Welcome back, Readers and History-Lovers!
I hope you’ve been enjoying this blog series about The World of The Blood Road. It has been a joy to share my research with you over the last little while.
In Part VII, we journeyed to see the Pythia at Delphi and experienced the beauty of the sanctuary there. If you missed that post, you can read it by CLICKING HERE.
Today, in Part VIII, we’re going to be taking a brief look at one of the richest cities in the Roman Empire: Antioch.
So, step aboard our corbita and let’s set sail for this magnificent city of the eastern Empire!
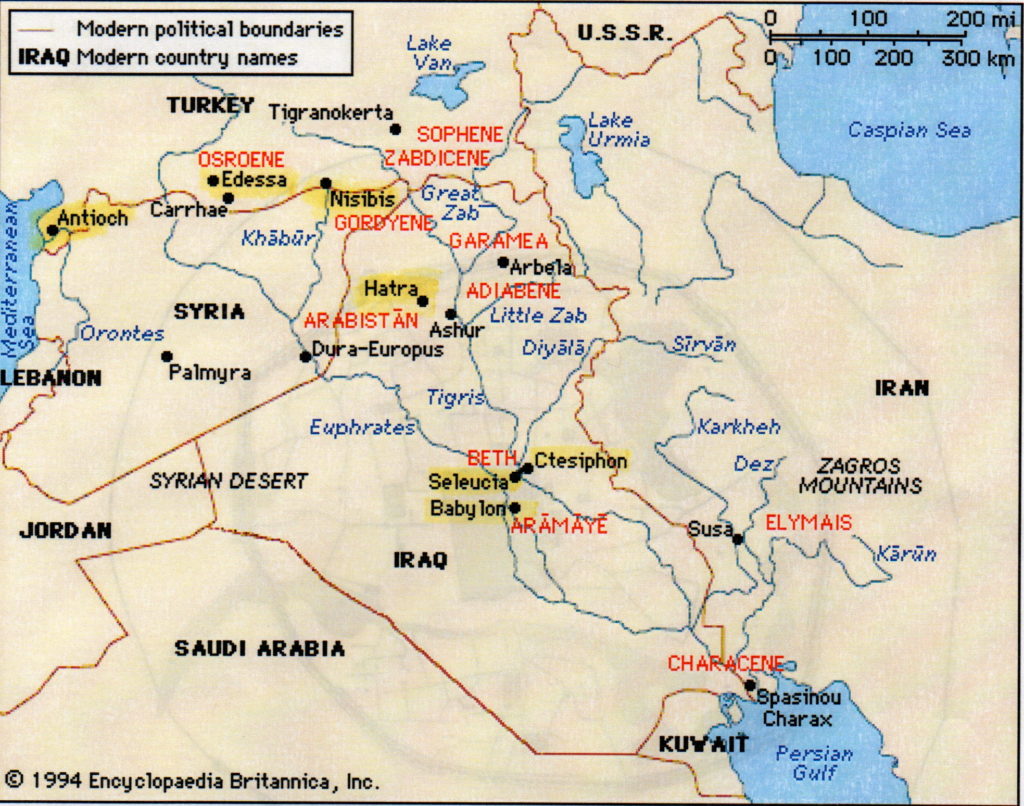
Map showing the Eastern Roman Empire and Parthian Empire. Note Antioch in the top left where the Silk Road meets the Mediterranean.
In the novel, The Blood Road, there are several locations across the Roman Empire that we visit. Antioch, however, is not an entirely new location in this series.
In A Dragon among the Eagles (Book 0), the legions of Septimius Severus assembled outside Antioch for the invasion of Parthia, and our protagonist, Lucius Metellus Anguis, was among them.
Well, we’ve come full circle now, and find ourselves back in Antioch, only this time it is not to await the order to march from inside a legionary tent on the plain outside the city. This time, we’re going into the city streets to explore what was known as the ‘Rome of the East’.
