Part I – Drama and Actors in Ancient Rome
Salvete Readers and Romanophiles!
Welcome to The World of Sincerity is a Goddess, our blog series about the research for the novel, Sincerity is a Goddess: A Dramatic and Romantic Comedy of Ancient Rome.
In this first post, we’re going to be taking a brief look at drama and actors in the world of ancient Rome. Both, of course, are central to Sincerity is a Goddess.
Let’s start with a look at the evolution of drama in Rome.
Life is like a play in the theatre: it does not matter how long it lasts, but how well it was played.
Seneca
There are many different forms of literary arts today, just as there were in ancient Rome. Actually, in Rome, no matter the literary form, there was something for everyone. You didn’t even have to be able to read to enjoy literature of a sort.
Literary sources that we know of from the world of ancient Rome include such things as histories, speeches, poems, plays, practical manuals, law books and biographies, treatises and personal letters.
More often than not, authors in ancient Rome were well-educated and even very wealthy, and as a result, the opinions often expressed in literature reflected the values of the upper classes either because the authors were of that class themselves, or because they were patronized by the wealthy.
The main types or classifications of literature were drama, poetry, prose and satire. Though much was written in each of these areas in ancient Rome, in some cases, very little has survived, which makes this a sort of tragedy in and of it self. For the purposes of this post, we’re going to be taking a look at drama.
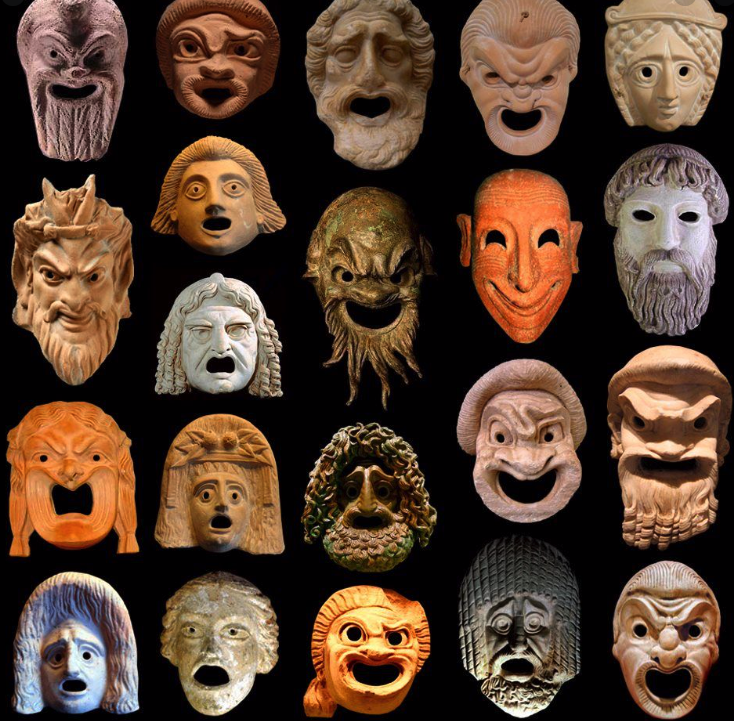

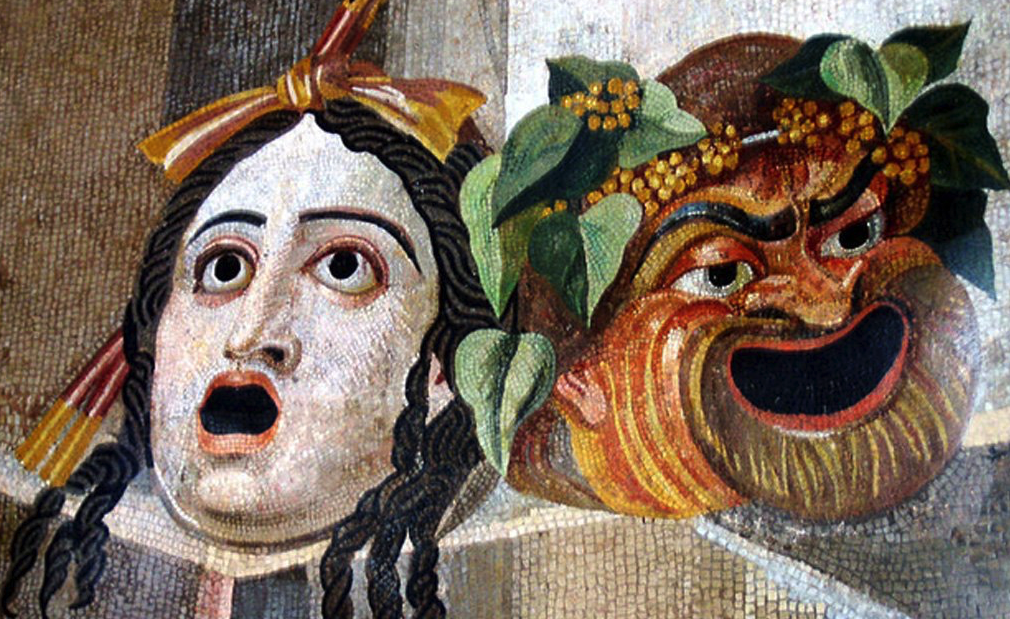
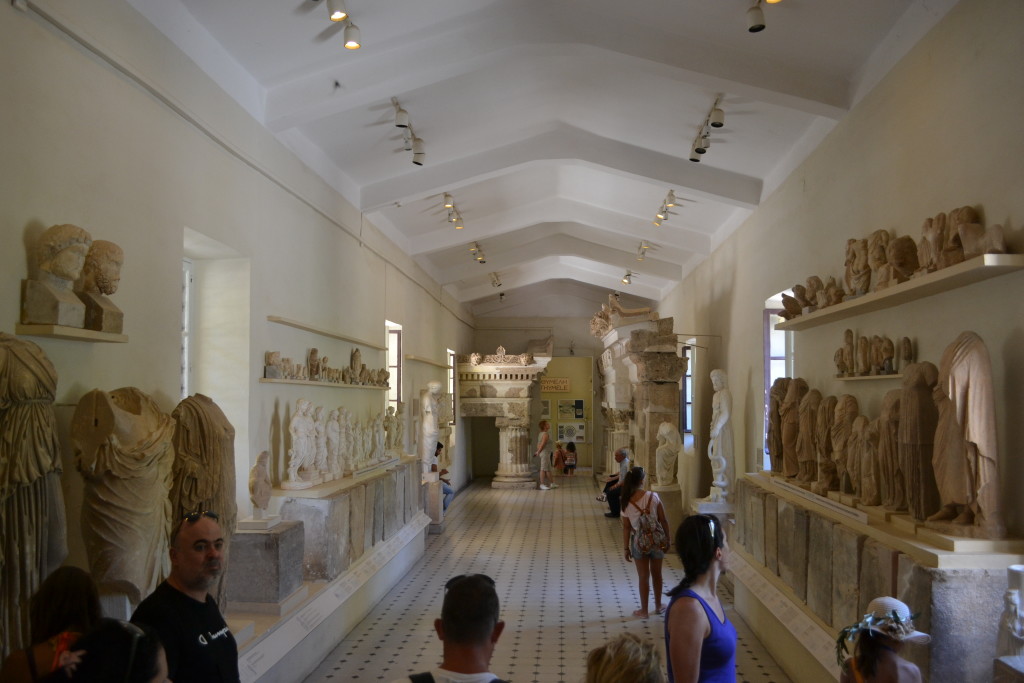
An array of Greek theatre masks
Drama is central to Sincerity is a Goddess. It was performed in Rome since before the 3rd century B.C., and these early performances took the form of mimes, dances, and farces.
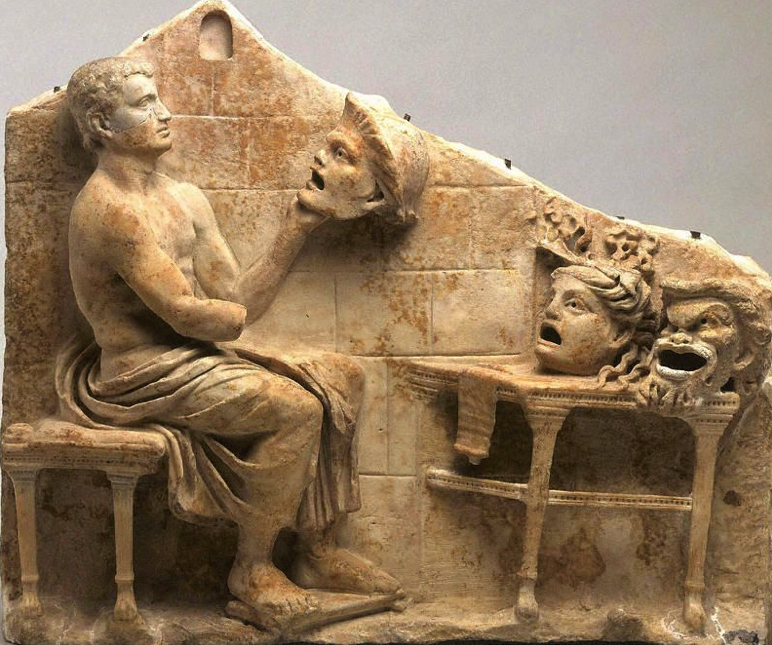
One example of these early forms of drama were the fabula atellana which originated in the town Atella. These were a collection of vulgar farces that contained a lot of low or buffoonish comedy and rude jokes. They were often improvised by the actors who wore masks.
Mimes were very similar and were dramatic performances by men and women that were more licentious in nature. They were highly popular, especially with the lower classes, but they have also been accused of being the cause of the decline of comedy in ancient Rome. By the early sixth century A.D. they were banned or suppressed.
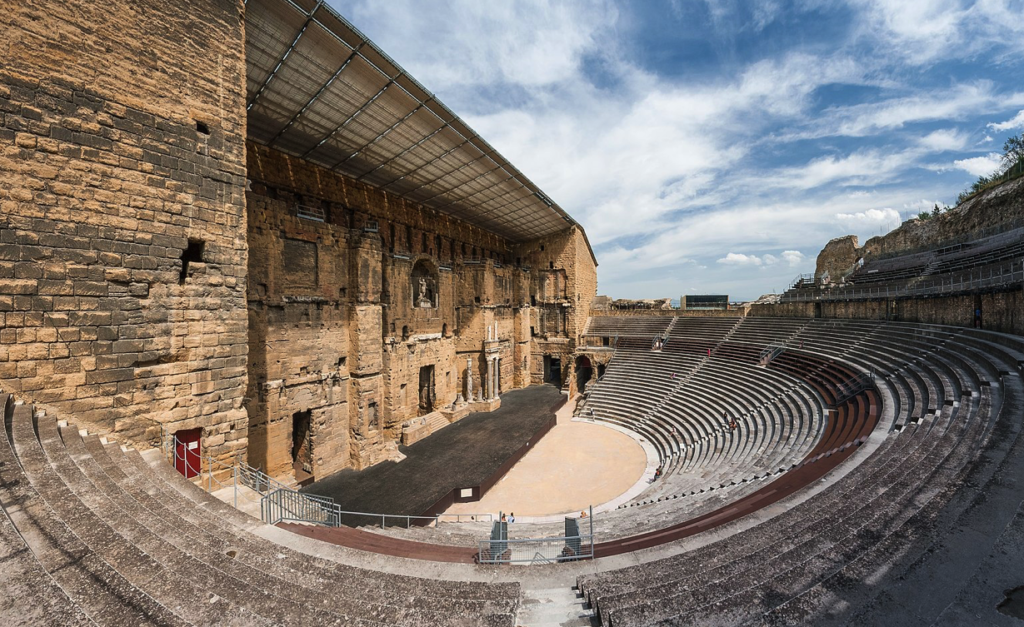

Roman Theatre in Orange (Wikimedia Commons)
When we think of ancient theatre, however, we cannot help but think first of ancient Greek drama, which was an art form in the lands of the Hellenes long before Romans began producing Latin literature. And like so many other things, the Romans adopted forms of drama from the Greeks as well, especially drama in the form of plays.
Greek ‘New Comedy’ was introduced in Latin in Rome around 240 B.C. by Livius Andonicus and Naevius, and shortly afterward, Greek plays were being adapted by Terence, Caecilus Statius and of course, Plautus, whose early works are the oldest Latin literary works to survive in their entirety. We’ll talk more about the latter later in this blog series. These plays were called fabulae palliatae, or ‘plays in Greek cloaks’.
However, Latin drama had begun to evolve out of this, and soon there emerged the fabulae togatae, or ‘plays in togas’, which were comic plays about Italian life and Italian characters. Sadly, there are no surviving examples of these early Latin comedies.
Surprisingly, by the first century B.C., Roman comic plays pretty much ceased to be written and were replaced by mime which was much more vulgar and thought by many to be of little literary merit.

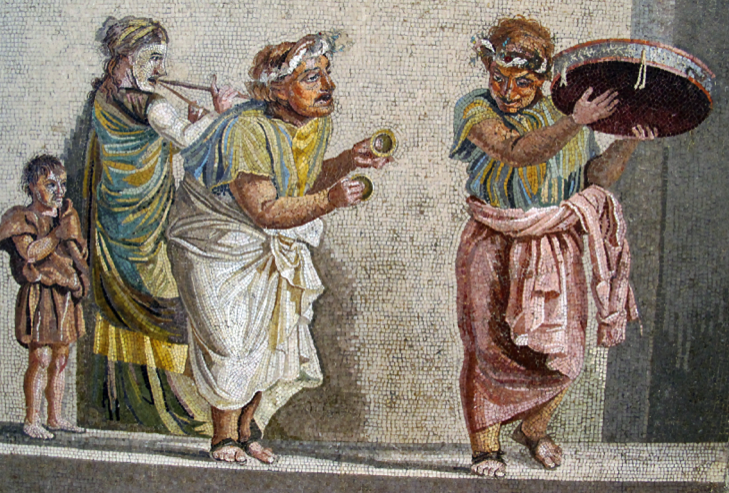
Illustration of Roman mime performance
Other fabulae were introduced by Livius Andronicus, including the fabula crepidata which was a Roman tragedy on a Greek theme, and the fabula praetexta which was a Roman drama based on a historical or legendary theme.
The latter, a form invented by Naevius, gained little popularity in Rome, and by the late Republican era, tragedy in general began to decline. There was a short revival under Augustus, but it did not last, and there are no surviving works of Roman tragedy that come down to us.
It seems the Romans would have leaned more toward Dumb and Dumber than Romeo and Juliet…
One theory about the lack of survival of tragedy in ancient Rome is that under the Empire, it was difficult to choose a safe subject.
But what about actors in ancient Rome, the people who performed before the masses in the streets, on temple steps, or in the great theatres that later adorned cities across the Empire?
Generally, actors were among the lowest on the social scale, the same as gladiators or prostitutes. People enjoyed their performances, and sometimes looked upon them with awe, but they were often kept at a distance for propriety sake. However, some actors were so famous that women, of high and low origin, had affairs with them, not unlike famous gladiators.
This is in contrast somewhat to how it was in ancient Greece where the creation of drama and acting were admired, well-respected.
In the world of ancient Rome, most actors were frowned upon, despite their ability to amuse the people. In truth, the majority of actors were either slaves or freedmen, a very few of which went on to achieve fame, respect, and personal fortune. Most of them likely performed in the lewd mimes favoured by the masses.
That said, a good pantomime slave actor could cost as much as 700,000 sestercii! And it is believed that many pantomime actors may have received training in dance, poetry, and even mythology, the stories of which they sometimes performed.
A famous Roman actor during the reign of Emperor Augustus, known as Pylades, accumulated so much wealth that he was able to produce his own plays. Despite their low social standing, a few actors could indeed be paid very well. In fact, it came to be such a problem that the Emperor Marcus Aurelius put a legal maximum on actor salaries.
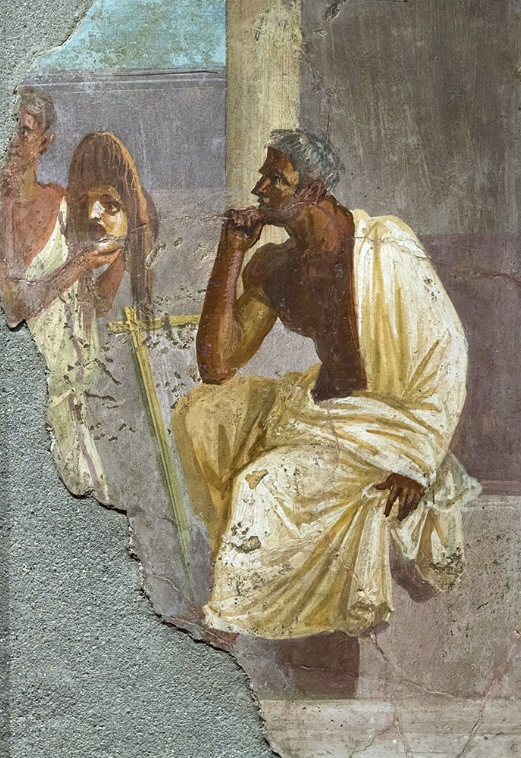

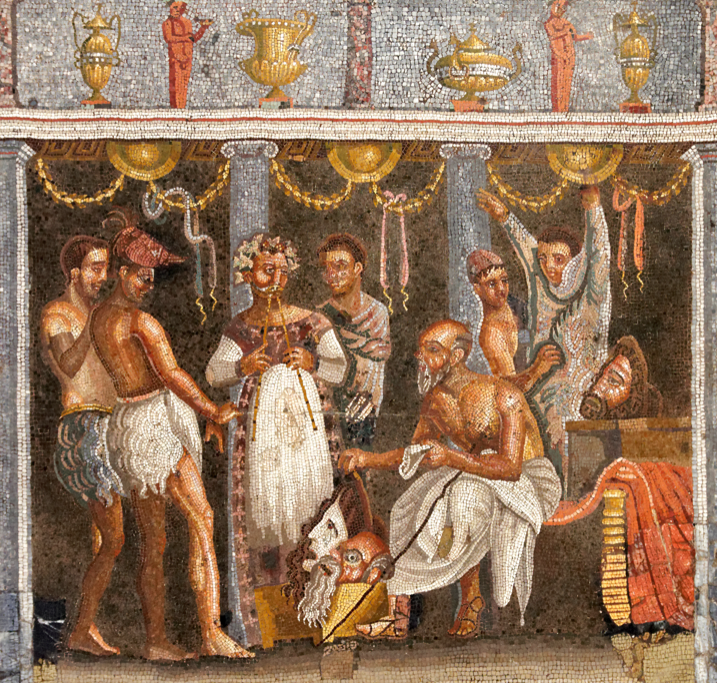
Actor and Mask from a Fresco at Pompeii (Wikimedia Commons)
There were companies of actors who moved about, usually performing at games, or ludi, in Rome and across the Empire. A company of actors, or a grex, was led by the dominus gregis, the leader and owner of the company. This person was likely a freedman who went on to have some success.
Despite the lack of respect for the actors themselves, they did have an association of theatrical authors and actors in ancient Rome known as the Collegium Scribarum Histrionumque whose patron goddess was Minerva. This was perhaps similar to modern organizations such as Actors Equity Association in the US, or the Association of Canadian Cinema Television and Radio Artists (ACTRA).
Acting in Rome was different than it was in the world of ancient Greece. We have already mentioned the general lack of respect toward the acting profession in Rome compared with Greece where there were festivals with prizes such as the Dionysia and Panathenaea at Athens, and even the Pythian Games at Delphi.
However, in ancient Greece, women were strictly barred from performing on stage. It was a man’s world with men performing the roles of female characters. It was seen as dangerous to have a woman on stage.
This carried over into early drama in the Roman world, influenced as it was by Greek tradition. Over time however, women were permitted to perform on Roman stages. At first, their roles were limited to performing in mimes or pantomimes as part of the chorus or as dancers.
Eventually, female actors began to take on greater roles in Roman drama, some of them becoming so famous that they were permitted to perform in the great theatres of Rome and across the Empire.
Such actresses were known as archimimae, or leading ladies, and some of their names have come down to us.
One incredible example is the actress Licinia Eucharis, a Greek-born slave who was so talented that she went on to earn her freedom and be allowed to perform Greek dramas upon the great stages of Rome before the nobles. And this was during the Roman Republic! Quite a feat! Eucharis amassed great wealth from her acting alone.
Another example of an actress who achieved fame as an archimima, this time during the imperial period, was the actress Fabia Arete. She was a freedwoman who was also a diuma, that is, a leading actress who toured and was invited to perform in different places because of her great skill.
Though there are examples of male and, more rarely, female actors achieving great fame, wealth, and respect in ancient Rome, most actors struggled and were relegated to the makeshift wooden stages that they erected in the streets, or upon temple steps, performing lewd mimes for the people who might have tossed a coin their way.
Being an actor was not an easy life, to be sure.
Perhaps it isn’t so different from today?
Sure, there are actors and actresses who achieve fame and accumulate massive amounts of wealth in the modern age, but the reality is that most performers (actors, dancers, musicians, and writers) struggle to make a living.
One thing does seem apparent when it comes to actors in ancient Rome, and that is that this was a time when women in the profession experienced some ascendency, between the strict rules of the ancient Greek theatre world which banned them, and the Medieval Christian era that seemed intent on demonizing them and, once again, banned from the stage.
Despite its shortcomings, the world of ancient Rome seemed to have been a bright spot, in a sense, in the historical timeline. However, when it came to actors, people admired them for their skill and performance, but perhaps mostly from a distance. It was, after all, a world that was foreign to most.
Thank you for reading.
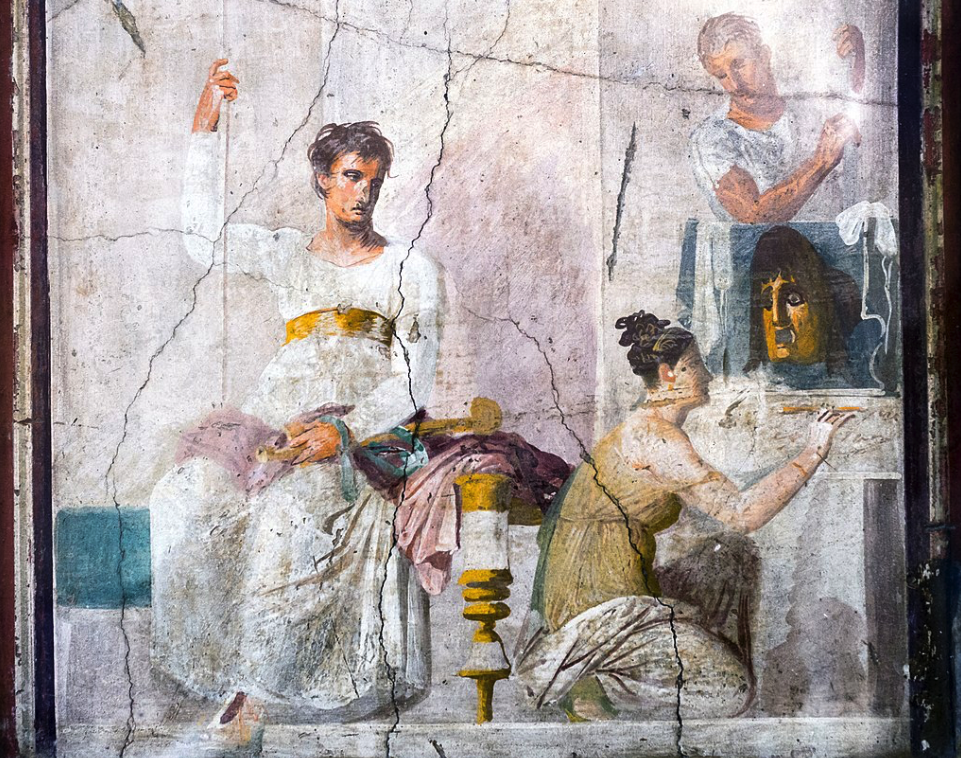

