Going to the doctor’s office is never something one looks forward to.
For most, myself included, it gets the heart rate and stress levels up to step into a building that’s full of ‘sick people’.
Sitting around in a waiting room with a group of scared, nervous, fidgety folks, is enough to drive you mad, and the sight of a white coat and stethoscope makes one want to run screaming from the building.
It was probably the same for our ancient Greek and Roman ancestors. Most civilians would have been loath to visit with a physician. It might not have been someone you wanted around, unless absolutely necessary.
‘Oh dear. That cough doesn’t sound good, my dear Septimius!’
Not so for the soldiers in the field.
I’m not an expert in ancient medical history, but I do know that the level of injury on an ancient battlefield would have been staggering. The sight or sound of your unit’s medicus would have been something sent from the gods themselves.
Imagine a clash of armies – thousands of men wielding swords, spears and daggers at close quarters. Then lob some volleys of arrows into the chaos. Perhaps a charge of heavy cavalry? How about heavy artillery bolts or boulders slamming into massed ranks of men?

Ancient surgical instruments, including forceps
It would have been one big, bloody, savage mess.
Apart from the usual cuts, slashes, and puncture wounds, the warriors would have suffered shattered bones, fractured skulls, lost limbs, severed arteries, sword, spear and arrow shafts that pushed through armour on into organs.
If you weren’t dead right away, you most likely would have been a short time later.
This is where the ancient field medic could have made the difference for an army. He would have been going through numerous patients in a short period of time. He would have had to decide who was a lost cause, who could no longer fight, and who could be patched up before being sent back out onto the field of slaughter.
The medicus of a Roman legion was an unsung hero whose skill was a product of accumulated centuries of knowledge, study, and experience.

Asklepios and Igia
Many of the physicians in the Roman Empire were Greek, and that’s because Greece was where western medicine was born. Indeed, the ancient Greeks had patron gods of health and healing in the form of Asklepios, Igeia, and sometimes Apollo.

Artist rendering of the Asklepion of Kos
The greatest medical school of the ancient world was in fact on the Aegean island of Cos, where students came from all over the Mediterranean world to learn at the great Asklepion. Hippocrates himself, the 5th century B.C. ‘father of medicine’, was from Cos and said to be a descendant of the god Asklepios himself.
When it comes to Roman medicine, much of it is owed to what discoveries and theories the Greeks had developed before, but with a definite Roman twist.

Hippocrates
The fusion of Greek and Roman medicine in the Empire consisted of two parts: the scientific, and the religious/magical.
The more scientific thinking behind ancient medical practices is a legacy owed to the Greeks, who separated scientific learning from religion. The religious aspects of medicine in the Roman Empire were a Roman introduction.
Because of this fusion of ideas and beliefs, you could sometimes end up with an odd assortment of treatments being prescribed.
‘To alleviate your hypertension over your new business venture, you should take three drops of this tincture before you sleep. You should also sacrifice a white goat to Janus as soon as possible.’
Many Roman deities had some form of healing power so it depended on one’s patron gods, and the nature of the problem, as to which god would receive prayers or votive offerings over another. Amulets and other magical incantations would have been employed as well.
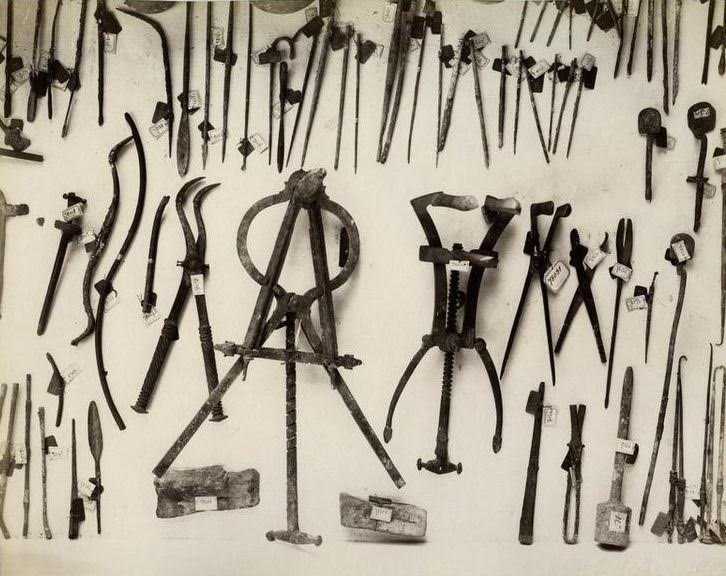

Roman surgical instruments
Romans had a god for everything, and soldiers were especially superstitious.
Greek medical thought rejected the idea of divine intervention, opting more for practicality in the treatment of wounds, and injuries; cleaning and bandaging wounds would have been more logical than putting another talisman about the neck.
All the gods were to be honoured, but in the Greek physician’s mind they had much better things to look after than the stab wound a man received in a Suburan tavern brawl.
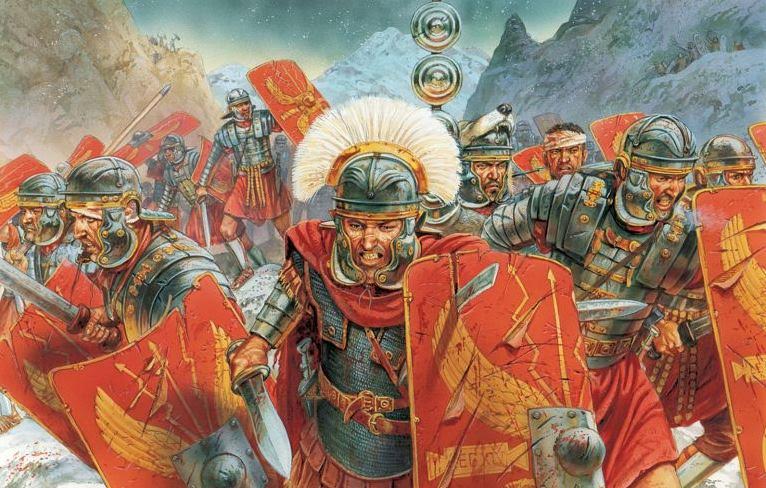

