As with The World of Children of Apollo, this blog series will take a look at many of the people and places that the series protagonist, Lucius Metellus Anguis, encounters throughout his journey.
So, let’s step back in time to the early 3rd century A.D., and explore the first place Lucius comes to in Book II.
The ruins of Leptis Magna are located at what is now Khoms, a site by the Mediterranean Sea at the northwestern corner of Libya. As a Roman city and archaeological site, it is not really familiar to the average person. Mainly academics have studied it, and excavated its wealth of cultural treasures.

Aerial view of Leptis Magna
It was founded around 1000 B.C. by Berbers and Phoenicians. Later, Carthage held sway over the polis until that great civilization finally succumbed to the Roman war machine at the end of the Third Punic War in 146 B.C.
It was during the reign of Emperor Tiberius (A.D. 14-37) that the city was officially incorporated into the Empire’s province of Africa Proconsularis. In A.D. 110, the Emperor Trajan (c. A.D. 98-117) made Leptis Magna a colonia, an official settlement for retired men of the Legions and Roman citizens. From then on, the city experienced a period of growth and success, making it the third largest city of Roman North Africa after Carthage and Alexandria.

Theatre of Leptis Magna
It had a theatre that was built during the reign of Augustus (27 B.C. – A.D. 14), and one of the most flourishing North African markets of its day. In Leptis Magna, you could buy slaves, exotic animals, olive oil from the rich estates that surrounded the city, garum (Romans’ favourite fish sauce), salted fish, ivory, precious gems, spices, etc. etc. etc.
There was also a forum, the heart of every city, which had a curia, a basilica, a Temple of Liber Pater, a Temple of Hercules, and a Temple of Rome and Augustus.
Finally, what’s a Roman city without a bath complex? In A.D. 126, on his tour of the Empire, Emperor Hadrian had a huge bath complex with a palaestra (exercise field or hall) built for the city. It certainly seemed like the emperors paid attention to this hot, wind-kissed settlement on the south side of the Middle Sea.

Emperor Septimius Severus
But the real heyday for Leptis Magna came when her own favoured son, Lucius Septimius Severus, became Emperor (A.D. 193-211). It was through this half-Punic (Carthaginian), and half-Roman ruler that the city truly felt the warmth of the sun on its face.
You can read more about the Severus and his family HERE.
Septimius Severus did what most rulers will do for their favourite cities – he gave it infrastructure, and he gave it beauty. Give a city these two things and it will attract population, trade, and the Empire’s attention.
Around A.D. 203 the imperial family and court descended on Leptis Magna; the Emperor had returned home and there were festivals, banquets, and the unveiling or dedication of monuments.
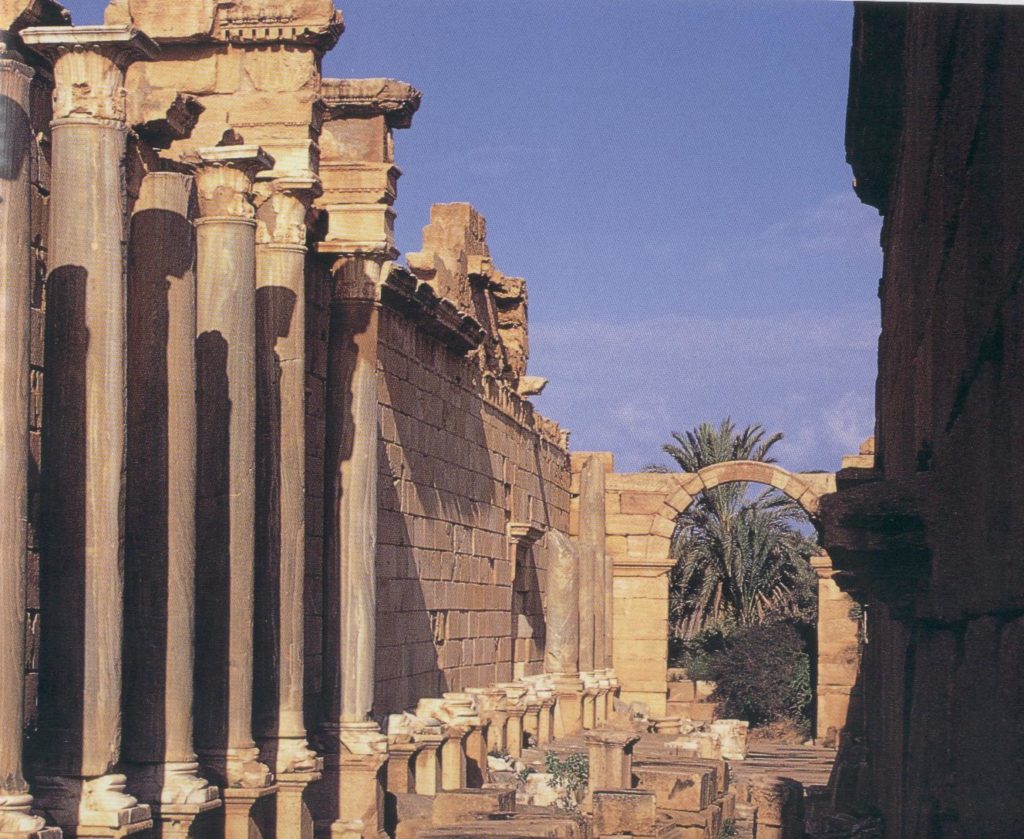