Roman Actors from Fresco at Herculaneum (Wikimedia Commons)
We hope that you’ve enjoyed this short post on drama and actors in ancient Rome. There is a lot more to learn on this subject, so if you want to read more, Professor Edith Hall at Durham University, a leading expert on the subject, has kindly made her books on ancient theatre freely available to the public. You can check them out HERE.
You can also learn more about other types of Roman literature in our popular post Literature in Ancient Rome by CLICKING HERE.
Part II – Theatres in Ancient Rome
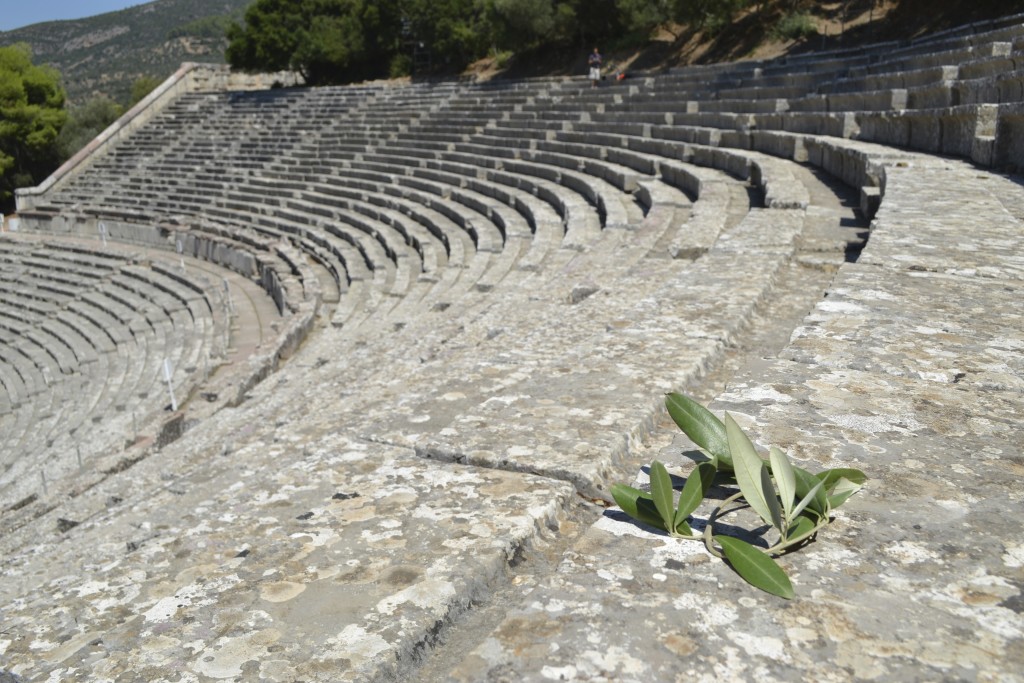

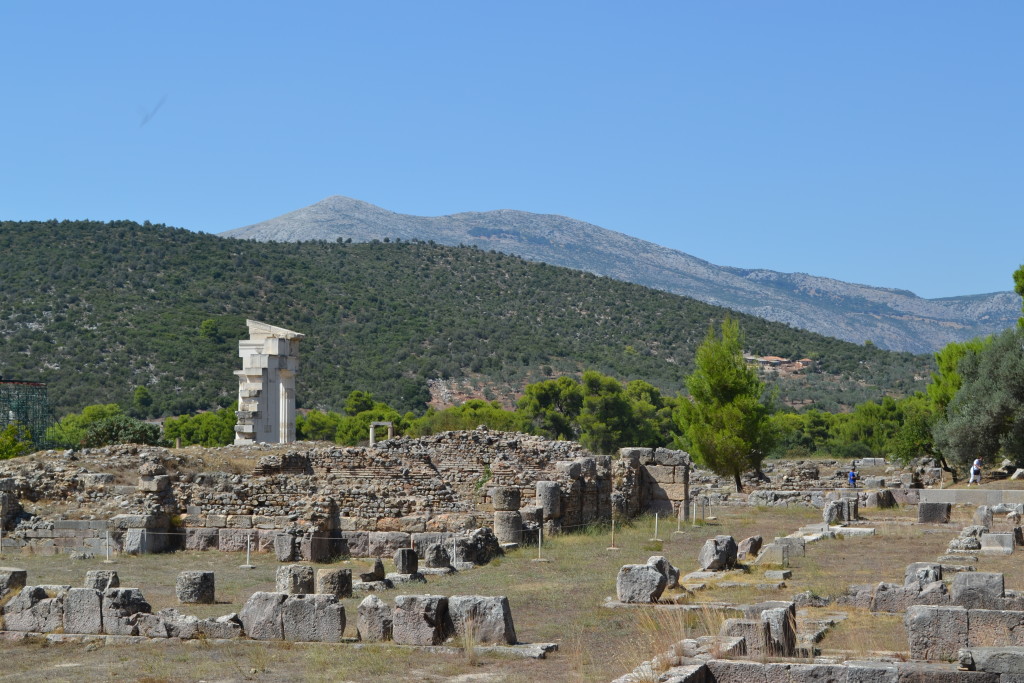
The ancient theatre of Epidaurus
One of the main questions I had when I set out on the research for this latest book was around the physical structure of the Roman theatre. Of course, I knew about ancient Greek theatres, having visited several in my travels over the years. But what about Roman theatres? Did the Romans simply re-use Greek odea? Did the Romans build their own theatres and, if so, how did they differ from those built by the Greeks?
In this blog post, we’re going to be taking a brief look at theatres in ancient Rome and how they differed structurally from those of the Greeks.
The ancient Greeks were, of course, the progenitors of drama and the theatre. When one thinks of ancient theatre, it’s difficult not to think first of an ancient Greek theatre such as the the magnificent, and still-used, example at ancient Epidaurus in the Peloponnese. Or even the beautiful, silent ruins of the great theatre of Argos. It is quite an experience to sit in the ancient seats and not feel some sort of communal awe from centuries past, looking out to the distant mountains or sea beyond the stage where ancient actors would have enacted stories of gods, goddesses, heroes, and the trials and tribulations of everyday people on their journey through this life.
The ancient Greek playwrights – Euripides, Sophocles, Aeschylus, Aristophanes and others – had a way delving deep into the heart of human emotion and experience and making people linger there so that they would, hopefully, come out of it a bit more enlightened. And in a setting such as those ancient theatres, it would be hard not to.
I’ve seen comedic and tragic plays performed while sitting with thousands of others beneath the stars in an ancient theatre. It is an experience I shall never forget.
But even if one is not moved by the words spoken by the actors, it is difficult not to marvel at the genius of the architecture that allows the audience at the top of the seats to hear a whispered word spoken from the centre of the orchestra.
Ancient theatres really are engineering wonders!

The ancient theatre of Argos, Peloponnese, Greece.
Of course, the men of the Tiber knew a good thing when they saw it, and so they eventually adopted drama and theatres while adding their own Roman flair.
But this took some time, and some convincing…
Drama and theatre first came to Rome through contact with the Greek cities to the south and the Etruscans to the north, who had regular contact with the Greeks. It might have been looked upon with suspicion by conservative Romans at first, but eventually, drama would take hold of the Roman people.
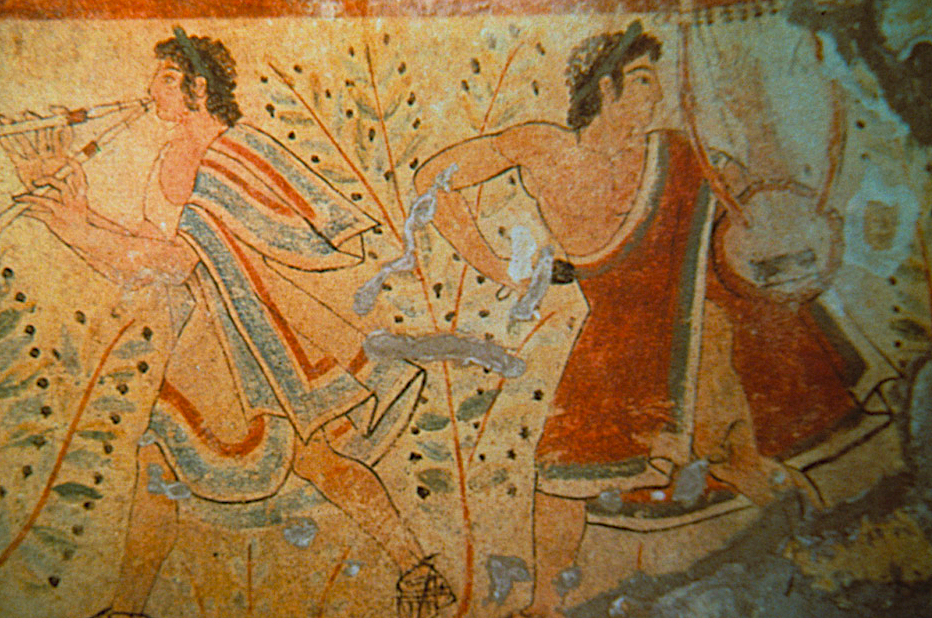

Etruscan Entertainers
In 364 B.C., the Roman Republic was hit by a plague, and in an effort to please the gods and entreat their aid, Rome vowed to hold theatrical festivals in their honour.
To do this, Etruscan actors were brought in and the rest is history. This considered by some to be the start of this new entertainment for the Roman public, an entertainment inspired by the Greek cities of southern Italy.

Theatre of Dionysos, Athens
Plays were originally performed in Greek, but over time Latin playwrights emerged, such as Plautus, Terence, and others. Of course, there were tragedies and comedies in the beginning, but then folk and bawdy plays began to take hold, and the mimes and pantomimes became the most popular among ancient Romans.
To read more about the types of literature in ancient Rome, including drama, CLICK HERE. Suffice it to say that theatrical performances eventually became nearly as popular as chariot racing and gladiatorial combat in ancient Rome.
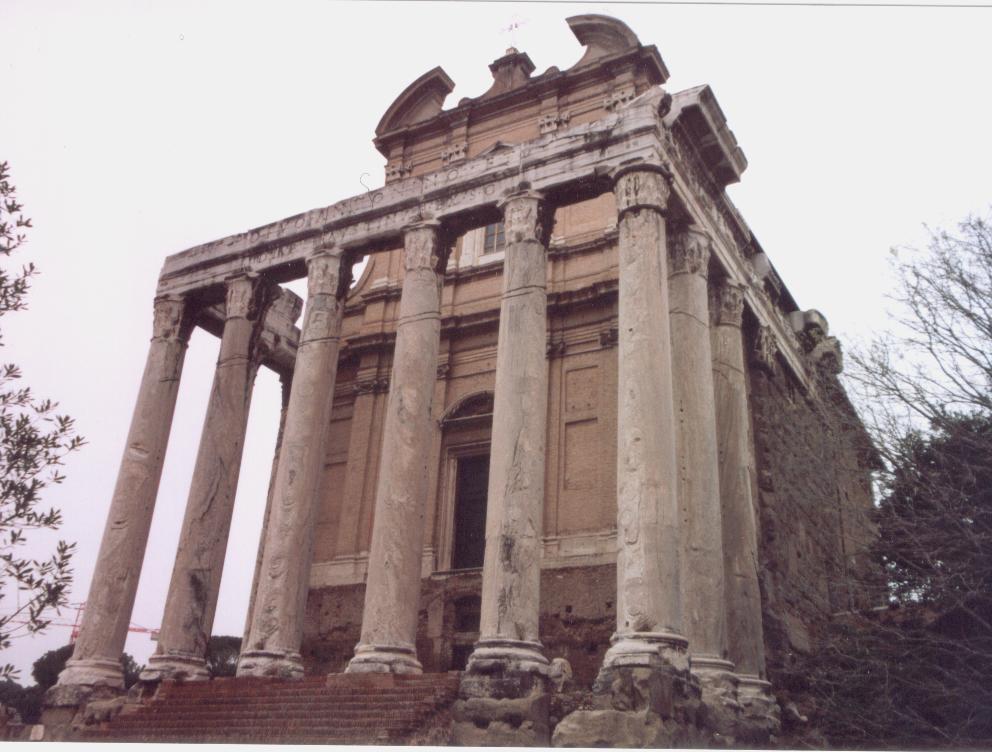

Temple of Antoninus and Faustina, Roman Forum. Play were sometimes performed on temple steps such as this.
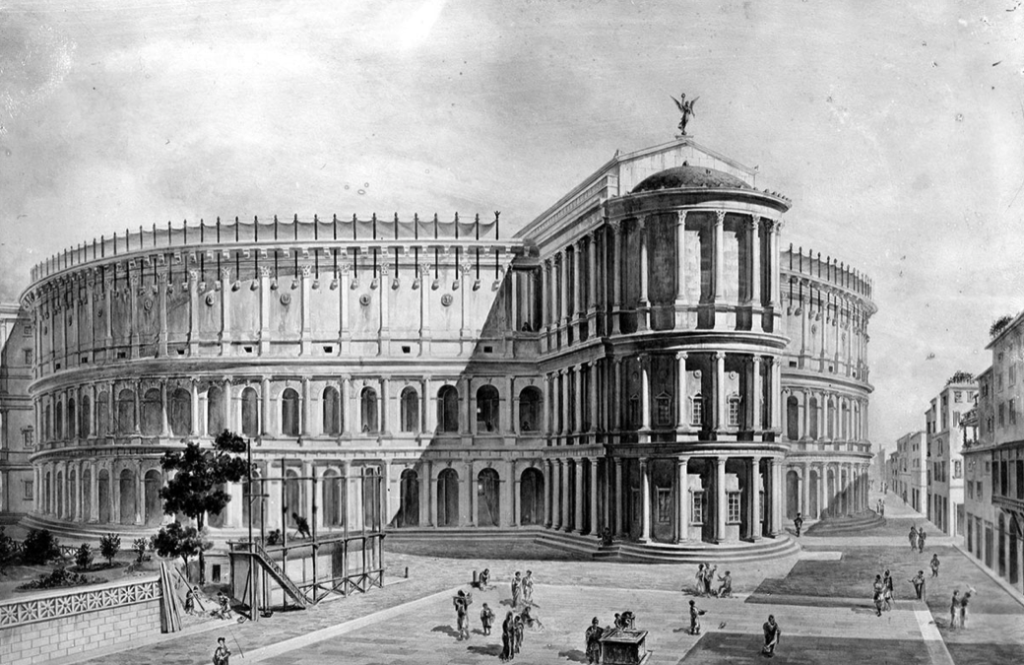
There may have been theatres dotted all over territories which Rome had conquered early on, but in the city of Rome itself, there were no stone theatres at first, not like in Greek cities where a theatre was a given sign of civilization.
Early dramatic performances in ancient Rome were either performed on the steps of temples or on temporary wooden stages which were constructed in the Circus Maximus or Roman Forum for festivals. After the performances were finished, they were torn down.
Despite the popular appeal of drama in ancient Rome, conservative elements had a deep dislike of the theatre, viewing it as ‘too Greek’ and opposed to Roman values. The theatre – especially the mimes and pantomimes – were viewed as lewd, and this is a view that continued into the Christian era.
But, even among conservative Romans, it was hard to fight popular appeal, and the theatre was indeed growing in popularity.