Roman Legionaries (illustrated by Peter Dennis)
For the battlefield medicus, things must have been much simpler than for the physician who was trying to diagnose mysterious ailments. They were faced mostly with physical wounds and employed all manner of surgical instruments such as probes, hooks, forceps, needles and scalpels.
Removing a barbed arrowhead from a warrior’s thigh must have required a little digging.
Of course, in the Roman world, there was no anaesthetic, so successful surgeons would have had to have been not only dexterous and accurate, but also very fast and strong. Luckily, sedatives such as opium and henbane would have helped.

Medic helping a warrior tend a wound
When it came to the treatment of wounds, a medicus would have used wine, vinegar, pitch, and turpentine as antiseptics. However, infection and gangrene would have meant amputation. The latter was probably terrifyingly frequent for soldiers, many of whom would end up begging on the streets of Rome.
It is interesting to note that medicine was one of the few professions that were open to women in the Roman Empire. Female doctors, or medicae, would also have been mainly of Greek origin, and either working with male doctors, or as midwives specializing in childbirth and women’s diseases and disorders. When it came to the army however, most doctors would have been male.

Roman shears
Army surgeons played a key role in spreading and improving Roman medical practice, especially in the treatment of wounds and other injuries. They also helped to gather new treatments from all over the Empire, and disseminated medical knowledge wherever the Legions marched. Many of the herbs and drugs that were used in the Empire were acquired by medics who were on campaign in foreign lands.
Early on, physicians did not enjoy high status. There was no standardized training and many were Greek slaves or freedmen. This began to improve, however, when in 46 B.C. Julius Caesar granted citizenship to all those doctors who were working in the city of Rome.
This last point really hits home when it has become common knowledge that foreign doctors who come to our own countries today find themselves driving taxis or buses because they are not allowed to practice.
Modern governments, take your cue from Caesar!

Galen
One of the most famous physicians of the Roman Empire is Galen of Pergamon (A.D. 129-c.199). Galen was a Greek physician and writer who was educated at the sanctuary of Asklepios at Pergamon in Asia Minor.
After working in various cities around the Empire, Galen returned to his home town to become the doctor at the local ludus, or gladiatorial school. He grew tired of that work and moved to Rome in A.D. 162 where he gained a reputation among the elite. He subsequently became the personal physician of the Emperors Marcus Aurelius, Commodus, and for a short time, Septimius Severus.
Galen’s work and writings provided the basis of medical teaching and practice on into the seventeenth century. No doubt many an army medicus referred to Galen’s work at one point or another.
Galen is also an important character in A Dragon among the Eagles, the FREE prequel in the Eagles and Dragon series. In the book, Galen, an old friend and colleague of Lucius Metellus’ late tutor, presents Lucius with a choice that could well change the direction of Lucius’ life. In fact and fiction, Galen is a fascinating person of history.
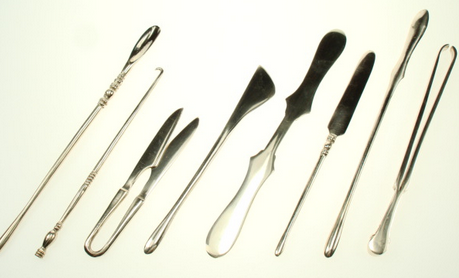
Re-created ancient surgical instruments
I’ve but barely scratched the vast surface of this topic.
For some, there is this assumption that ancient medicine was somehow false, crude and barbaric. But modern western medicine owes much to the Greeks and Romans, civilian and military, who travelled the Empire caring for their troops and gathering what knowledge and knowhow they could.
The fusion of science, religious practice, and magic provides for a fascinating mix. In truth, medical practices in medieval Europe might have been more barbaric than in the ancient world.
Thank you for reading, and may Asklepios, Igeia and Apollo grant you good health!
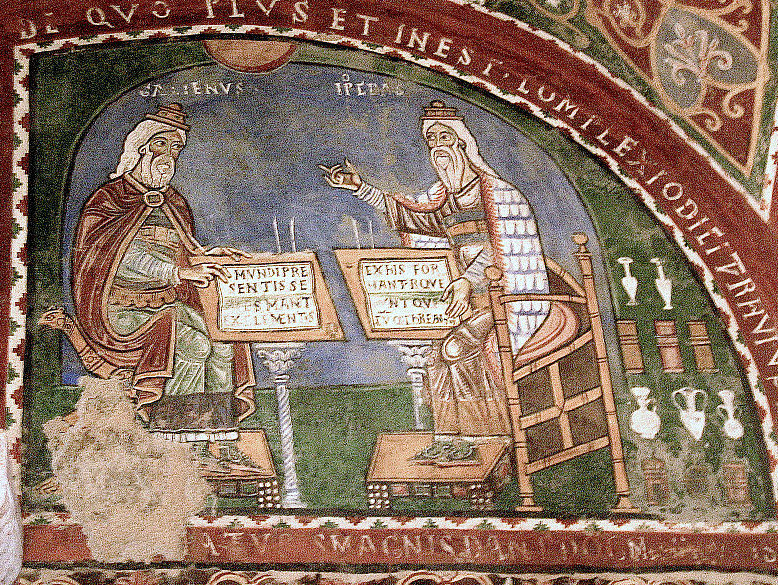

12th century mural of Galen and Hippocrates in conversation

















