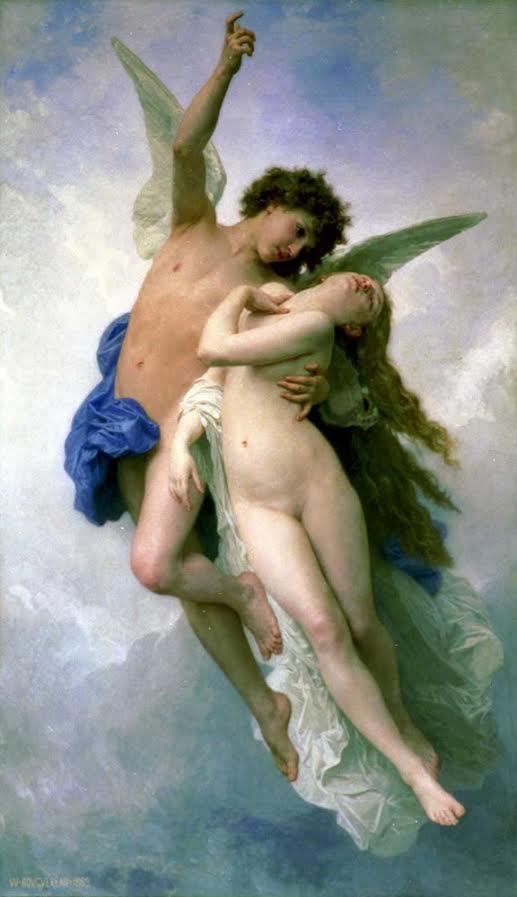

Cupid and Psyche flying
Similar to Beauty and the Beast, the mysterious monster Psyche is to be sacrificed to lives in an enchanted palace. Invisible musical instruments play, and invisible servants make and serve delicious meals. Unlike Beauty and the Beast, in my version, Psyche is fed an aphrodisiac of wild hyacinth bulbs soaked in honey. She is then blindfolded and bound to the bed where she awaits the monster.
He comes to her in the dark of night and makes her his wife after she promises to never look at him. He tells her she can’t see him because he’s a monster, but after spending the night with him, she does not really believe him. In the magical palace, in the dark, they get to know each other and fall deeply in love. But, Psyche wonders how she can love him if she cannot know him completely. Like all mortals in myths, she is overcome with curiosity and risks losing it all for just one peek.
I’ll skip the next part of Psyche Unbound and the Psyche myth and say that after being banished from the magical palace, Psyche must face her nemesis—Venus—a goddess who does not believe in mercy. Although we now think of love as a warm, fuzzy feeling, the ancient gods were—to quote the introduction of Xena Warrior Princess—“petty and cruel.”
What better villain is there than the Goddess of Love and Beauty? Although we now celebrate love with ideas of sweetness and kindness, it is also said that people don’t experience real love until their first heartbreak. That pain and fury is the other side of love—the aspect represented by beautiful, fickle Venus.
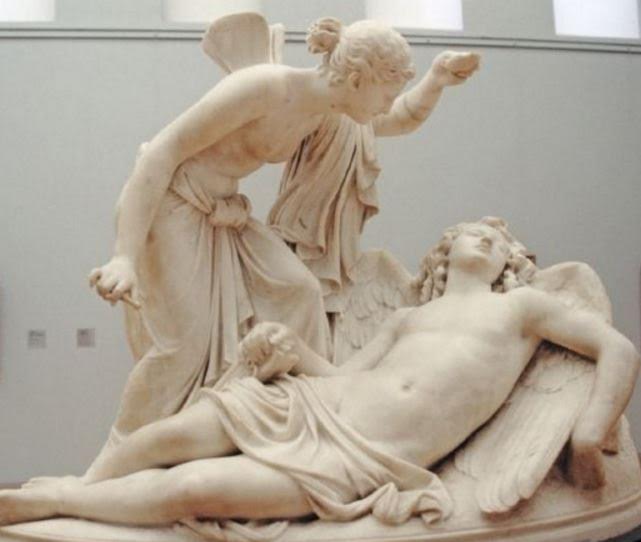

Psyche looking at Cupid while he sleeps
The story of Cupid and Psyche has many exciting aspects, a Roman princess, a renegade god, a vengeful goddess, and an epic quest. However, the most intriguing idea to me was that Psyche, a lowly albeit beautiful mortal, was the one who knew more about love than either Venus or Cupid. The ancient gods and goddesses did not really understand the things they stood for in that they had often never experienced them.
And this beautiful irony is part of what has always drawn me to Greek myths. For many of the gods, there is an amazing juxtaposition: Diana, Goddess of Childbirth, is an eternal virgin; Juno, Goddess of Marriage, was tricked into marriage by her brother and then watched him be unfaithful for centuries; Hades, King of the Dead, is immortal and in many ways has never even been alive; Apollo, God of Healing, can also cause plagues; Mars, God of War, the perfect companion to Venus, fights but never dies. He knows the rage of war but not the cost of loss. And Venus, the Goddess of Love and Beauty, does not understand what we would think of as true love, and her fickle shallowness is not what many people think of as true beauty. And lastly, Cupid, God of Love, had shot his arrows into many unsuspecting victims without ever falling prey to love himself. Until Psyche. Until a mortal taught him and the gods what it was to find love and helped changed love from a monster into something we now celebrate.
I’d like to thank Zenobia for taking the time to write this great piece for us, and for showing us a different side of Love.
I’m actually reading her book, Psyche Unbound, now, and I have to say that it’s a spicy, wonderfully-written retelling of the Eros and Psyche myth.
If you like a bit of erotica and Greek and Roman mythology, then you have to check out Zenobia’s book.
CLICK HERE to learn more.
Also, be sure to sign-up for her newsletter so that you can be notified when her next book comes out: https://www.zenobianeil.com/
Thank you for reading!

Author, Zenobia Neil
Zenobia Neil was born with a shock of red hair and named after an ancient warrior woman who fought against the Romans. In college, Zenobia studied Ancient Greece, Voodoo, and world mythology. Realizing she needed a job, she got a master’s in teaching English in Monterey, California.
Needing an escape from the unrelenting though joyous nature of motherhood, Zenobia returned to one of her first loves, writing fiction. Having always been interested in Greek and Roman mythology, she became obsessed with reading and writing about the ancient world and began writing Greek god erotica.
Still an English teacher, Zenobia spends her time imagining interesting people and putting them in terrible situations. She lives with her husband, two children, and dog in an overpriced hipster neighborhood of Los Angeles.