Roman Re-enactors on the steps of a temple in Spain (photo: Turismo de Merida)
As we know, the Romans loved their games, or ludi, and by sponsoring these games, Roman magistrates had found a way to win the political favour – and hence, votes! – of the people.
Some examples of games which featured theatrical performances were the Ludi Apollinaris in honour of Apollo (July 6-13) and the Ludi Megalenses in honour of Cybele (April 4-10).
The building of theatres became a way to win the favour of the people. Unlike today when, sadly, theatre is viewed as something more for the elite or well-to-do, the theatre was, in ancient Rome, for people of all classes!
As mentioned, at first theatres in Rome were temporary and constructed of wood, but as time went on, even these wooden ones became more elaborate.
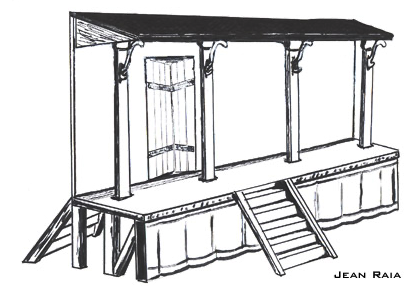
Artist Impression of temporary wooden stage of Roman period (image: Jean Raia)
In 58 B.C. Marcus Aemilius Scaurus built a wooden stage for performances, but this one had columns of African marble, as well as statues, glass, gold and fabrics to adorn it. The people loved it!
In 52/51 B.C. Gaius Scribonius Curio even built two moveable semi-circular theatres that could be pushed together to build an amphitheatre so that plays could be performed during the day and gladiatorial games viewed at night!
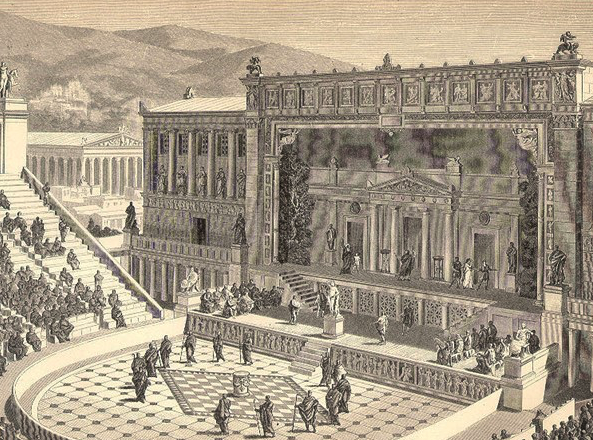
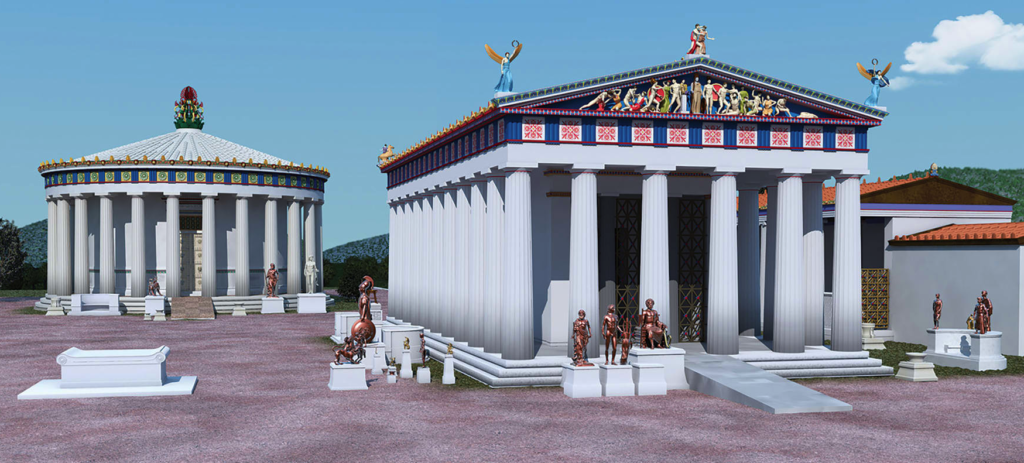
Eventually the time would come when Rome would receive its first stone theatre, despite conservative opposition, and this was given to the people by none other than Pompey the Great.
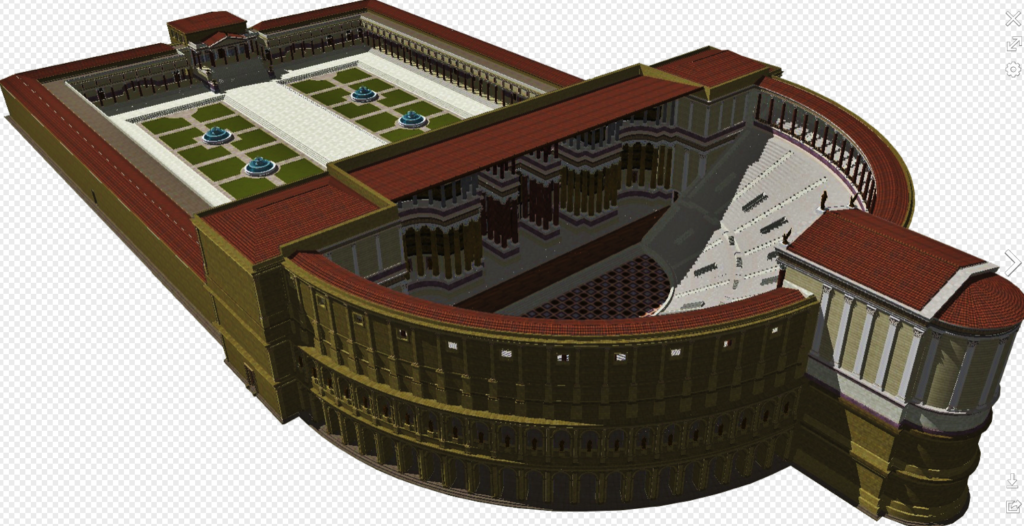
Reconstruction of the Theatre of Pompey in Rome with attached gardens and temple above the theatre seating. More on this magnificent setting in a later post!
From 61-55 B.C., Pompey built a magnificent stone theatre for Rome, and he appears to have used his general’s wiles to get it done in a way that tricked conservative dictates. You see, this was not only a theatre, but also a temple complex dedicated to the goddess Venus herself.
Atop the great theatre of Pompey, resting above and behind the seats of the auditorium, was a magnificent temple of Venus. The argument was, it seems, that the theatre itself was simply the substructure of the temple, the ‘real’ purpose of the construction. The gods were now present in the theatre, and no one would have dared to tear it down!
The theatre of Pompey is now, perhaps sadly, known as the place where Julius Caesar was murdered (the senate was meeting there at the time), but more importantly, it was the beginning of a greater acceptance of theatre in the city of Rome.
Indeed, after the accession of Augustus, one of his supporters, one Lucius Cornelius Balbus, built a second stone theatre in Rome, on the Campus Martius, known today as the Theatre of Balbus.
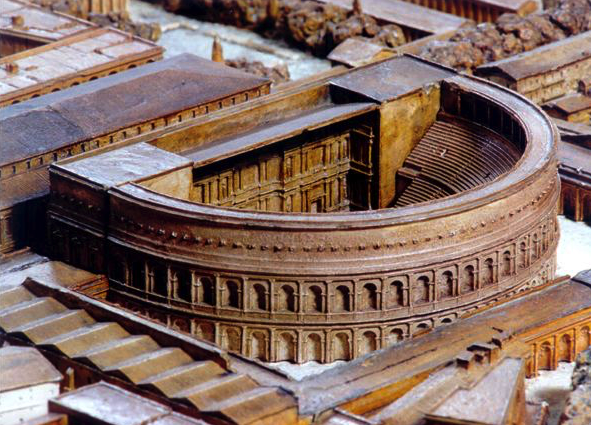

Model of the Theatre of Balbus
These permanent Roman theatres, however, were more than places to stage dramatic performances. They were also meeting places that incorporated religious elements. There were temples, and gardens and courtyards where people could stroll between acts, or meet outside of performances. They became part of the fabric of the city of ancient Rome.
But what were the structural differences between ancient Greek and Roman theatres?
It is impossible to deny the simple beauty of ancient Greek theatres, and the brilliance of their acoustic design. It is truly astounding to sit at the top of the seats and hear someone drop a coin or light a match in the middle of the orchestra!
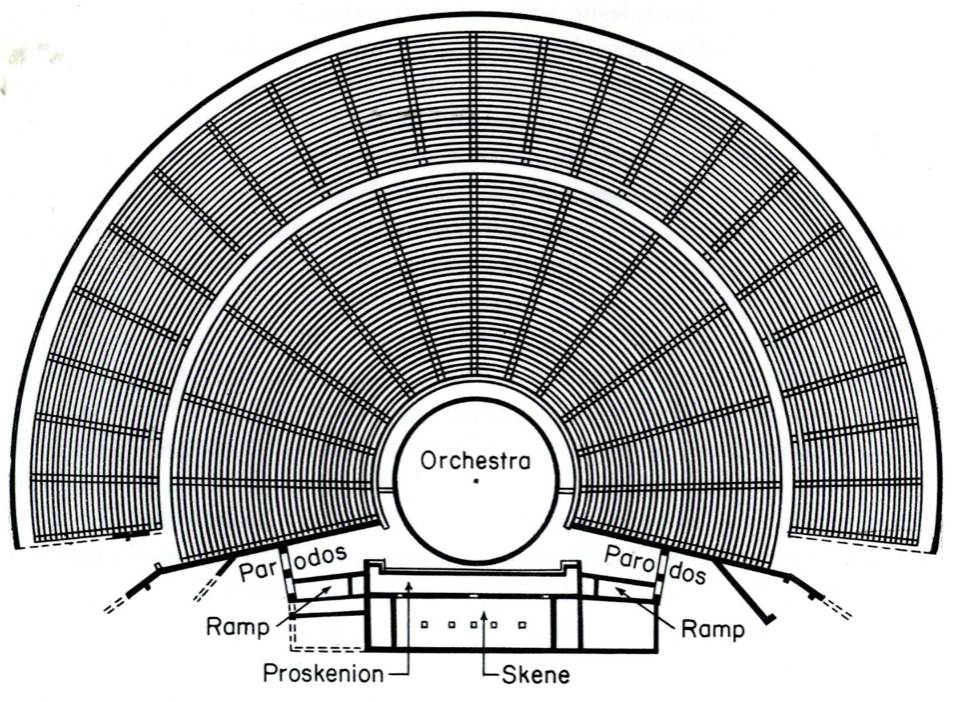
Plan of an Ancient Greek Theatre
Roman theatres were of course, based on Greek designs. Even the Romans could not deny the acoustic uses!
But whereas Greek theatres, or odea, were normally built into a hillside and had round orchestras where the performance took place, Roman theatres were more often stand-alone structures with semi-circular orchestras where seating was reserved for high-ranking officials, senators, or members of the imperial family. Roman theatres were constructed with solid masonry or vaults that supported the curved or sloping auditorium seats, or cavea. This design sometimes included a colonnaded gallery around the outside that gave easier access to the tiers of seats.
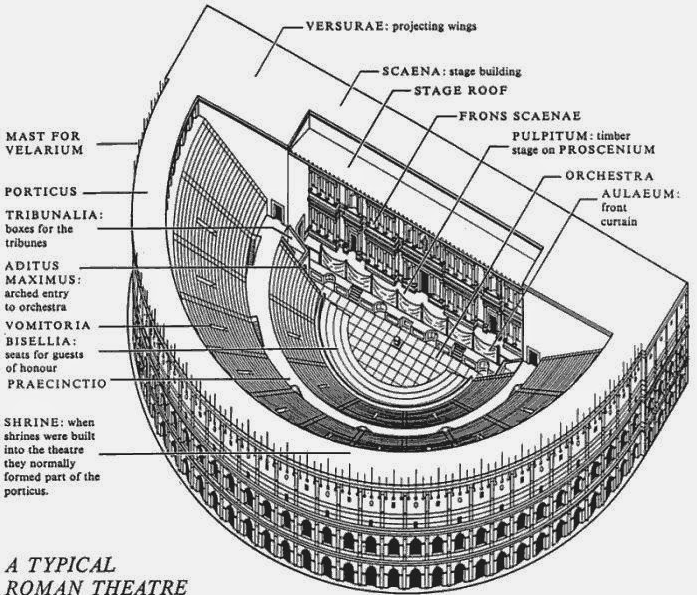
Plan of a Typical Roman Theatre
Another innovation given to the theatre by the Romans was the inclusion of a curtain before the stage. Today, it is hard not to think of a curtain in a theatre, and we owe this to the Romans. The difference was that where today the curtain hangs from above, in a Roman theatre, the curtain, or aulaeum as it was known, retracted into a pit in the floor before the stage at the beginning of the performance, and rose out of it at the end.
The most noticeable difference between Greek and Roman theatres, however, was the Roman scaena.
In an ancient Greek theatre, initially, the chorus and actors performed on the round orchestra, but later on, a raised stage, or proskenion, was incorporated. At the back of this stage, they began to build a one or two-story backdrop known as a skene, the ‘scene’ before which the action took place, and behind which the actors could change. The Greek skene did not obstruct the view beyond the theatre, however, but rather just provided the ornate backdrop.

The scaena frons of the Theatre of Pompey
The Roman scaena, however, was much more substantial, for it more or less enclosed theatre completely and provided a full divider between the audience and backstage.
Scaenae frons in Roman theatres had three or five doors flanked by columns and statues in niches. The scaena and its doors could provide the setting for a street scene, houses, palaces etc., and sometimes it was even sectioned off with smaller curtains called siparia as needed.
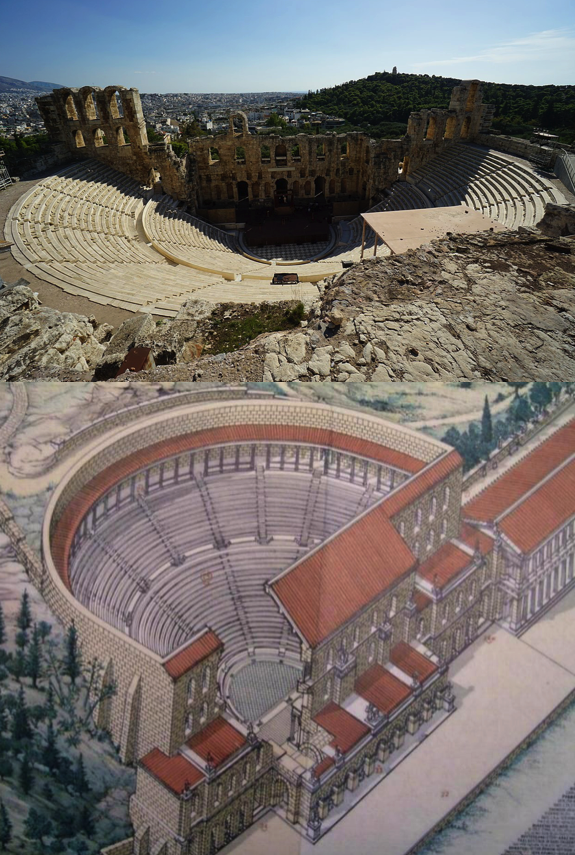
The Roman-era theatre of Herodes Atticus, Athens
The Roman scaena also rose to the full height of the theatre itself, either level with the rear seats of the auditorium, or even higher. There was also a wooden roof above the stage of Roman theatres that also acted as a sounding board.
It wasn’t just the actors who were protected from above either, for in some Roman theatres there could also be an awning above the auditorium known as a velarium, to shield the viewers from sun and rain. Roman theatres also had covered porticoes where audience members could go between performances.
The Romans did like their comfort!
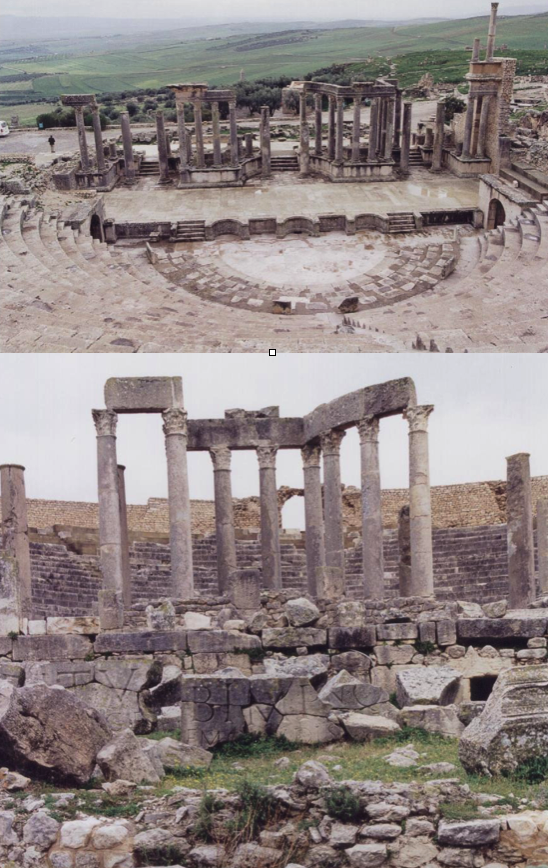

The Roman theatre in Thugga, Tunisia, featured in Killing the Hydra (Eagles and Dragons Book II)
Were Roman theatres built across the Empire once Rome had made its own innovations in theatrical architecture?
Well, it seems the Romans did make adjustments to some Greek theatres by adding their own scaenae. However, especially in the Hellenistic east, Greek odea continued to be used, only just for more refined performances of music and poetry recitations rather than for populist mimes and pantomimes.
Romans continued to use the odeon design when called for, but sometimes with the addition of a roof. This type of smaller, enclosed and roofed theatre was known as a theatrum tectum. An example of this is the one built in Pompeii in 79 B.C.
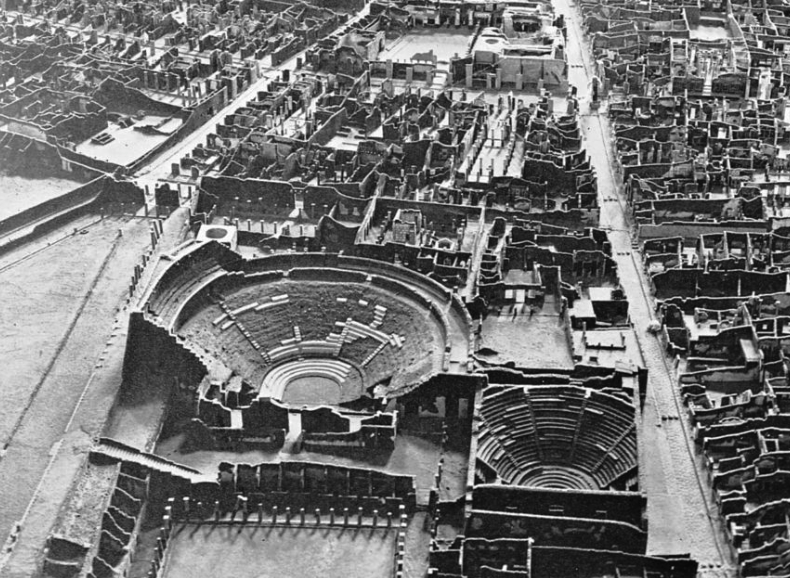

Aerial view of theatres of Pompeii. Note the theatrum tectum on bottom right which would have been fully enclosed.
When it comes to theatres and theatrical performance, whatever the genre, the Greeks and Romans did have this in common: theatre was extremely popular with the people and important for the social life of the community, be it in the cultured metropolises of the Empire, or on the distant borders, far from the beating heart of Rome.
The Greeks may have invented theatres, but some might argue that it was the Romans who perfected them.
Part III – Humour and Comedy in Ancient Rome

Laughing Legionaries
An Abderite [from Abdera in Thrace] saw a eunuch and asked him how many kids he had. When that guy said that he didn’t have the balls, so as to be able to have children, the Abderite asked when he was going to get the balls.
(Philagelos, #114)
Is that funny to you? Maybe a little? Or does it make you scratch your head and wonder?
The joke above is actually a Roman joke about 2000 years old. Yes, that old. It’s one of 250-odd jokes in the oldest joke book in the world known as the Philagelos, or ‘The Laughter Lover’. It is thought that this text is a compendium of jokes over several hundred years. The earliest manuscript is thought to date to the 4th or 5th centuries A.D.
Humour in the ancient world was not really something I’d thought about in my writing and research until I began work on Sincerity is a Goddess. If there has ever been humour in my books, it has been a reflection of my own modern perceptions of what humour is, or should be. Otherwise, my modern readers would be left scratching their heads.

Salve, Titus! Heard any good jokes lately?
Several years ago, I heard an interview with eminent classicist and historian Mary Beard on the subject of her book about humour in the Roman world entitled: Laughter in Ancient Rome: On Joking, Tickling, and Cracking Up. This is a wonderful book that will give you a whole new perspective on people in ancient Rome.
Anyway, until my research for this novel, my idea of humour in the ancient world was partly based on the musical A Funny Thing Happened on the Way to the Forum by the brilliant Stephen Sondheim. The latter is not a completely inaccurate view since the story is based on the farces of the Roman playwright Plautus (251–183 BC) – more on him later in this series.
Bawdiness played a large role from the theatre to the marching songs of Rome’s legionaries.
Slap stick comedy was a part of humour in the ancient world, but Professor Beard put forth the idea that there are other aspects of ancient humour which we might not, or cannot, understand.
A professional beggar had been letting his girlfriend think that he was rich and of noble birth. Once, when he was getting a handout at the neighbour’s house, he suddenly saw her. He turned around and said: “Have my dinner-clothes sent here.”
(Philagelos, #106)
When it comes to many ancient jokes, our cultural and temporal disconnect make them simply ‘not funny’. For better or for worse, depending on your point of view, we have also grown much more sensitive today.
Another reason why the humour of some ancient jokes may be lost on us is that perhaps the medieval monks copying these down simply made mistakes or interpreted them incorrectly.