The Severan Basilica
The ruins that have been uncovered in Leptis Magna reveal an ancient city that was wealthy, efficient, and enjoying the good life.
Among the things that Severus built in Leptis Magna were a new harbour and docks, complete with a lighthouse, warehouses and a Temple of Jupiter. For a city involved heavily in trade, this was a big bonus.
Leading from the docks to the nymphaeum (a monument, spring, or fountain dedicated to the Nymphs), Severus ordered the building of a long colonnaded street that was sixty-five feet wide.

Gorgon head from the Forum of Leptis Magna
He added many new public buildings too, including a large basilica which was decorated with red granite columns with white marble capitals. And even though Leptis Magna already possessed a forum, Severus built a new one that was graced with the enormous Medusa heads that remain to this day.
One of the most interesting pieces of new architecture that appeared in the city during Severus’ reign was the four-sided Arch of Severus. Its design was something new, the friezes and political and religious scenes displaying an artistic style that had not been seen before.
It must have felt like a true ‘Golden Age’ to the citizens of Leptis Magna.

The four-sided arch of Severus at Leptis Magna
You can imagine the palpable excitement among the people in the streets as the Emperor, Empress and their sons disembarked from their ship in the harbour and processed to their palace. The entourage would have been enormous, as well as the force of Praetorians who would have followed the Emperor. After all, Gaius Fulvius Plautianus, Prefect of the Praetorian Guard, was also a son of Leptis Magna.
It is in the midst of all this excitement, among all these powerful and wealthy people, that Lucius Metellus Anguis’ journey in Killing the Hydra begins.
There is a lot going on in the world, and many dangers lurking in the shadows about Lucius.
He will have to tread very carefully indeed…
Thank you for reading!
In the meantime, here are a few more stunning photos of the magnificent artwork discovered at Leptis Magna:
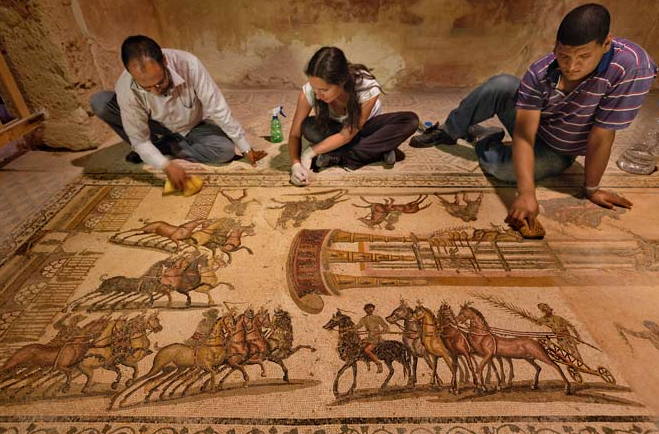