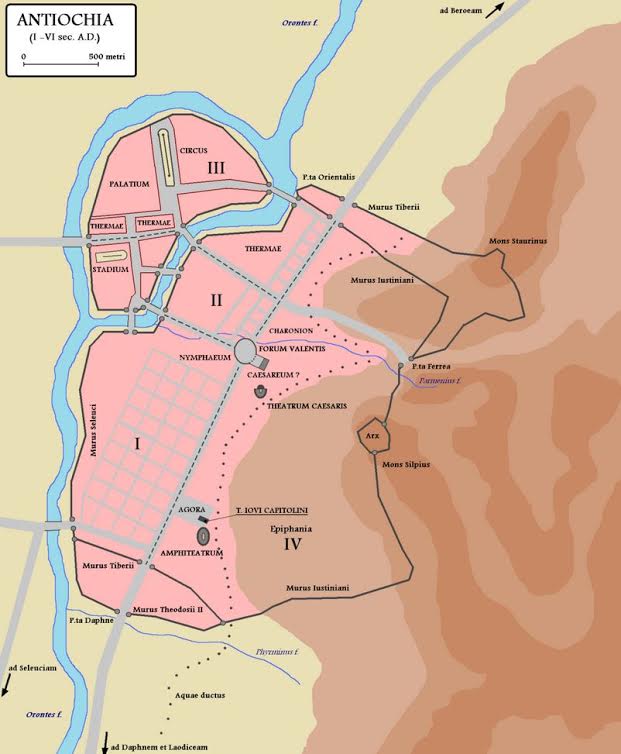
Antioch in the Roman Empire (Wikimedia Commons)
Antioch was the gateway to Mesopotamia which is said to be the cradle of civilization. It is a land of alternating fertility and desert where the first cities were built, and empires made. It also was, and is, a land of war, a land of terrible beauty.
For millennia, successive civilizations have fought over this rich land, a land from which Alexander the Great had decided to rule his massive empire.
In A Dragon among the Eagles, Lucius Metellus Anguis’ legion arrives at the port of Antioch where Emperor Severus has assembled over thirty legions on the plains east of the city.
Antioch, which was then located in Syria, now lies in modern Turkey, near the city of Antyaka. It was founded in the fourth century B.C. by one of Alexander’s successor-generals, Seleucus I Nicator, the founder of the Seleucid Empire. Seleucus named this city after his son, Antiochus, a name that would be taken by later kings of that dynasty.

Ancient Roman road in Syria which connected Antioch and Chalcis to the North. (Wikimedia Commons)
Antioch was called the ‘Rome of the East’, and for good reason. It was rich, mostly due to its location along the Silk Road. Indeed, Antioch was a sort of gateway between the Mediterranean and the East, with many goods, especially spices, travelling through it. It is located on the Orontes river, and overlooked by Mt. Silpius.
This Ancient Greek city was greatly enhanced by the Romans who saw much value in it. Actually, most of the development in Antioch took place during the period of Roman occupation. Enhancements included aqueducts, numerous baths, stoas, palaces and gardens for visiting emperors, and perhaps most impressive of all, a hippodrome for chariot racing that was 490 meters long and based on the Circus Maximus in Rome.
Antioch, during the late second century A.D., rivalled both Rome and Alexandria. It was a place of luxury and civility that was in stark contrast to the world of war where, in The Blood Road, the legions are headed once more.
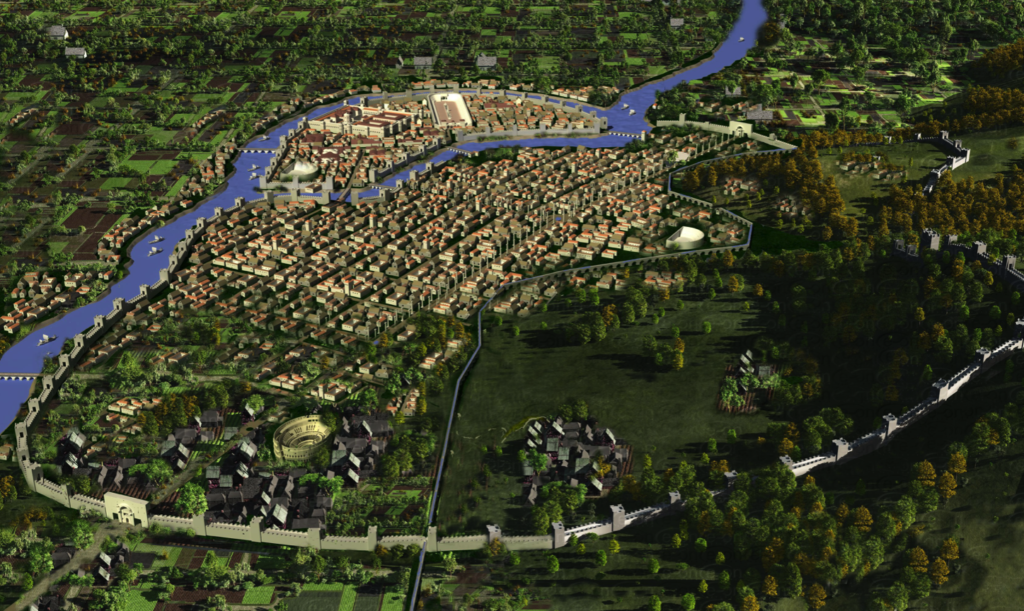
Reconstruction of Roman Antioch (art by Papertowns)
This time in Antioch, however, we are not so concerned with war. We’re not on the front lines so to speak, though at the time this novel takes place, Caracalla is mounting another Parthian campaign.