Roman Comic from The New Yorker
Mary Beard has also pointed out that there is no real way to know how ancient people laughed either. This is a bit of a trickier concept to wrap one’s head around. What were ancients’ reactions to laughing? Did they have uncontrollable laughter?
My thought is that yes, maybe our jokes are different from what Roman jokes were, just like how some people find Monty Python funny (I know I do!), while others wonder what the big deal is. I also think that we are perhaps not so different in our physical reactions. For example, there is the quote from Cassius Dio, whom I have used as a source for much of my writing.
Here is a portion from the Roman History in which Cassius Dio and other senators are watching Emperor Commodus slay ostriches in the amphitheatre. As we know, Commodus was off his head, and prone to killing whomever he wanted.
This fear was shared by all, by us senators as well as by the rest. And here is another thing that he did to us senators which gave us every reason to look for our death. Having killed an ostrich and cut off his head, he came up to where we were sitting, holding the head in his left hand and in his right hand raising aloft his bloody sword; and though he spoke not a word, yet he wagged his head with a grin, indicating that he would treat us in the same way. And many would indeed have perished by the sword on the spot, for laughing at him (for it was laughter rather than indignation that overcame us), if I had not chewed some laurel leaves, which I got from my garland, myself, and persuaded the others who were sitting near me to do the same, so that in the steady movement of our armies we might conceal the fact that we were laughing.
(Cassius Dio, Roman History LXXIII)
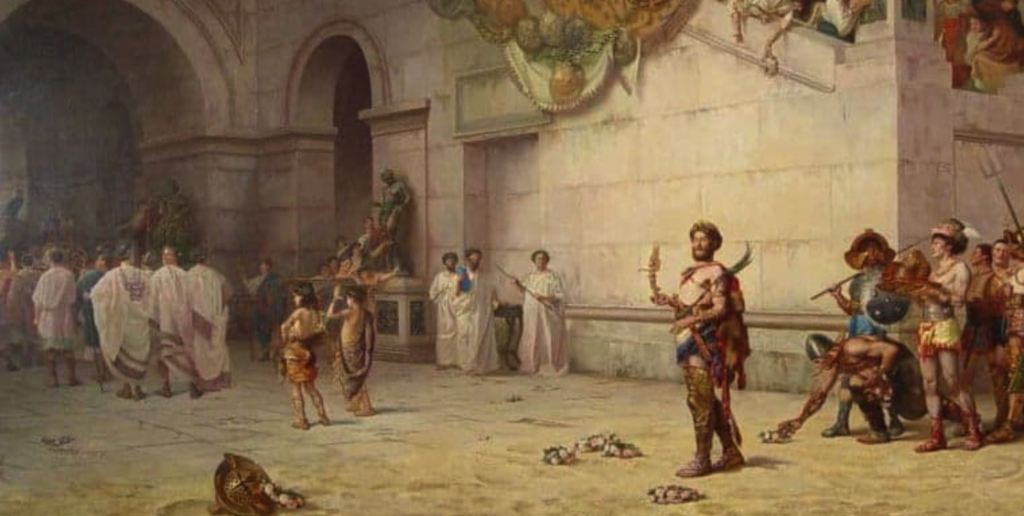

Emperor Commodus in the Arena
What a sight that must have been! Even though it meant certain death, Dio and the other senators had to chew laurels so as not to give in to what was presumably an urge to laugh hysterically.
A young man said to his libido-driven wife: “What should we do, darling? Eat or have sex?” And she replied: “You can choose. But there’s not a crumb in the house.”
(Philagelos, #244)
Bawdiness creeps in all the time in ancient humour, and why not? Everyone (well almost everyone) likes a sex joke. If you peruse the jokes in the Philagelos, you’ll see that many of them have to do with sex.
And this didn’t just apply to the Romans. The ancient Greeks found sex and humour to be comfortable bedfellows (no pun intended).

You’re not getting any until you end this stupid war!
I remember going to an evening performance of Aristophanes’ Lysistrata at the ancient theatre of Epidaurus one summer night. It was a beautiful setting with the mountains as a backdrop to the ancient odeon, the sun setting orange and red, and then a great canopy of silver stars in the sky above.
Lysistrata is a play about a woman’s determination to stop the Peloponnesian War by withholding sex from her husband, and getting all other women to do the same. It seemed quite the political statement on the waste and futility of war, as well as ancient gender issues.
But then the men, who had not had sex for a long time, came prancing about the stage with giant, bulbous phalluses dangling between their legs, moaning with the pain of their ancient world blue balls. Some of the crowd roared with laughter, others tittered in embarrassment, and still others sat stock-still like the statues in the site museum.
Perhaps that is the point? Maybe in ancient times, just as today, some jokes were funny to some and not to others? Are we that different from our ancient Roman and Greek counterparts?
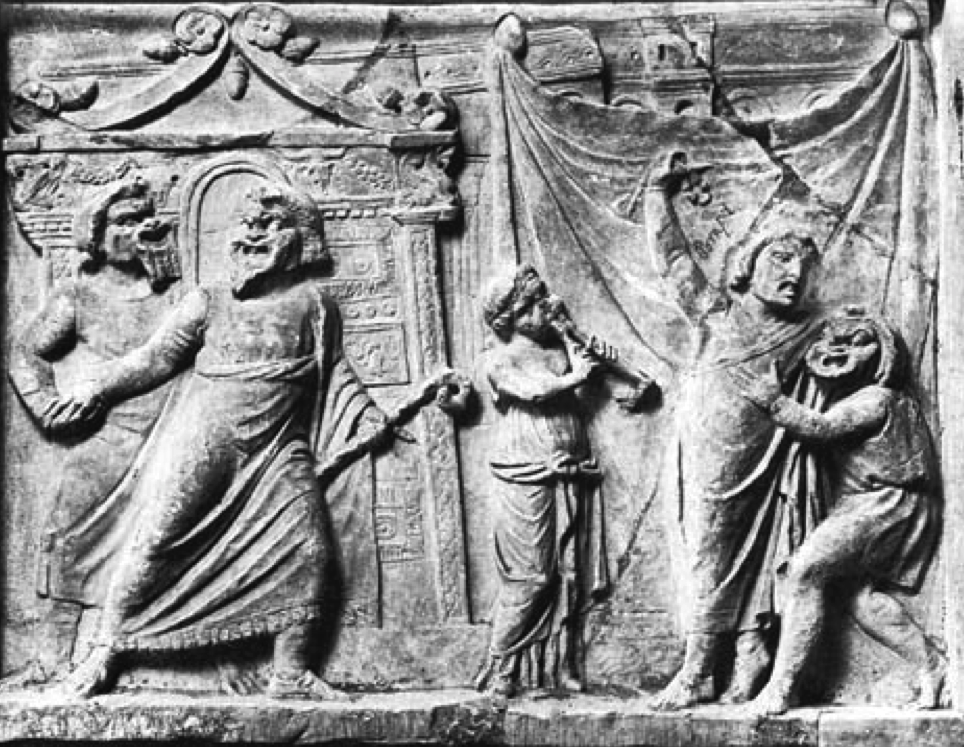

Relief of a Roman Comedic Performance
In her book, Professor Beard points out that ancient writers like Cicero speak of the different types of humour. There is derision (laughing at others), puns (word play), incongruity (pairing of opposites), and humour as a release from tension.
During my research, I found this to be a much bigger topic than I had expected. It’s fascinating to think of laughter in an ancient context.
Do I find ancient jokes funnier than before? Not really, though I do find they reveal something more of Roman society.
But what about comedy in ancient Rome, when it came to plays and the theatre?
In the first part of this blog series, we discussed drama and the various types that developed in Rome, including the pantomimes, mimes, and farces.
Pantomimes tended to be tragic, and mimes were comic in nature, both being more sophisticated or high-brow than farces. Actors in pantomime and mime received training in dance, poetry, and mythology. Often, a performance involved an expressive dance by one actor accompanied by a chorus and ensemble of string, wind or percussion instruments. The artists could be very famous, bringing in large crowds. Often, the subjects of pantomimes were mythological in nature.
That said, in the world of ancient Rome, it was the racier, more bawdy and often improvised, farces, that were popular with the people.
It seems that the people, especially among the lower classes would have much preferred American Pie or Porky’s, to An Ideal Husband or Much Ado about Nothing.

How about some tickles?
Theatrical comedy in general did have certain archetypes when it came to costumes, characters, and themes.
As in ancient Greek theatre, masks, made of linen or cork, were worn, and were brown for male characters, and white for female. Purple was the colour more often worn by rich male and female characters, and red by characters who were supposed to be poor. Slaves boys in comedies were dressed in striped tunics.
Characters and themes in Roman comedy had strong links to ancient Greek comedy, especially those of Menander.
These stock characters often included the young man (adulescens), the young woman (virgo), the young married woman (uxor), the prostitute who could have her own household (meretrix), the pimp (leno), and others such as hostile fathers, unscrupulous pimps, or pirates.
The main stock Roman comedy characters, however, were most often the clever slave, the mean brothel keeper, and the boastful but stupid soldier.
The musical, A Funny Thing Happened on the Way to the Forum, by Stephen Sondheim, is a modern play/musical that perfectly illustrates all of these stock characters. In some ways, it is closest to Roman mimes and farces, performed as they were with an array of songs, and musical accompaniment and dancing.

Scene from A Funny thing Happened on the Way to the Forum (1966)
In researching Sincerity is a Goddess, it was surprising to find out that the themes in ancient Greek and Roman comedy are the origins of our modern slap-stick and romantic comedies.
Intrigues and misunderstandings are common and added to stories of boy-meets-girl, pairs of lovers, pregnancies, marriages, and mistaken identities.
It all makes for a sort of basic training in comedy writing.
Though there were a lot of similarities with comedy today, ancient comedy, high or low brow, was also unique, reflecting the worries, values and everyday lives of the Roman people.
However, it seems that, though we and the Romans may have found different things humorous, they enjoyed an escape from the everyday and a good laugh as much as we do.
Part IV – The Games of Apollo
Ludi, or public games, were an important occurrence on the Roman calendar. Not only did they give the gods their due through religious rites and rituals, but they also gave the people a chance to unwind and enjoy themselves.
Apart from the often very specific religious rituals dedicated to whichever deity the games honoured, there were often also processions, chariot races and theatrical performances. Early on, most ludi did not include gladiatorial combat as these were reserved for funeral games alone, or ludi funebris.
Not only did games in ancient Rome provide some much needed distraction for the people from the dangers of the day, they were also a way for politicians to buy votes. The reason for this is that, though games received some funding from the state, most of the cost of ludi were paid for by wealthy citizens.

General representation of the steps along the cursus honorum during the Republican and Imperial periods.
When it came to positions on the Cursus Honorum of Roman politics, the responsibility of putting on, and funding, games most often lay with the aediles, those four politicians who were at least 37 years old and were charged with looking after the interests of the city of Rome. They looked after temples, markets, streets, squares, brothels, baths, and the water supply. Very important jobs indeed.
The aediles – and sometimes praetors – were also to ensure the success of the public games.
As mentioned, the Roman state did provide a very basic operating budget for games. For example, the Ludi Romani in honour of Jupiter, held from September 5-19, at one point received 760,000 sestercii, and the Ludi Plebii, held from November 4-17, received 600,000 sestercii. The rest – which was the majority of the expense – was paid for by the aedile or praetor sponsoring the games.
These games were extremely important events on the Roman calendar, a time when the lower classes could let go and enjoy feasts and entertainments for free, and when the upper classes could see and be seen.
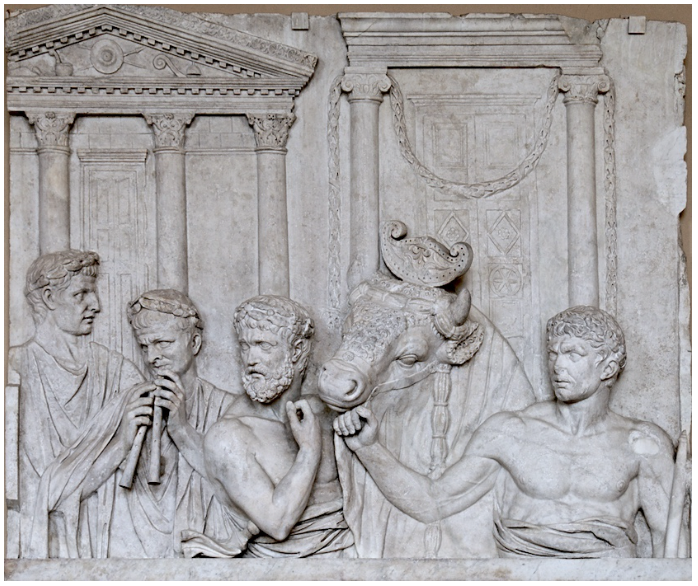

Preparation for a Sacrifice
Different ludi were dedicated to individual deities, and so religious ceremonies, often with very specific sacrifices, were also a part of the games.
Games were, first and foremost, considered sacred acts.
Games were also founded to commemorate victories, and this became a point of pride for rulers and politicians. An example of this is in the Emperor Augustus’ Res Gestae, or ‘Things Done’:
Three times I held gladiatorial spectacle in my own name and five times in the names of my sons or grandsons; in which spectacles some ten-thousand men took part in combat. Twice in my own name and a third time in the name of my grandson, I provided a public display of athletes summoned from all parts. I held games four times in my own name and twenty-three times on behalf of other magistrates… I have provided public spectacles of the hunting of wild beasts twenty-six times in my own name or that of my sons and grandsons, in the Circus or the Forum or the amphitheatres in which three-thousand five-hundred beasts have been killed.
(Res Gestae XXII)
Today, if someone boasted of so much killing, they would be considered a human abomination in most countries, but in the world of ancient Rome, acts such as these were considered extremely generous, gifts for the people, actions which helped to secure the favour of the people.
If the mob of Rome was happy, they did not cause trouble.
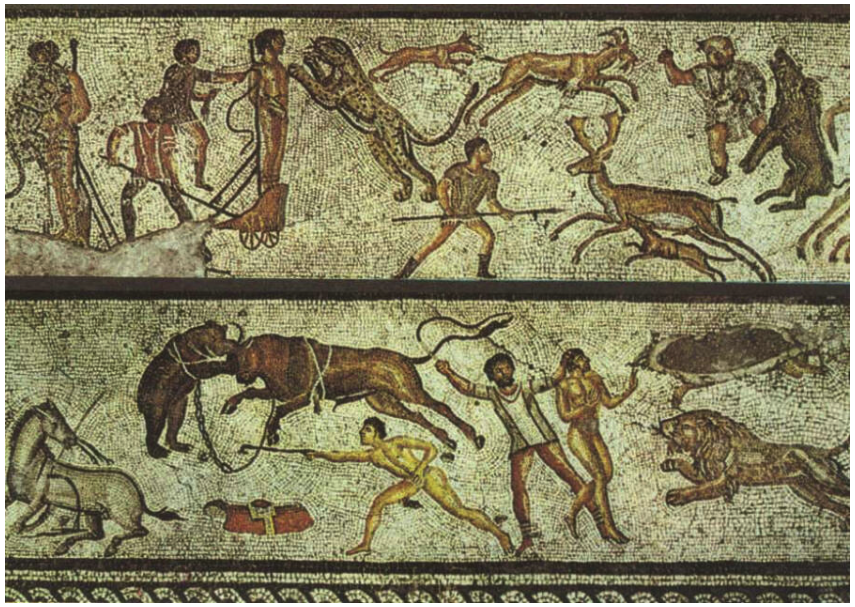

A Venatio – A Roman Animal Hunt
There were different types of ludi as well. There could be ludi votivi, which were held in fulfillment of a vow, or ludi funebris, which were funeral games paid for by a dead person’s family. Public ludi, as we have mentioned, were paid for by the state and the aediles or praetors.
The oldest games are said to be the Ludi Romani which were dedicated to Jupiter and are thought to have been held since 509 B.C. when the temple of Jupiter was dedicated on the Capitol of Rome.
Other games that dotted the Roman calendar were the Ludi Cereri held in honour of Ceres from about 202 B.C., the Ludi Plebii also held for Jupiter from about 216 B.C., the Ludi Megalensi, held in honour of Cybele, and the Ludi Taurii, held in honour of Mars.
And then there were the Ludi Apollinares which are a part of the story of Sincerity is a Goddess.
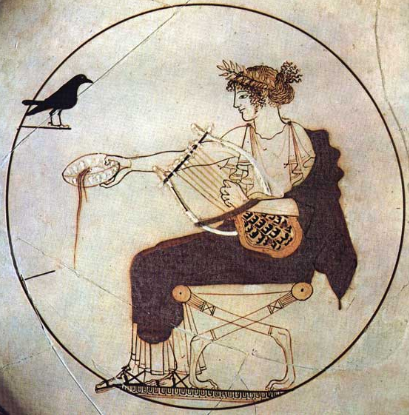

Apollo pouring a libation
The advent of the Ludi Apollinares, the Games of Apollo, are a bit different in their origin from some of the other games. They were begun in the wake of one of the worst defeats in Rome’s history, and born out of a prophecy that was found after the fact. Let me explain…
The Ludi Apollinares were first held in 212 B.C. during the second Punic War, four years after Hannibal’s crushing defeat of Rome’s legions at the battle of Cannae.
In the wake of this defeat, with Hannibal at the gates of Rome, Hannibal ante portas!, the Romans found a prophecy in the Carmina Marciana, the prophecies of the seer, Marcius. Livy, recounts this in his history of Rome…
The importance attached to one of the two predictions of Marcius, which was brought to light after the event to which it related had occurred, and the truth of which was confirmed by the event, attached credence to the other, the time of whose fulfilment had not yet arrived. In the former prophecy, the disaster at Cannae was predicted in nearly these words: “Roman of Trojan descent, fly the river Canna, lest foreigners should compel thee to fight in the plain of Diomede. But thou wilt not believe me until thou shalt have filled the plain with blood, and the river carries into the great sea, from the fruitful land, many thousands of your slain countrymen, and thy flesh becomes a prey for fishes, birds, and beasts inhabiting the earth. For thus hath Jupiter declared to me.” Those who had served in that quarter recognized the correspondence with respect to the plains of the Argive Diomede and the river Canna, as well as the defeat itself.
(Livy, The History of Rome, Book XXV, 12)
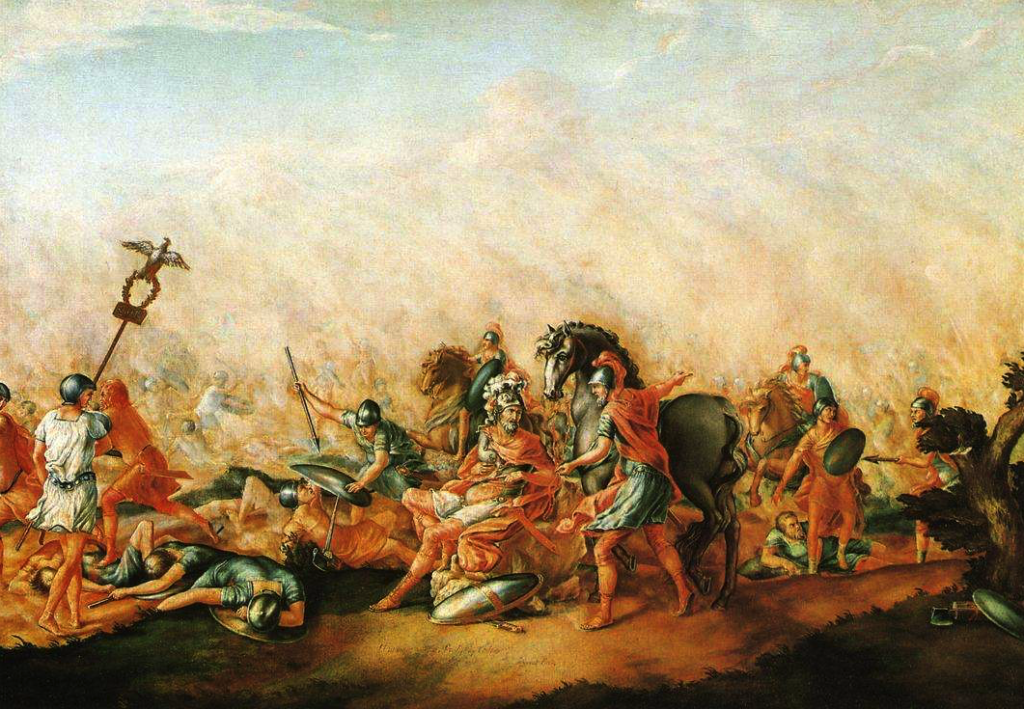