Libyan and Italian archaeologists uncover chariot race mosaic at Roman villa (National Geographic)
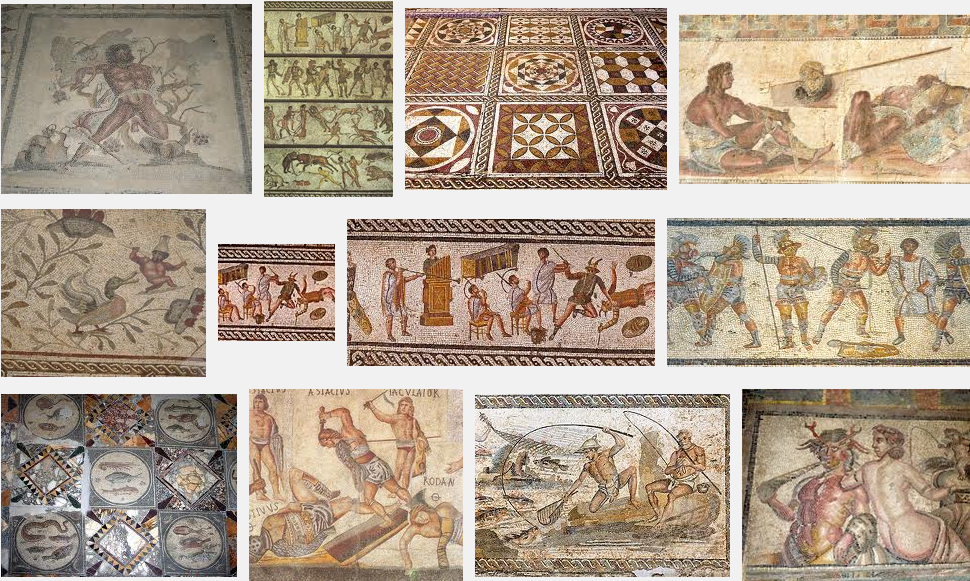

An magnificent array of more Leptis Magna mosaics
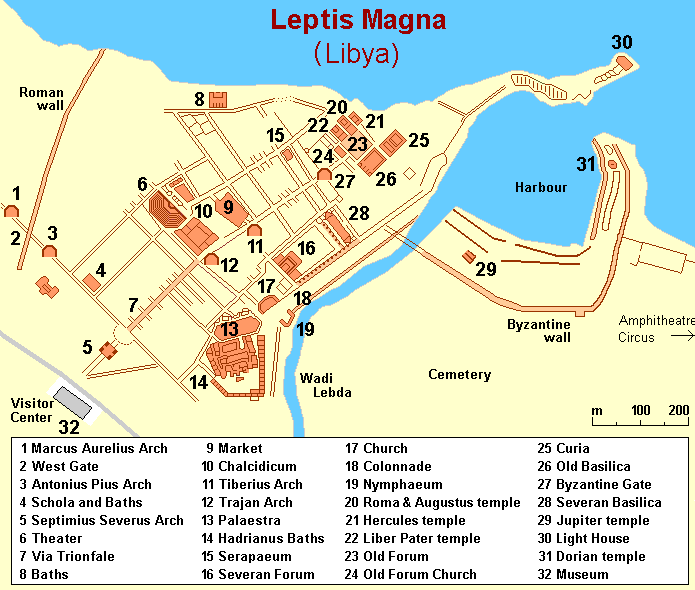
Site map of Leptis Magna (Wikimedia Commons)