In The Blood Road, we get a more intimate look at Antioch and its city streets. However, we’re not delving into the palaces, the great circus, or the amphitheatre. This time around we will be among the people in the agora, and also in the quarter known as the Kerateion.
Around the time this novel takes place (A.D. 211-217) the population of Antioch was below 400,000 people. That’s a big city, and like most cities, there were certain quarters that were better than others, areas where certain population groups were relegated.

Site of Antioch on the Orontes River c.1934
Antioch was of utmost importance to trade, as it was the Mediterranean gateway to the Silk Road that crossed the former Persian Empire to the East. The agora would have been a thriving place were many people gathered to buy and sell. The main agora of Antioch was located along the western wall, just above the Orontes river.
On the map, Antioch doesn’t actually appear that big, but, as stated above, it had everything that was needed in a ‘Rome of the East’.
Antioch did well under Roman rule. It was enriched, and it flourished.
But was it the same for all peoples living there? Likely not.
In the southeast corner of the city, pressed between the Daphne Gate and the main colonnaded thoroughfare of the city, the amphitheatre and the eastern wall along the slopes of Mount Silpius, there was a neighbourhood known as the ‘Kerateion’.
This was the Judea-Christian quarter of Antioch, and it is here that our time is mostly spent in The Blood Road.
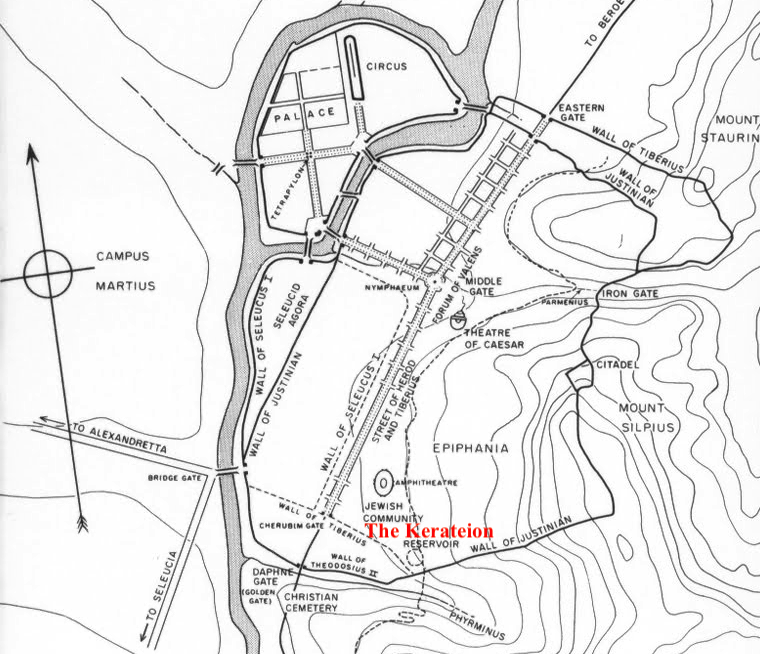
Map of Ancient Antioch (Google Arts and Culture). Note the Judeo-Christian quarter of the Kerateion in red.
During the early days of Christianity, some of the earliest missionaries came to Antioch to preach to Jews and Gentiles alike, and over time, during the Roman Empire, the city became the centre of early Christianity.