The Death of Paulus Aemilius at the Battle of Cannae (John Trumbull 1773)
The discovery of this prophecy made the Romans take action. We have to remember that this was one of the most terrifying periods in Rome’s history. Hannibal was at the gates of the city, he had defeated a far larger force in one of history’s great victories at the battle of Cannae to the south, on Italian soil.
The Romans did not want to experience such a defeat again and so the Ludi Apollinares were instituted originally as votive games for two purposes: to acquire the gods’ aid in expelling the Carthaginians from Italy, and to protect the Roman Republic from all dangers. They were, originally to be held once, but the year after, the senate passed a decree based on the proposal of the praetor, Calpurnius, that the Ludi Apollinares be held every year as circumstances allowed, i.e. with no fixed date.
In 208 B.C., after a plague in the city, the praetor, Varus, put forward a bill that the Games be held every year on the specific date of July 6th.
And so, the Ludi Apollinares became a permanent part of the Roman festival calendar.
But what did these games entail?
Luckily, another prophecy in the Carmina Marciana prescribed the specific rituals and sacrifices that should be performed to honour Apollo. Again, Livy recounts this:
The other prophecy was then read, which was more obscure, not only because future events are more uncertain than past, but also from being more perplexed in its style of composition. “Romans, if you wish to expel the enemy and the ulcer which has come from afar, I advise, that games should be vowed, which may be performed in a cheerful manner annually to Apollo; when the people shall have given a portion of money from the public coffers, that private individuals then contribute, each according to his ability. That the praetor shall preside in the celebration of these games, who holds the supreme administration of justice to the people and commons. Let the decemviri perform sacrifice with victims after the Grecian fashion. If you do these things properly you will ever rejoice, and your affairs will be more prosperous, for that deity will destroy your enemies who now, composedly, feed upon your plains.” They took one day to explain this prophecy. The next day a decree of the senate was passed, that the decemviri should inspect the books relating to the celebration of games and sacred rites in honour of Apollo. After they had been consulted, and a report made to the senate, the fathers voted, that “games should be vowed to Apollo and celebrated; and that when the games were concluded, twelve thousand asses should be given to the praetor to defray the expense of sacred ceremonies, and also two victims of the larger sort.” A second decree was passed, that “the decemviri should perform sacrifice in the Grecian mode, and with the following victims: to Apollo, with a gilded ox, and two white goats gilded; to Latona, with a gilded heifer.” When the praetor was about to celebrate the games in the Circus Maximus, he issued an order, that during the celebration of the games, the people should pay a contribution, as large as was convenient, for the service of Apollo. This is the origin of the Apollinarian games, which were vowed and celebrated in order to achieve victory, and not restoration to health, as is commonly supposed. The people viewed the spectacle in garlands; the matrons made supplications; the people in general feasted in the courts of their houses, throwing the doors open; and the day was distinguished by every description of ceremony.
(Livy, The History of Rome, Book XXV, 12)
It is truly fascinating to read this passage for it is quite specific from the amount to be spent by the state, and the specific animals with gilded horns to be offered to Apollo and Latona (i.e. Leto, his mother), and that this should be done in the Greek fashion, the ritus Graecus, that is, with the head uncovered for the sacrifice.
The prophecy also prescribes a joyful atmosphere that is pleasing to the gods in which people offer what they can, wear garlands, and dine together with the doors of their homes thrown open.
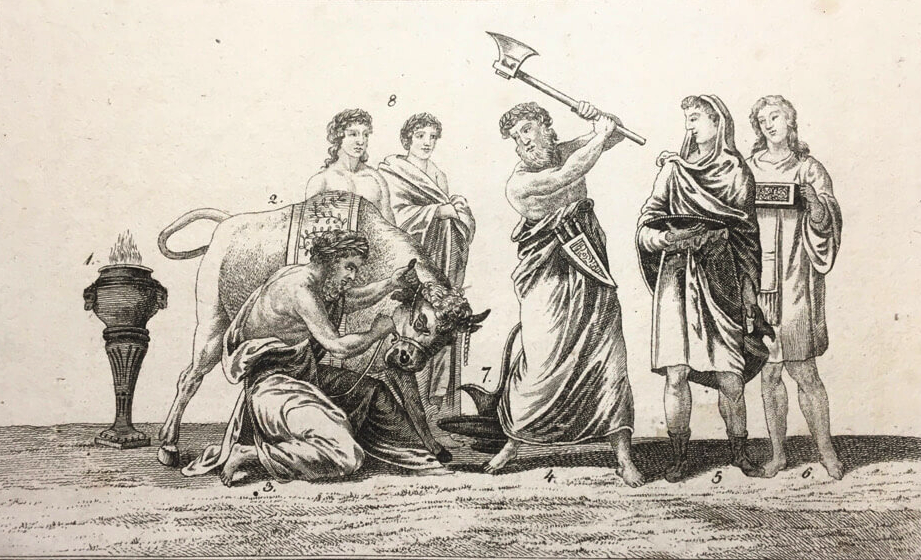

Sacrifices were central to Roman Ludi
At these first games of Apollo, most of the events took place in the Circus Maximus of Rome and included chariot races – by far Rome’s most popular pastime – animal hunts, religious processions and, most importantly to our story, theatrical performances.
Interestingly, we have a record of one of the specific plays performed in the games of 169 B.C. and that was the revenge tragedy of Thyestes who was King of Olympia and the son of Pelops and Hippodameia.
I think it is a safe assumption that though theatrical performance was originally a small part of the games of Apollo, over time, more would have been included, especially under such emperors as Nero, who saw himself as a great performer.
The Ludi Apollinares were smaller games than the Ludi Romani or Ludi Plebii. After all, they received less funding. But, they did grow in popularity and, eventually, they went from being celebrated for one day on July 13th, to being held for eight days from July 6th to 13th.
More events would have been held over this extended period, and though it was still, at heart, a religious and votive festival, the theatre played a large part in it.

Apollo
We can end on a small anecdote that I came across in my research that illustrates this and the importance of properly seeing through the required rituals.
In the second year of the games, in 211 B.C. there is a story that during a theatrical performance for the Ludi Apollinares, a cry and panic went up in the audience that Hannibal was at the gates – Hannibal ante portas!
The spectators rushed from the theatre to get their weapons and fight to defend the city. However, it turned out to be a false alarm.
When the audience members returned to the theatre, and the play that had been so harshly interrupted, they found the dancer still dancing, and the accompanying flute player still playing! It was a marathon performance for the two, and the audience cried out “All is saved!”
Hannibal did not attack the city.
I don’t know for certain if this story is true, but it is a good one!
The show must go on and, it seems, in ancient Rome, it was indeed a matter of life and death!
Part V – Prostitution in Ancient Rome
WARNING: The topic discussed in this post, as well as some of the images of ancient frescoes shown, may be offensive to some readers. Discretion is advised.
Now, it should be stated at the outset that Sincerity is a Goddess is not an erotic romp through the streets of Rome. It is a heartwarming comedy. However, as mentioned in Part III of this blog series, on humour and comedy in ancient Rome, the prostitute was a stock character in Roman comedic drama.
In truth, you can’t really write about the Roman world without touching on the long-standing role that prostitution and brothels had to play in society. They were a large part of that world, an element of life in ancient Rome that spanned classes.
They existed, and they most certainly flourished. People – that is, men – of all levels of society made it a normal practice to visit their favourite brothel or prostitute.
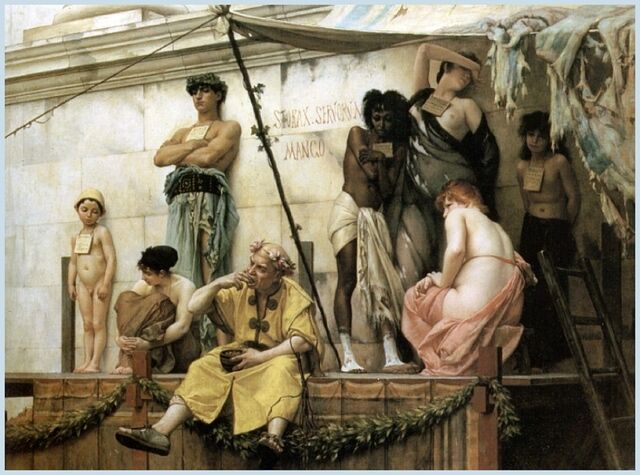

The Slave Market – oil painting by Gustave Boulanger, 1886 (Wikimedia Commons)
If you liked the HBO show ROME – which is fantastic by the way! – you might have an image of Titus Pullo whoring his way through the Suburra with his jug of wine in hand. Certainly, this sort of behaviour was not uncommon, especially for troops fresh back from the wars and looking for a good time.
The flip side might be the richer, upper class nobility who may have believed visiting prostitutes was fine, as long as it was done in moderation and didn’t cause a scandal.
The prostitution scene in the Empire was as large and varied as the workers and clients who kept it running. There was something for everyone!
But let’s look at things a bit more closely.
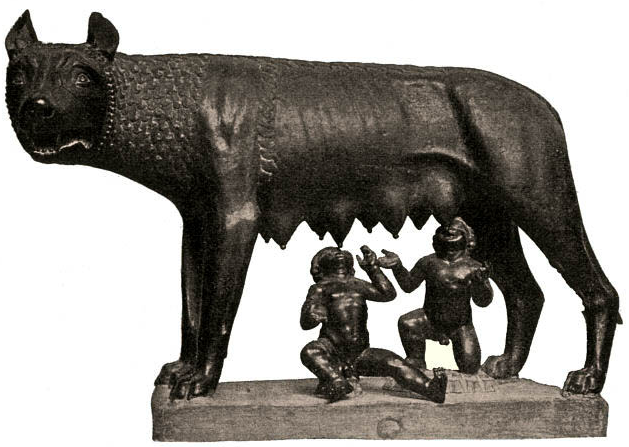

The She-Wolf suckling the brothers, Romulus and Remus
One could say that prostitution has ties to the founding of Rome itself.
You may have read about Romulus and Remus, the brothers who founded Rome and were suckled by the She Wolf, or Lupa.
We have heard of lost children being raised by wolves before, but in the instance of Romulus and Remus, many believe that they were actually raised by a prostitute who found them on the banks of the Tiber. The slang word for prostitute in Latin was lupa.
And the word for brothel was in fact lupanar or lupanarium.
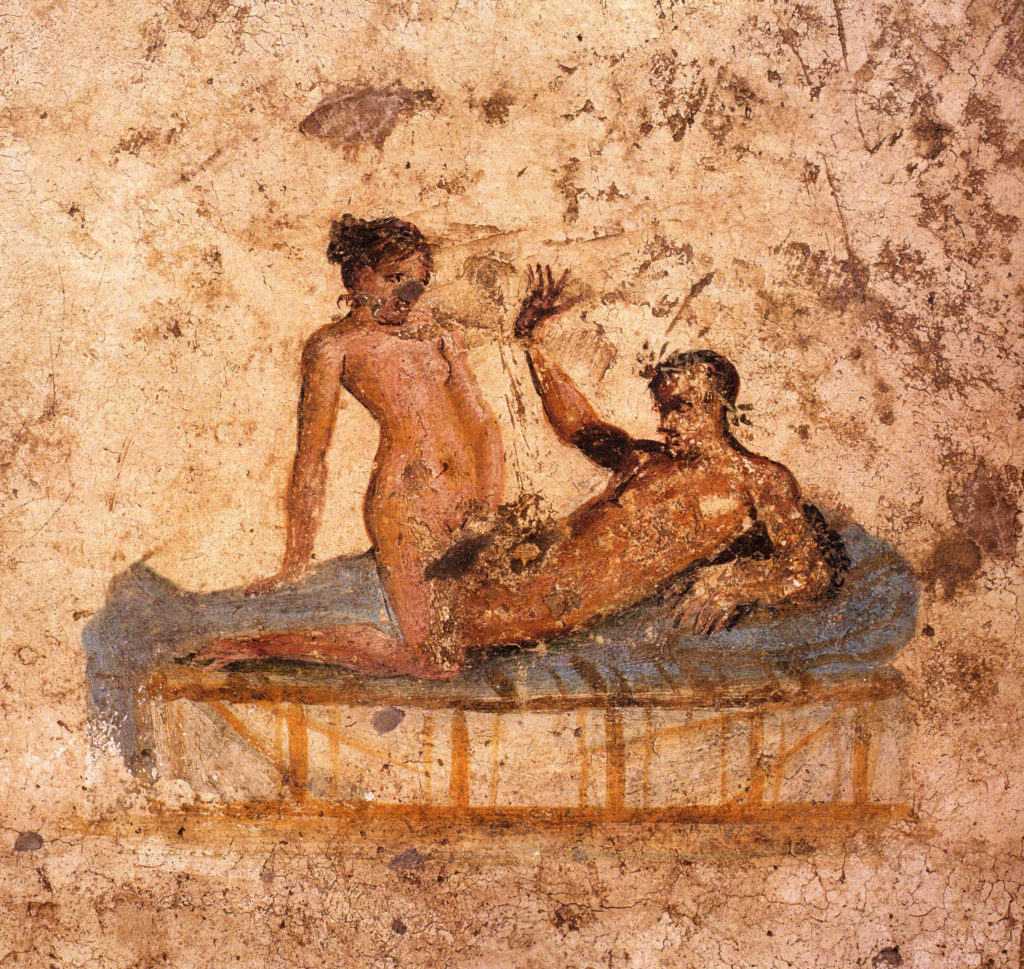

A lupa and her patron
Clients were drawn in by the sexual allure of displayed ‘wares’, sometimes lined up naked on the curb outside, and the various experiences to be had within. The latter were sometimes illustrated in frescoes or mosaics on the walls of the lupanar. These were intended to add to the atmosphere, or were a sort of menu of pleasures to be had.
There were of course ‘high-class’ prostitutes who catered to wealthy and powerful patrons, women who were skilled at conversation, music and poetry. These high end lupae provided an escape, or a feast with friends, in lavish surroundings coupled with a sort of blissful oblivion. Some might have been purchased by their wealthy clients to keep for themselves, and if that was the case they might have ‘enjoyed’ a relatively easy life compared to the alternative.
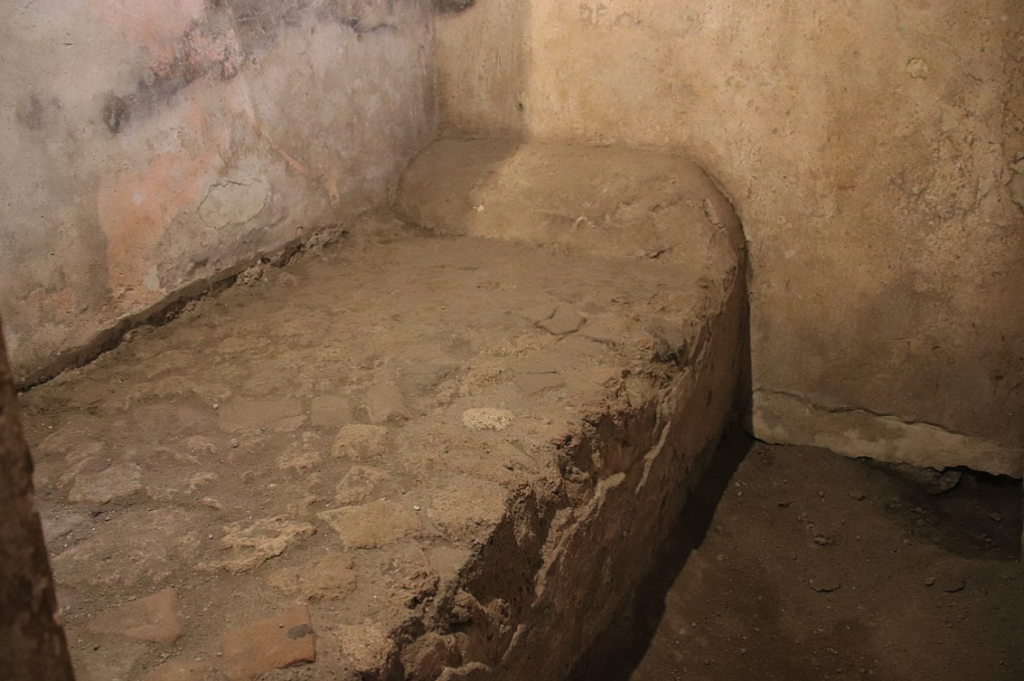

A lupa’s ‘office’ or ‘cell’ in Pompeii – a cement bed that would have been covered with a matress and pillows
The truth for most, however, was that they were slaves. And slaves in ancient Rome, as we all know, were objects, property to be used and disposed of on a whim.
Prostitutes – women, boys, girls, eunuchs etc. – were at the bottom of the social scale, along with actors and gladiators. They could be adored by clients one moment, and shunned the next. And if a lupa was no longer profitable, the leno (pimp), or the lena (madam) might sell them off as a liability, sending them to a life that was possibly even worse.
In ancient Rome, prostitution was legal and licensed, and it was normal for men of any social rank to enjoy the range of pleasures that were on offer. Every budget and taste was catered to, and because of Rome’s conquests, and the length and breadth of the Roman Empire in the early 3rd century, there would have been slaves of every nationality and colour. Clients of the lupanar would have had their choice of Egyptians, Parthians and Numidians, Germans, Britons, slaves from the far East and anywhere else, including Italians.
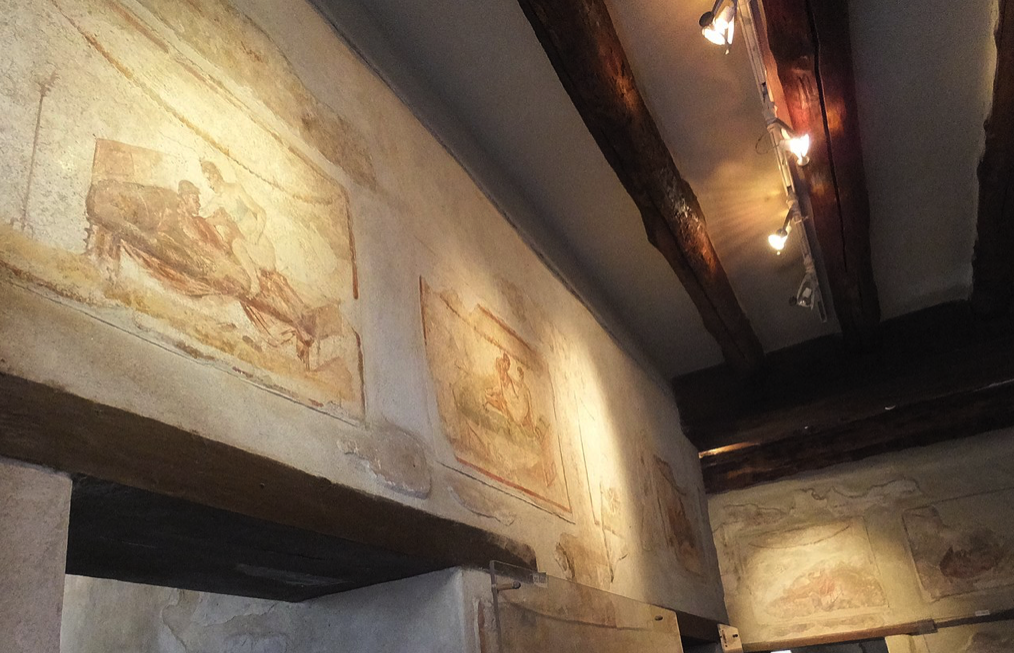

The decor of Pompeii’s lupanar – a ‘menu’ of sorts (Wikimedia Commons)
However, even though prostitution was regulated, we should not delude ourselves. This was not a question of morality, or curbing venereal diseases. This was about maximizing profit – prostitution was also taxed!
In Pompeii, prostitution became a sort of tourist trade. One theory contends that on the street pavement you just had to follow the phalluses to find the nearest brothel! There were numerous brothels, and that’s not counting the small curbside cells or niches where the cheapest lupae provided quickies to passers-by.

The Great Lupanar of Pompeii
Because of the archaeological finds, the most well-known brothel in the Roman world was the ‘Great Lupanar’ of Pompeii, located at a crossroads two blocks from the Forum. Many of the frescoes pictured here are from that building which had ten rooms, where most brothels had just a few.
A sexual scene from Pompeii’s great lupanar
One might think that the subject of this particular post was rather fun to write about, that the images above are titillating. And sure, they are to an extent. I don’t mind a bit of risqué material on occasion. Why not?
But then, I can’t help thinking of the lives that these female, and sometimes male, prostitutes had to endure. Very few enjoyed the favour of kind and wealthy clients, living in luxurious surroundings.
Prostitutes were slaves and most were probably pumped and beaten for a bronze coin or two before having to receive their next tormentor. These people were objects to the rest of the world, not human beings. They were people’s daughters and sons, mothers, and sisters. In many cases they’d been taken from their homes on the other side of the world. Perhaps they were all that was left of their family?
For most prostitutes in the Roman Empire, life was a living Hades.

Lupanar scene from Pompeii
One thing is certain however. On the whole, prostitutes in the Roman world – be it Rome, Pompeii, or some far flung corner of the Empire – likely led tortured lives, living in squalid conditions while being brutalized by the male population. No matter how much one might like to romanticize the perceived sexual freedom of the Roman world, one cannot escape the fact that this freedom was supremely one-sided.
For some very interesting and sobering thoughts on the subject, watch this SHORT VIDEO interview with historian Mary Beard.
However, as I said, Sincerity is a Goddess is a comedy. The lupa in this book is not a tortured individual, but a more mature and savvy business woman who is quite skilled at reading people. She has, of course, had her share of hardship in her life, but by the time of our story, she has come through her toils a wiser and more confident person. Her character is crucial to the story and the journey one of our protagonists takes.
Part VI – Epidaurus: Place of Dreams and Healing
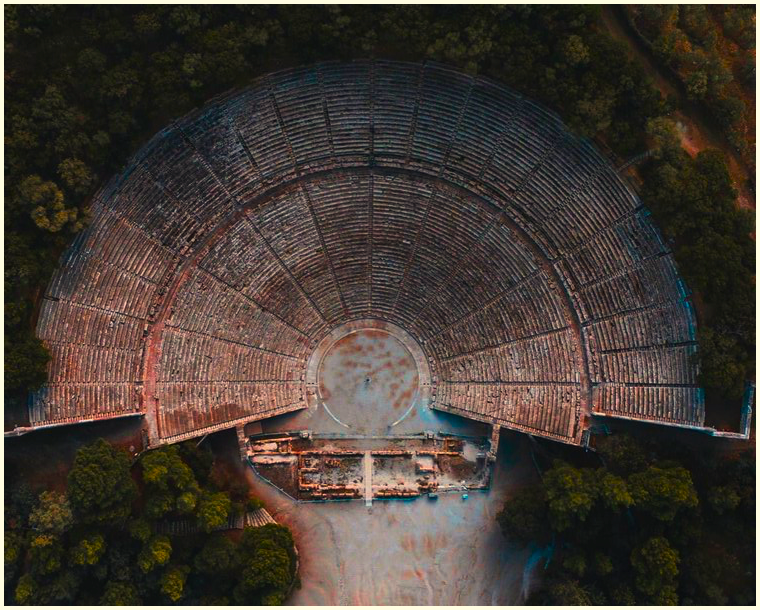

Theatre of Epidaurus (photo: Dimitrios Pallis, IG @pallisd)
You may be wondering what a blog post about an ancient Greek theatre and sanctuary has to do with a story set in ancient Rome.
Well, let me tell you, it has a lot to do with it. Not only was the healing sanctuary at ancient Epidaurus well-known in the Roman world, but the great theatre there also plays an important role in Sincerity is a Goddess. However, not in the way you might think.
Don’t worry though, for there are no spoilers if you haven’t read the book yet.
In this post, we’re going to be taking a brief look at the two faces of ancient Epidaurus – the theatre itself, and the sanctuary of Asklepios which was renowned across the ancient world for its healing…and snakes!
Let’s get into it!
Plan of the Theatre of Epidaurus
Firstly, as Epidaurus is, today, famous for its well preserved odeon, and as Sincerity is a Goddess is partially a story about a theatre troupe, we’ll start with the theatre itself.
I’ve been to this site several times in the past, and I never tire of it. Some places are like that, I suppose. You can visit them again and again, and each time you do you get a different perspective that adds to your overall impression of the site.
The theatre of Epidaurus is like that.
For the history-lover in me, going there is like visiting a wise old friend. We greet each other, sit back in the sunshine, reminisce, and contemplate the world before us.
There is something comforting about going back to familiar places.
When you enter the archaeological site from the ticket booths and follow the path, you find the museum on your left, its wall lined with marble blocks covered in votive inscriptions from the sanctuary of Asklepios (more on that shortly).
I don’t know why, but every time we visit Epidaurus, I’m always drawn to the theatre first. Perhaps it is more familiar, simpler than the archaeological site of the sanctuary opposite? You walk up the steep stone steps beneath scented pine trees and then, there it is!
The theatre lies in the blinding sunlight all limestone and marble, rising up in perfect symmetry before you with the mountains beyond.
It’s always a shock to stand there and see it for the first time, this perfect titan, an ancient stage beneath a clear blue sky where the works of Euripides, Aeschylus, Aristophanes, Sophocles and so many more have entertained the masses and provoked thought in the minds of mortals for well over two thousand years.
In ancient times, one’s view from this vantage would have been partially blocked by the stage building, or scaena, but as it is today, you have a perfect view over the ruins of that building’s foundations.

Side entrance to the orchestra
The Epidaurians have a theatre within the sanctuary, in my opinion very well worth seeing. For while the Roman theatres are far superior to those anywhere else in their splendour, and the Arcadian theatre at Megalopolis is unequalled for size, what architect could seriously rival Polycleitus in symmetry and beauty? For it was Polycleitus who built both this theatre and the circular building.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece, 2.27.5)
The theatre of Epidaurus is considered the best-constructed and most elegant theatre of the ancient world. It was built in the 4th century B.C by the sculptor and architect, Polykleitos the Younger, who also designed the tholos in the sanctuary nearby.
The theatre sat 14,000 spectators, and every one of them could see the stage and hear every momentous word that was spoken.
As people are wont to do when visiting this theatre, I’ve stood at the centre of the stage (the orchestra), and dropped a coin so that my family and friends could hear it where they sat at the top row.
Then I speak…
It is a surreal, dreamlike experience to do so, from that orchestra, for your voice is so loud in your ears, you can’t quite grasp what is happening at first. It feels like you are speaking into a microphone, your voice amplified. But there are, of course, no electronics, just an ancient perfection of design that has set the standard for ages.
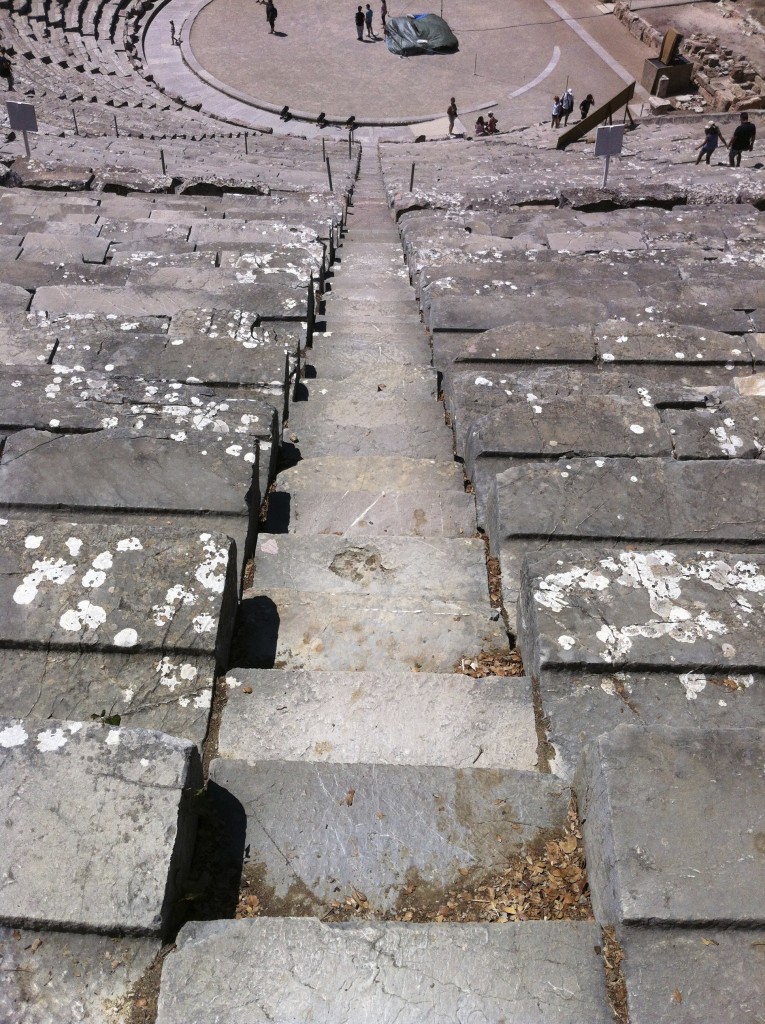

You don’t want to tumble down this aisle!
I always climb the long central isle to the top row and sit down to take it all in. It’s a long way up, but the top provides the perfect vantage point of the sanctuary and landscape surrounding Epidaurus. I love to just sit there and listen to the cicadas, take in the view, and enjoy the dry, pine-scented air.
I’ve had the privilege of seeing Gerard Dépardieu perform in Sophocles’ Oedipus Rex, and Isabella Rossellini in an adaptation of Stravinsky’s Persephone in the theatre of Epidaurus. It was amazing to watch such wonderful actors giving a performance there, and it was obvious too that they were enjoying the space, the tradition they were taking part in.
The last play I saw at Epidaurus was a performance of Aristophanes’ Lysistrata, a comedy in which the women of Greece withhold sex from all the men in order to put an end to the Peloponnesian War.
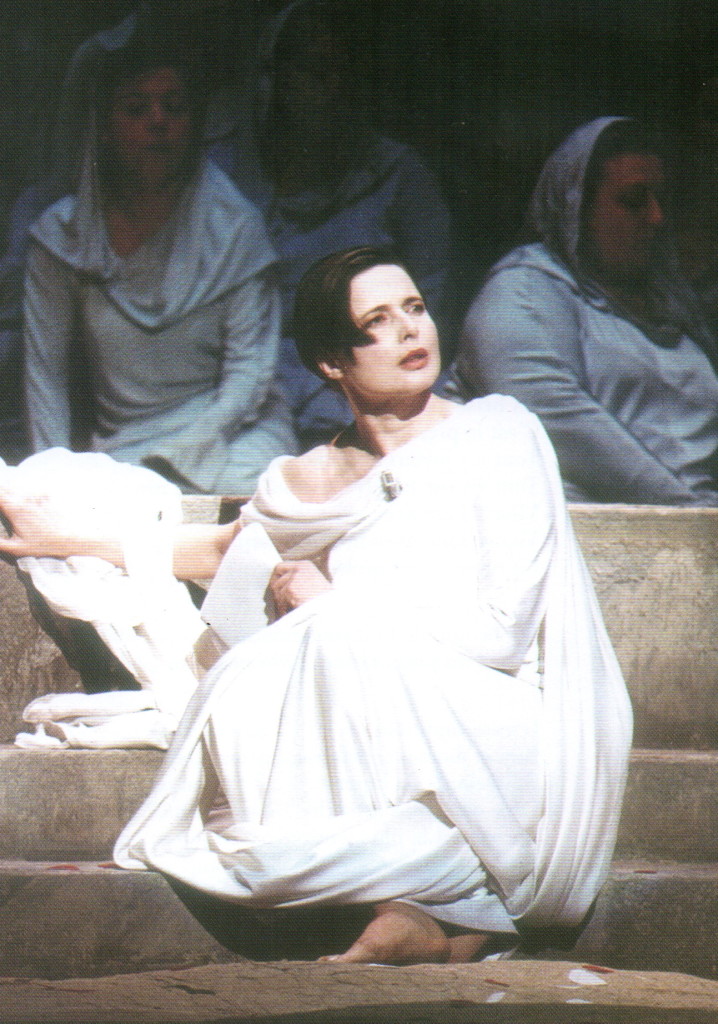

Isabella Rossellini in ‘Persephone’
When you see a play at Epidaurus, the audience is also participating in an ancient tradition. How many people have gone before us, sat in those seats, laughed and wept at the drama being played out before them?
It’s difficult not to think about that when you sit in the seats of Epidaurus. Whether you are basking in the hot rays of the Mediterranean sun, or waiting for a play to begin as the sun goes down and the stars appear, Centaurus and Cygnus twinkling in the sky above, one thing is certain – you will never forget the moments that you spend there.
Next, we’re going to venture away from the theatre for a brief visit to the museum, and then on into the peace and quiet of the Sanctuary of Asklepios, a place of miracles and ancient healing that was famous across the Greek and Roman worlds.

Looking north from the theatre to the sanctuary
When you enter the abode of the god
Which smells of incense, you must be pure
And thought is pure when you think with piety
This is the inscription that greeted pilgrims who passed through the propylaia, the main gate to the north, into the sanctuary of the god, Asklepios, at ancient Epidaurus.
The ancient writer, Pausanias, gives us some interesting insights…
The sacred grove of Asclepius is surrounded on all sides by boundary marks. No death or birth takes place within the enclosure. The same custom prevails also in the island of Delos. All the offerings, whether the offerer be one of the Epidaurians themselves or a stranger, are entirely consumed within the bounds.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece, 2.27.1)
After the glory of the ancient theatre, it feels like something of a contrast to step into the quiet realm of the sanctuary of the God of Healing. This was a place that was famous around the ancient world for the miracles of health and healing that occurred there.
But perhaps the contrast is not so great? After all, Asklepios was the son of Apollo – an interesting union of healing and art – and it could be argued that the experiences one had in the theatre and the sanctuary were both transformative and healing.
Toward the back of the sanctuary there is a small, but wonderful, site museum that is well worth a visit for the collection of architectural and everyday artifacts.
The vestibule contains cabinets filled with oil lamps, containers and phials that were used for medicines and ointments within the sanctuary, as well as surgical implements and votive offerings.

Medical Instruments in the Epidaurus museum
Above the cabinets and into the main room of the museum, there are reliefs and cornices from the temple of Asklepios decorated with lion heads, acanthus and meander designs, many of which still have the original paint on them.
However, in the first part of the museum are some plain-looking stele that are covered in inscriptions recording the remedies given at Epidaurus, and the miracles of healing at the sanctuary in ancient times. These inscriptions are where much of our knowledge of the sanctuary comes from.

Stele with accounts of healing at the sanctuary, as well as quotes of the Hymn to Apollo
In the main part of the museum, your eyes are drawn, once more, to the magnificent remains of the tholos and the temple of Asklepios – ornate Corinthian capitals, cornices decorated with lion heads, and the elaborately-carved roof sections of the temple’s cella, the inner sanctum.
There are statues of Athena and Asklepios that had adorned various parts of the sanctuary, and the winged Nikes that stood high above pilgrims, gazing out from the corners of the roof of the temple of Artemis, the second largest temple of the sanctuary.

The Museum Interior
I wonder if people walking through the museum realize how beautiful the statues are, the meaning they held for those who came to the sanctuary in search of help?
After one cools off in the museum, it’s time to head for the sanctuary of Asklepios just north of the museum and theatre.
Every time I’ve visited, the sanctuary itself is usually completely empty.
It seems that most visitors head for the theatre alone, some to the museum afterward, but most do not want to tough it out among the ruins of one of the most famous sanctuaries in the ancient world.

The Sanctuary of Asklepios from the North
The Sanctuary of Asklepios lies on the Argolid plain, with Mt. Arachnaio and Mr. Titthion to the north. The former was said to have been a home of Zeus and Hera, and the latter, whose gentle slopes lead down to the plain, was said to have been where Asklepios was born.
To the south of the sanctuary is Mt. Kynortion, where there was a shrine to Apollo, Asklepios’ father. Farther to the south are the wooded slopes of Mt. Koryphaia, where the goddess Artemis is said to have wandered.
This is a land of myth and legend, a world of peace and healing, green and mild, dotted with springs. The sanctuary was actually called ‘the sacred grove’.
Asklepios, as a god of healing, was worshiped at Epidaurus from the 5th century B.C. to the 4th century A.D. According to archaeologist Angeliki Charitsonidou, it was the sick who turned to Asklepios, people who had lost all hope of recovery – the blind, the lame, the paralyzed, the dumb, the wounded, the sterile – all of them wanting a miracle.

Asklepios
But who was Asklepios?
Some believed he learned medicine from the famous centaur, Cheiron, in Thessaly. Another tale from the Homeric age makes Asklepios a mortal man, a king of Thessaly, whose sons Machaon and Podaleirios fought in the Trojan War and learned medicine from their father.
Eventually, it came to be believed that Asklepios was a demigod, born of a union between Apollo and a mortal woman. His father was also a god of healing, and prophecy and healing, in the ancient world, went hand-in-hand. The snake was a prophetic creature, and a creature of healing, so it is no wonder this animal came to be associated with Asklepios and medicine.
At Epidaurus, snakes were regarded as sacred, as a daemonic force used in healing at the sanctuary. These small, tame, blondish snakes were so revered that Roman emperors would send for them when in need. Once again, Pausanias gives us some insight:
The serpents, including a peculiar kind of a yellowish colour, are considered sacred to Asklepios, and are tame with men. These are peculiar to Epidauria, and I have noticed that other lands have their peculiar animals. For in Libya only are to be found land crocodiles at least two cubits long; from India alone are brought, among other creatures, parrots. But the big snakes that grow to more than thirty cubits, such as are found in India and in Libya, are said by the Epidaurians not to be serpents, but some other kind of creature.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece, 2.28.1)