While many emperors were brutal toward Christians, under Severus and Caracalla that portion of the population fared better than at other times. They were even made Roman citizens by Caracalla’s Constitutio Antoniniana.
It is believed that one of the earliest Christian missionaries here was none other than the apostle Peter. One can even see the ruins of St. Peter’s Cave Church (built in the Middle Ages) where he is said to have preached to some of the people of Antioch. To this day, it is said the Christian Patriarch of Antioch claims primacy in the church because of this association with Peter.
Another strong Christian association with Antioch is that the Gospel of Matthew is believed to have been written there.
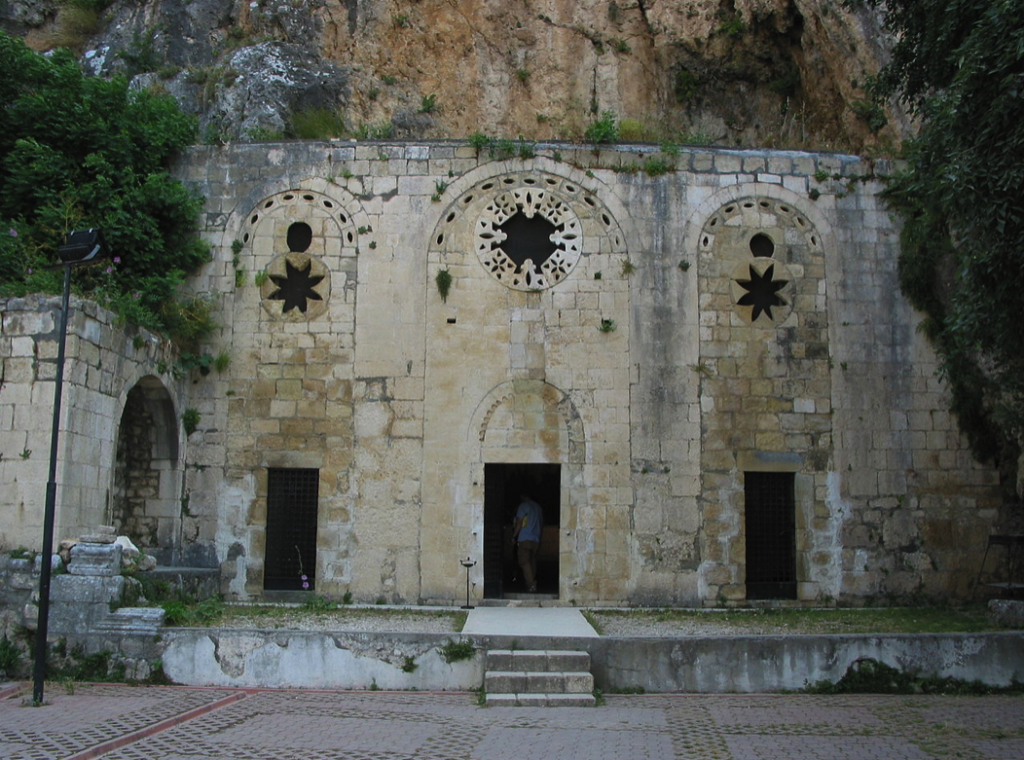

Facade of the Church of St Peter, originally built ca. 1100 by Crusaders and rebuilt in the 19th century (Wikimedia Commons)
In the Eagles and Dragons series, we have not delved very deeply into Christianity and its beliefs. The main characters are mostly Pagan. However, from Book III, Warriors of Epona, we are introduced to early Christians in Britannia, mainly the character of Father Gilmore.
Now, with The Blood Road, we explore Christianity just a little more, and what better place to do that than at one of the centres of early Christianity where the Christian ideal of forgiveness of one’s enemies is in direct contrast to the theme of vengeance in our story.
Stay tuned for our final part in The World of The Blood Road when we will be looking briefly at the reign of Caracalla and the rise and fall of Macrinus.
Thank you for reading.
The Blood Road is available on-line now in e-book and paperback at major retailers. CLICK HERE to get your copy. You can also purchase directly from Eagles and Dragons Publishing HERE.
If you are new to the Eagles and Dragons historical fantasy series, you can check out the #1 best selling prequel, A Dragon among the Eagles for just 1.99 HERE.