Now you know where this symbol comes from!
I’ll stick with the tame blond snakes, thank you very much!
The thing about Asklepios was that he was said to know the secret of death, that he had the ability to reverse it because he was born of his own mother’s death. Zeus, as king of the gods, believed that this went against the natural order, and so he killed Asklepios with a bolt of lightning.
There are no written records of medical interventions by the priests of Epidaurus in the early centuries of its existence. The healing that occurred was only through the appearance of the god himself. However, over time the priesthood of Epidaurus began to question patients about their ailments, and prescribe routines of healing or exercise that would carry out the instructions given to pilgrims by Asklepios in the all-important dreams, the enkoimesis, which they had in the abato of the sanctuary.
It is quite a feeling to walk the grounds of the sanctuary at Epidaurus, to be in a place where people believed they had been touched or aided by a god, and actual miracles had occurred and were recorded.
Faith and the Gods are a big part of ancient history, and cannot be separated from the everyday. I’ve always found that I get much more out of a site, a better connection, when I keep that in mind. You have to remove the goggles of hindsight and modern doubt to understand the ancient world and its people.
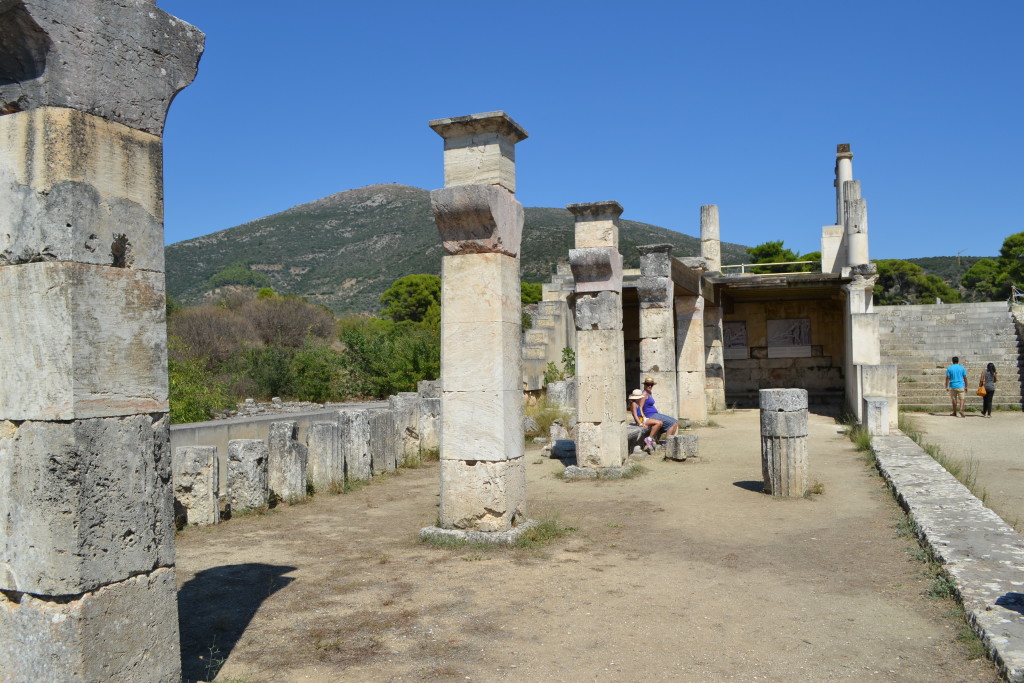
From the museum you walk past the ruins of the hospice, or the ‘Great Lodge’, a massive square building that was 76 meters on each side, two-storied, and contained rooms around four courtyards. This is where later pilgrims and visitors to the sanctuary, and the games that were held in the stadium there, would stay.
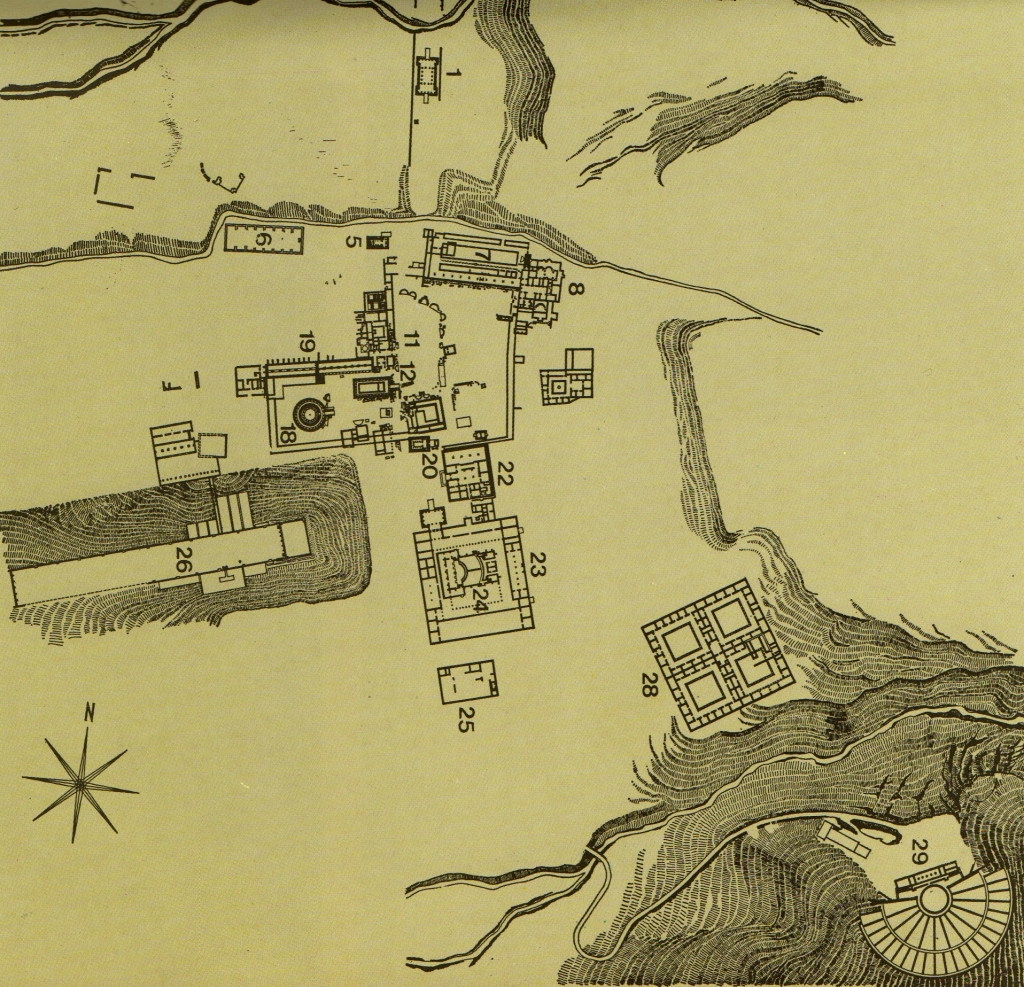
Map of the Sanctuary (from the site guide book)
Without a map of what you are looking at, it’s difficult to pick out the various structures. Most of the remains are rubble with only the foundations visible. This sanctuary was packed with buildings, and apart from a few bath houses, a palaestra, a gymnasium, a Roman odeion, the stadium and a large stoa, there are some ruins that one is drawn to, notably the temples.
The sanctuary of Asklepios has several temples the largest being dedicated to the God of Healing himself, within which there stood a large chryselephantine statue of Asklepios.
There were also temples to Artemis (the second largest on-site), Aphrodite, Themis, Apollo and Asklepios of Egypt (a Roman addition), and the Epidoteio which was a shrine to the divinities Hypnos (sleep), Oneiros (Dream), and Hygeia (Health). These latter divinities were key to the healing process at Epidaurus.
Ancient Epidaurus was a sacred escape where the mind, body, and soul could recuperate. It is a place of sunlight and heat, of fresh air and green trees set against a backdrop of mountains tinged with salt from the not-too-distant sea. Cicadas yammer on in a bucolic frenzy, and bees and butterflies wend their way among the fallen pieces of the ancient world as your feet crunch along on the gravel pathway, past the ruins of the palaestra, gymnasium, and odeion to an intersection in the sacred precinct of the sanctuary.
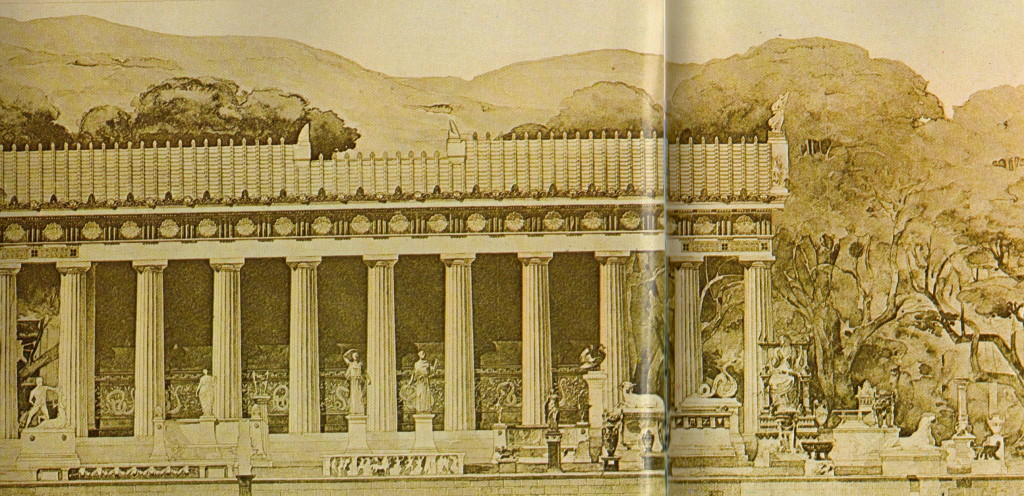
Reconstruction of the Temple of Asklepios’ south side (from site guide book)
Here you find the temple of Artemis to your right as you face the ruins of what was the magnificent temple of Asklepios to the north. You can see the foundations, the steps leading up.
The image of Asklepios is, in size, half as big as the Olympian Zeus at Athens, and is made of ivory and gold. An inscription tells us that the artist was Thrasymedes, a Parian, son of Arignotus. The god is sitting on a seat grasping a staff; the other hand he is holding above the head of the serpent; there is also a figure of a dog lying by his side. On the seat are wrought in relief the exploits of Argive heroes, that of Bellerophon against the Chimaera, and Perseus, who has cut off the head of Medusa.
(Pausanias, Description of Greece, Book 2.27.2)
It is interesting that in a place where dreams were part of healing, the images carved on the seat of Asklepios portray some of the greatest heroes fighting and defeating their own ‘monsters’.
How many people in need had walked, limped or crawled up those steps seeking the god’s favour.
On your left you see a large, flat area of worn marble that was once the great altar of Apollo where pilgrims made blood sacrifices to Apollo and Asklepios in the form of oxen or cockerels, or bloodless offerings like fruit, flowers, or money.
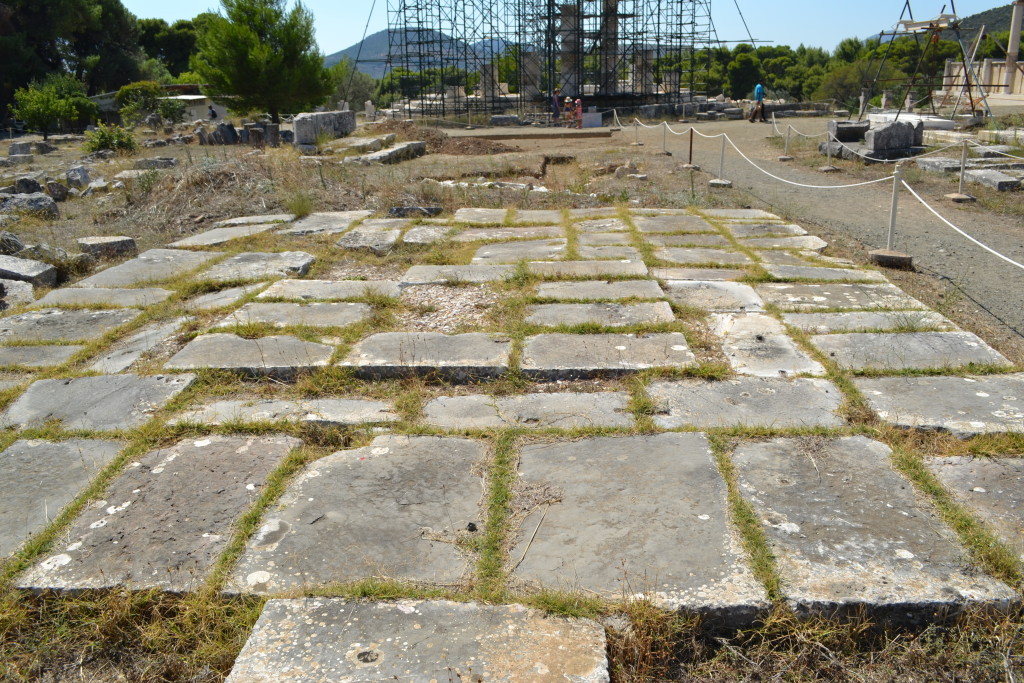

Remains of the Great Altar of Apollo
Standing there, you can imagine the scene – smoke wafting out of the surrounding temples with the strong smell of incense, the slow drip of blood down the sides of the great altar, the tender laying of herbs and flowers upon the white marble, all in the hopes of healing.
As people would have stood at the great altar, they would have seen one of the key structures of the sanctuary beyond it, just to the west – the tholos.
The tholos was a round temple that was believed to be the dwelling place of Asklepios himself. It was here that, after a ritual purification with water from the sanctuary, that pilgrims underwent some sort of religious ordeal underground in the narrow corridors of a labyrinth that lay beneath the floor of the tholos’ cella, the inner sanctum.

Reconstruction of Epidaurian Tholos and Temple of Asklepios (photo reconstruction: CNN)
After their ritual ordeal, pilgrims would be led to the abato, a long rectangular building to the north of the tholos and temple of Asklepios.
The abato is where pilgrims’ souls would be tested by way of the enkoimesis, a curative dream that they had while spending the night in the abato.
Miracles happened in this place, and there are over 70 recorded inscriptions that have survived which detail some of them – mute children suddenly being able to speak, sterile women conceiving after their visit to sanctuary, a boy covered in blemishes that went away after carrying out the treatment given to him by Asklepios in a dream. There are many such stories that have survived, and probably many that we do not know of.

Inside the partially restored Abato
As you stand in the abato, careful not to step on any snakes that may be hiding along the base of the walls, it’s a time to reflect on the examples of healing on the posted placard. It seemed that the common thread to all the dreams that patients had was that Asklepios visited them in their dreams and, either touched them, or prescribed a treatment which subsequently worked.

Relief of Asklepios healing a dreamer
Sleep. Dream. Health.
When I think of those divinities who were also worshiped at Epidaurus, right alongside Asklepios, it doesn’t seem so far-fetched. In fact, standing there, in that place of peace and tranquility, it seems highly likely.
The people mentioned on the votive inscriptions – those who left vases, bronzes, statues, altars, buildings and fountains as thank offerings to the god and his sanctuary for the help they received – those people were real, as real as you and me. They confronted sickness, disease, and worry, just as we do.
Today, some people turn to their chosen god for help when they are in despair. Others turn to the medical professionals whom they hope have the skill and compassion to cure them.
At ancient Epidaurus, people could get help from both gods and skilled healers, each one dependent on and respectful of the other.
This place haunts me in a way. I always think about how special this place is, how the voices of Epidaurus, its sanctuary, and its great theatre, will never die or fade.
Indeed, just as Asklepios was said to have done, this is a place that defies death and time.

Remains of Temple of Asklepios
It is indeed fitting that the theatre and sanctuary go together, for both are healing experiences, forcing the mortal attendees to look inward, to delve into the darker depths of their selves to observe their own trials and tribulations so that they can manage their healing.
Theatre is a transformative experience, and so it and the healing sanctuary both deserve their places beside each other, as well they do in the pages of Sincerity is a Goddess.
Part VI – Doctors in the Roman Empire

A doctor making a house call.
Going to the doctor’s office is never something one looks forward to.
For most, myself included, it gets the heart rate and stress levels up to step into a building that’s full of ‘sick people’. With our modern plague, I’m sure many of us are feeling that.
Sitting around in a waiting room with a group of scared, nervous, fidgety folks, is enough to drive you mad, and the sight of a white coat and stethoscope makes one want to run screaming from the building.
In a way, it was probably the same for our ancient Greek and Roman ancestors. Most civilians would have been loath to visit with a physician. It might not have been someone you wanted around, unless absolutely necessary.
When it comes to physicians in the Roman Empire, it has to be said that many, if not most, were Greek, and that’s because Greece was where western medicine was born. Indeed, the ancient Greeks had patron gods of health and healing in the form of Asklepios, Igeia, and sometimes Apollo.

Artist rendering of the Asklepion of Kos
The greatest medical school of the ancient world was in fact on the Aegean island of Cos, where students came from all over the Mediterranean world to learn at the great Asklepion. Hippocrates, the 5th century B.C. ‘father of medicine’, was from Cos and said to be a descendant of the god Asklepios himself.
When it comes to Roman medicine, much of it is owed to what discoveries and theories the Greeks had developed before, but with a definite Roman twist.

Hippocrates
The fusion of Greek and Roman medicine in the Roman Empire consisted of two parts: the scientific, and the religious/magical.
The more scientific thinking behind ancient medical practices is a legacy owed to the Greeks, who separated scientific learning from religion. The religious, or rather superstitious, aspects of medicine in the Roman Empire were a Roman introduction.
Because of this fusion of ideas and beliefs, you could sometimes end up with an odd assortment of treatments being prescribed.
A Roman physician blood letting (by Robert Thom, c. 1958)
To alleviate your anxiety over your new business venture, you should take three drops of this tincture before you sleep. You should also sacrifice a white goat to Janus as soon as possible.
Many Roman deities had some form of healing power so it depended on one’s patron gods, and the nature of the problem, as to which god would receive prayers or votive offerings over another. Amulets and other magical incantations would have been employed as well.

Roman surgical instruments
Romans had a god for everything, and soldiers were especially superstitious.
Much of Greek medical thought opted for practicality in the treatment of wounds, and injuries; cleaning and bandaging wounds would have been more logical than putting another talisman about the neck. That said, let us not forget the aspect if divine intervention when it came to some aspects of healing in such places as Epidaurus.
All the gods were to be honoured, but in the Greek physician’s mind they had much better things to look after than the stab wound a man received in a tavern brawl.
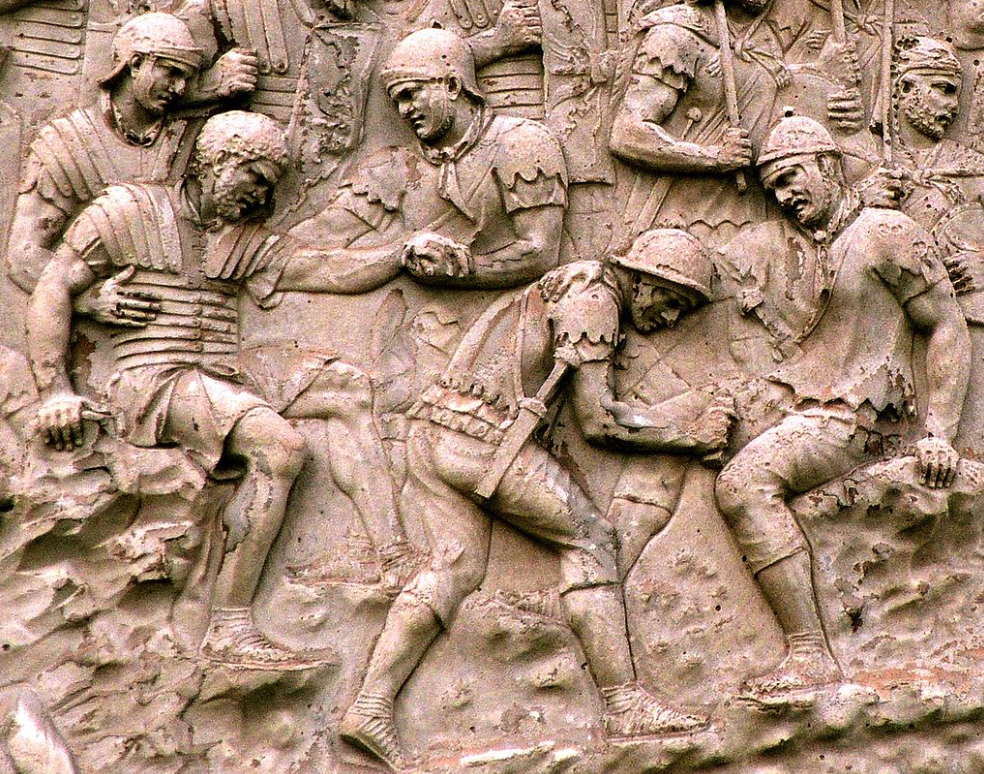

Battlefield medics treating wounded soldiers on Trajan’s Column
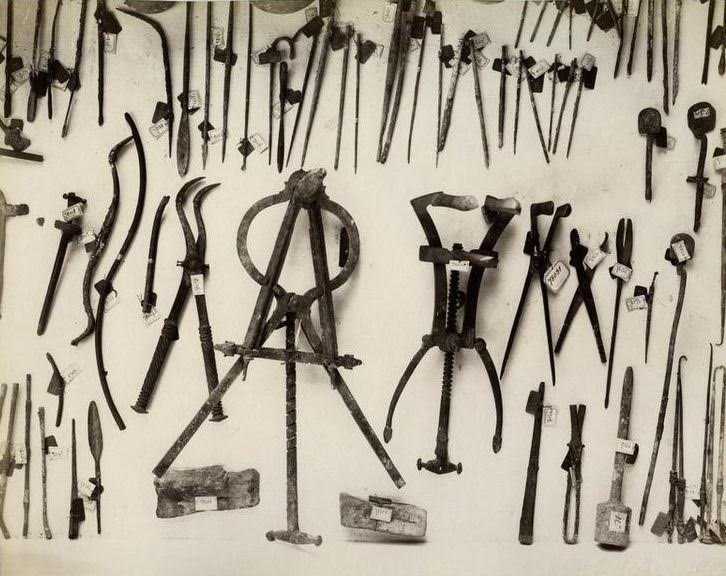
For the battlefield medicus, things must have been much simpler than for the physician who was trying to diagnose mysterious ailments for someone in the heart of Rome. They were faced mostly with physical wounds and employed all manner of surgical instruments such as probes, hooks, forceps, needles and scalpels.
Removing a barbed arrowhead from a warrior’s thigh must have required a little digging.
Of course, in the Roman world, there was no anaesthetic, so successful surgeons would have had to have been not only dexterous and accurate, but also very fast and strong. Luckily, sedatives such as opium and henbane would have helped.
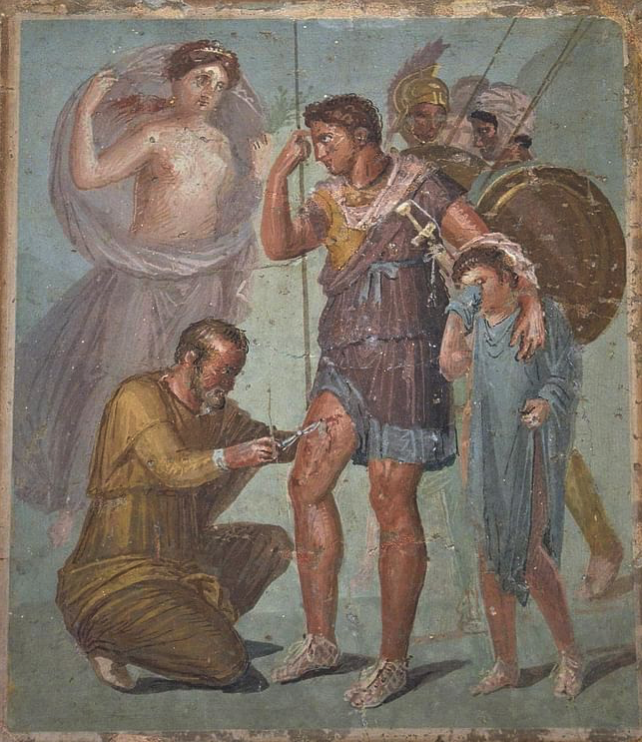

Medic helping a warrior tend a wound
When it came to the treatment of wounds, a medicus would have used wine, vinegar, pitch, and turpentine as antiseptics. However, infection and gangrene would have meant amputation. The latter was probably terrifyingly frequent for soldiers, many of whom would end up begging on the streets of Rome.
It is interesting to note that medicine was one of the few professions that were open to women in the Roman Empire. Female doctors, or medicae, would also have been mainly of Greek origin, and either working with male doctors, or as midwives specializing in childbirth and women’s diseases and disorders. When it came to the army however, most doctors would have been male.

Ancient surgical instruments, including forceps
Army surgeons played a key role in spreading and improving Roman medical practice, especially in the treatment of wounds and other injuries. They also helped to gather new treatments from all over the Empire, and disseminated medical knowledge wherever the legions marched. Many of the herbs and drugs that were used in the Empire were acquired by medics who were on campaign in foreign lands.
Early on, physicians did not enjoy high status. There was no standardized training and many were Greek slaves or freedmen. This began to improve, however, when in 46 B.C. Julius Caesar granted citizenship to all those doctors who were working in the city of Rome.
This last point really hits home when it has become common knowledge that foreign doctors who come to our own countries today find themselves driving taxis or buses because they are not allowed to practice.
Modern governments, take your cue from Caesar!

Galen
One of the most famous physicians of the Roman Empire is Galen of Pergamon (A.D. 129-c.199). Galen was a Greek physician and writer who was educated at the sanctuary of Asklepios at Pergamon in Asia Minor.
After working in various cities around the Empire, Galen returned to his home town to become the doctor at the local ludus, or gladiatorial school. He grew tired of that work and moved to Rome in A.D. 162 where he gained a reputation among the elite. He subsequently became the personal physician of the Emperors Marcus Aurelius, Commodus, and for a short time, Septimius Severus.
Galen’s work and writings provided the basis of medical teaching and practice on into the seventeenth century. No doubt many an army medicus referred to Galen’s work at one point or another.
Galen is also an important character in A Dragon among the Eagles, the prequel in the Eagles and Dragon series. In the book, Galen, an old friend and colleague of Lucius Metellus’ late tutor, presents Lucius with a choice that could well change the direction of Lucius’ life. In fact and fiction, Galen is a fascinating person of history.
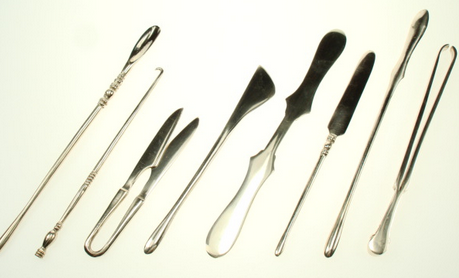
Re-created ancient surgical instruments
There was, of course, a difference between medical procedures that were frequently carried out on civilians in Rome versus what was needed on the battlefields of the Empire.
I’m not an expert in ancient medical history, but I do know that the level of injury on an ancient battlefield would have been staggering. The sight or sound of your unit’s medicus would have been something sent from the gods themselves.
Imagine a clash of armies – thousands of men wielding swords, spears and daggers at close quarters. Then lob some volleys of arrows into the chaos. Perhaps a charge of heavy cavalry? How about heavy artillery bolts or boulders slamming into massed ranks of men?

Roman Legionaries (illustrated by Peter Dennis)
It would have been one big, bloody, savage mess.
Apart from the usual cuts, slashes, and puncture wounds, the warriors would have suffered shattered bones, fractured skulls, lost limbs, severed arteries, sword, spear and arrow shafts that pushed through armour on into organs.
If you weren’t dead right away, you most likely would have been a short time later.
This is where the ancient field medic could have made the difference for an army. He would have been going through numerous patients in a short period of time. He would have had to decide who was a lost cause, who could no longer fight, and who could be patched up before being sent back out onto the field of slaughter.
The medicus of a Roman legion was an unsung hero whose skill was a product of accumulated centuries of knowledge, study, and experience.

Model showing Tiber Island
When it came to ancient Rome, the centre of health and healing was Tiber Island, and its foundation has a most fascinating story…
Tiber Island is a boat-shaped mass in the middle of the River Tiber where it runs through Rome. It was connected to the Field of Mars by the Pons Fabricius, and to the right bank, where modern Trastevere is, by the Pons Cestius.
The legend goes that the island was formed when, after the fall of the Etruscan tyrant, Tarquinius Superbus, in 510 B.C., the angry Romans threw his body into the Tiber where silt subsequently formed around it.
Another legend is that after the same tyrant died, the people hated him so much that they took all of his grain stores and threw it all into the river where it became the island.
Sic semper tyrannis, as the Romans would say…

Tarquinius Superbus
Whatever the reason for the creation of Tiber Island, it seems that it was, early on, a place to be avoided as it was where criminals and the terminally ill were sent.
The story gets very interesting in 293 B.C. when a great plague hit Rome.
When the plague arrived, the Senate consulted the Sibyl, the Oracle of Apollo at Cumae, who told the Romans that they should build a temple to Aesculapius (Asklepios in Greek) in the city of Rome.
A delegation of Romans was sent to Epidaurus where Aesculapius’ most famous sanctuary was located, so that they could obtain a statue of the god for the proposed temple.
The delegation also obtained one of the sacred snakes from Epidaurus.

Aesculapian Snake – zemenis longissimus (Wikimedia Commons)
The story goes that as soon as the delegation returned to their ship with the statue and sacred serpent, the snake immediately curled itself about the main mast for the return journey to Rome. They took this as a good omen.
When the ship sailed down the Tiber and entered the city of Rome, the snake moved, slithered off of the ship into the water, and swam to Tiber Island where it settled itself.
The Romans took it as a sign that this was where they should build the temple of Aesculapius.
Since that time, Tiber Island has been identified with that ship, and even modelled to resemble it with travertine facing forming it to look like a ship’s prow and stern in the first century B.C., and an enormous obelisk erected to represent the mast of the ship that brought the statue and sacred serpent to Rome from Greece.
One can still see the carving of Aesculapius’ rod and serpent on the ship’s prow to this day!

Carving of the serpent and rod on the ‘prow’ of Tiber Island
In time, other shrines were built on Tiber Island such as to Jupiter Jurarius (Guarantor of Oaths), Semo Sancus Dius Fidius (Witness of Oaths), Faunus (the spirit of Boundaries), Vediovis (God of Healing), Tiberinus (the River God), and to Bellona (Goddess of War).
There was also a festival of Aesculapius and Vediovis every year on the first of January.
Just as it is today, good health was important to the Romans!
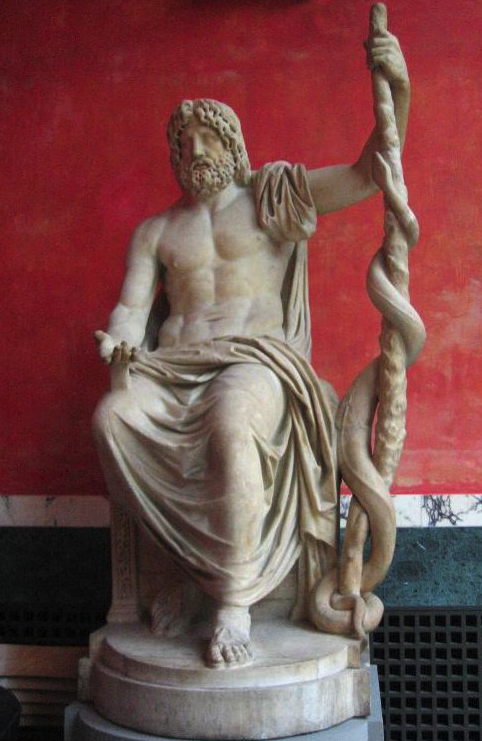

Statue of Aesculapius (Asklepios)
With the establishment of the sanctuary of Aesculapius on Tiber Island, the healing practices of Epidaurus were brought to Rome, including the use of the sacred snakes which were, it is believed, the species known as zemenis longissimus, a non-venomous serpent that could grow up to two meters in length.
The doctors also employed the use of sacred dogs whose licks were said to be healing for some patients. It is not surprising, I suppose, considering that some dogs can sniff out cancer, or restore circulation to injured limbs through licking.
Do the practices of the doctors of Tiber Island actually work in the story of Sincerity is a Goddess? Well, you have to read the book to find out. There is, we can say with certainty, a bit with a dog, a doctor with some interesting prescriptions, healing dreams, votive offerings, and a connection between Rome and ancient Epidaurus that is certainly felt on a deep level.

Votive fingurine of a ‘healing dog’ (Museum of Wales)
I’ve but barely scratched the vast surface on this topic.
For some, there is this assumption that ancient medicine was somehow false, crude and barbaric. But modern western medicine owes much to the Greeks and Romans, civilian and military, who travelled the Empire caring for their troops and gathering what knowledge and knowhow they could.
The fusion of science, religious practice, and magic provides for a fascinating mix. In truth, medical practices in medieval Europe were more barbaric than in the ancient world.
We owe much to the followers of Aesculapius and the traditions that flowed from ancient Epidaurus to the heart of Rome where there is still a working hospital on Tiber Island.
Part VIII – The Theatre of Pompey
When designing a theater, you should include porticoes behind the stage to house the audience when a sudden downpour disrupts the performances, and to provide some open space for the preparation of stage sets. The Pompeian Portico is an example of this.
(Vitruvius, Architecture 5.9.1)
In a previous post in this blog series, we already discussed the history of theatres in ancient Rome and how they started out as temporary wooden stages set up for festivals, only to be torn down at the end of the show. If you missed that post, you can read it HERE.
The Theatre of Pompey, or the Theatrum Pompeii, is different in that it changed the game, so to speak. Its creation not only gave theatre its first permanent home in ancient Rome, but it also changed the architecture and purpose of theatres in general, an influence that can still be felt to this day!

Theatre of Mytilene that inspired Pompey
The Theatre of Pompey was, of course, built by the general and politician Pompey the Great, a contemporary of Julius Caesar who had also been married to Caesar’s daughter, Julia.
In 62 B.C. it is said that on a visit to the island of Mytilene (Lesvos), Pompey was inspired by the theatre there. He was in his second consulship and so, to solidify his popularity he conceived of the idea of building a permanent theatre for the people of Rome.
However, Roman law forbid the building of stone theatres within the pomerium, the sacred boundary of the city of Rome. So, Pompey decided to build his theatre in the ager Romanus, the area outside the boundary of the pomerium, on the Campus Martius, the Field of Mars.
Construction is said to have begun around 61 B.C. with the theatre being completed around 55 B.C.
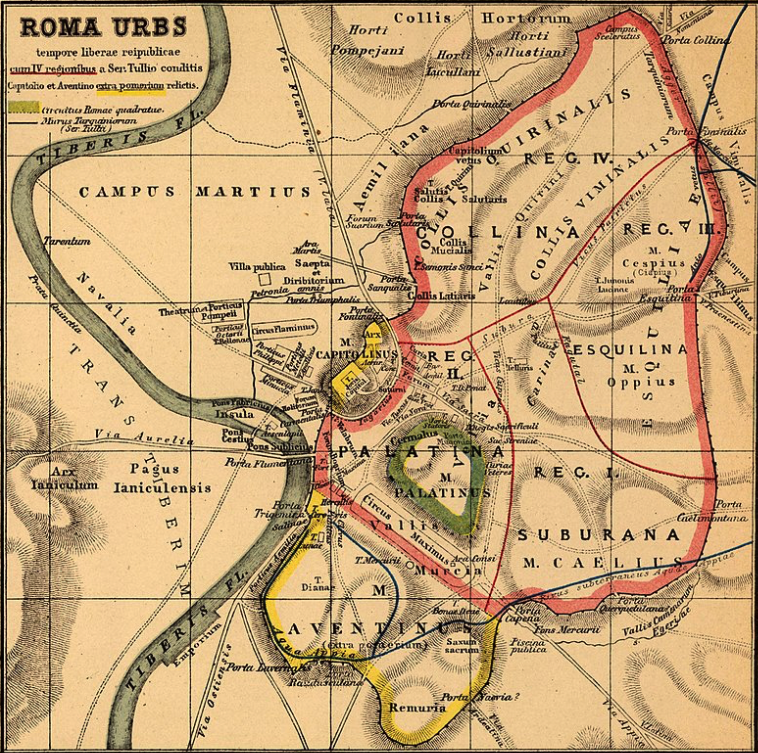
Map of Republican Rome with the borders of the Pomerium in pink.
Despite building outside of the pomerium, there were still some conservative parties who opposed the construction of a permanent theatre.
Pompey, cunning general that he was, further circumvented the law against theatres by making the theatre itself a sort of substructure for the temple of his patron goddess, Venus Victrix. Opposite the stage at the top of the cavea, the auditorium, Pompey built a magnificent temple to the goddess. The seats of the auditorium, which had a capacity for well over 22,000 people, provided the steps leading up to the temple!
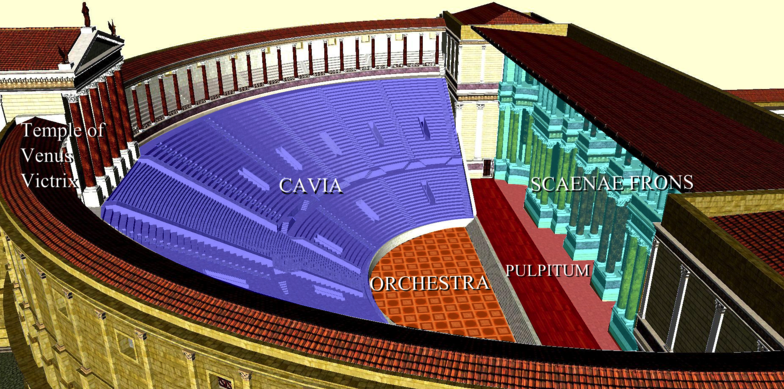
Digital reconstruction of the Theatre of Pompey (Wikimedia Commons)
Now that the structure was mainly a structure dedicated to the goddess Venus herself, none could dare oppose its construction! The Christian writer, Tertullian, writes about this:
I especially wish to demonstrate for other Christians how those traditional spectacles of Roman entertainment are not compatible with the true religion and the true worship of the one true God.…
Let us consider the true nature of theatrical entertainment, beginning with the vice inherent in its setting. The theater, rightly seen, is a shrine to Venus. Indeed, this type of building came into the world in the name of Venus. For originally, even the heathen censors were concerned to destroy theaters as quickly as they arose, foreseeing the serious moral damage that would result from the licentious spirit of the theater.… Because of this attitude, when Pompey the Great (only his theater was greater than he!) had constructed that citadel of every vice and was afraid that because of this his memory might one day suffer from official censure, he added on to his theatre a temple to Venus, and when he summoned the people to the dedication, he did not call the structure a theatre, but a temple “to which we have added,” he said, “some seating for shows.”
(Tertullian, Pagan Entertainments 1, 10)
Rome had received its first, permanent, stone theatre complete with a large, wide stage, or pulpitum, aulaeum, the curtain that rose out of the ground before the stage, and a towering decorative scaena frons which provided the backdrop for performances, complete with doorways for the plays, and niches with statues above.
The Theatre of Pompey had it all!
According to the sources, the performances that were put on as part of the theatre’s dedication were Accius’ Clytemnestra, and Equos Troianus by either Andronicus or Naevius. It was a big event, such that the famous actor Clodius Aesopus was brought out of his retirement to perform in the opening show which was, of course, accompanied by gladiatorial matches with exotic animals. It was Rome, after all!
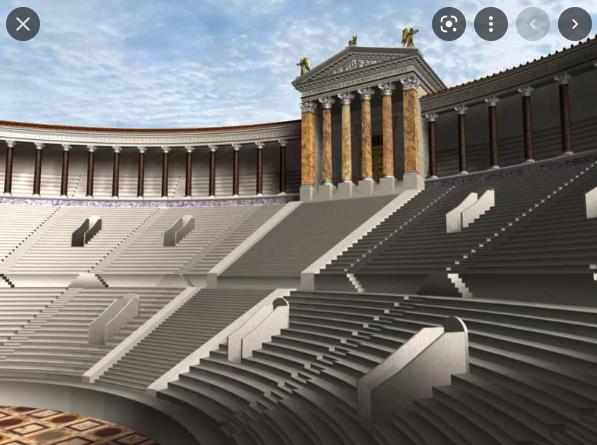

Digital Recreation of the temple of Venus Victrix at the top of the auditorium.
The Theatre of Pompey, however, was much more than a theatre, or a temple for that matter. It was an entertainment and administrative complex where the elite of Rome could meet, and where citizens could gather. It was something of an oasis in the city of Rome. Even poets praised its beauty…
Why, Cynthia, do you flee the city for smaller towns nearby?
I suppose the Portico of Pompey, with its columns of shade
And tapestries of threaded gold, seems squalid to you,
With its solid rows of plane trees shaped to an even height,
The streams of flowing water that slide off the Slumbering Satyr,
And the liquid sounds of splashing around the entire basin
When Triton suddenly blows the water from his mouth.
(Propertius, Elegies 2.32.11-16)
Connected to the theatre was a large area known as the quadriporticus which comprised an enormous area of groomed gardens with magnificent statues and fountains surrounded by columned porticoes.
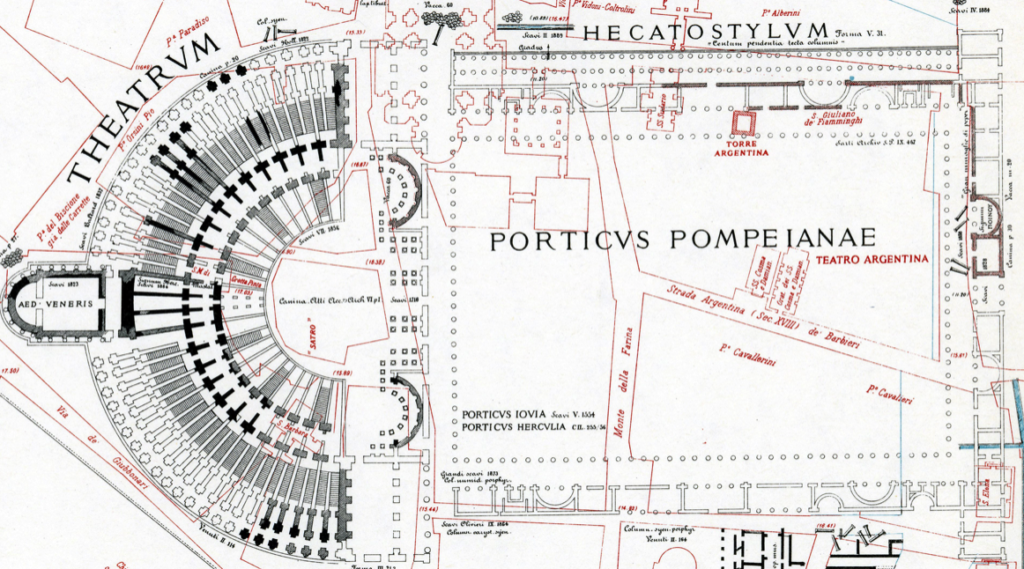
Architectural plan of the theatre and quadriporticus of the complex.
Outside the far end of the quadriporticus, opposite the theatre, another temple complex was incorporated. This sacred area included more ancient temples to Juturna (A – 241 B.C.), the Aedes Fortunae (B – 101 B.C.), Feronia (C – 4th century B.C.), and the Lares Permarini (D – 2nd century B.C.).
As was often the case in ancient Rome, religious belief was a part of the everyday, including theatre.
Republican-era temples in the sacred area at the far end of the quadriporticus. (Wikimedia Commons)
As we mentioned, Pompey’s wonderful theatre complex was much more than an entertainment and social venue. It was also an administrative centre.
In fact, included in the complex of the quadriporticus was the Curia of Pompey. This meeting space was sometimes used as a place for the Senate of Rome to meet.
This is exactly what was happening on March 15th, 44 B.C.
Because of work being done on the Senate house in the Forum Romanum, the Senate of Rome was meeting in the Curia of Pompey. It was a day that would shake the Roman world, and set off another bloody civil war.
As Julius Caesar arrived at the Curia of Pompey for the meeting of the Senate, he was surrounded by a conspiring group of Roman senators and murdered.
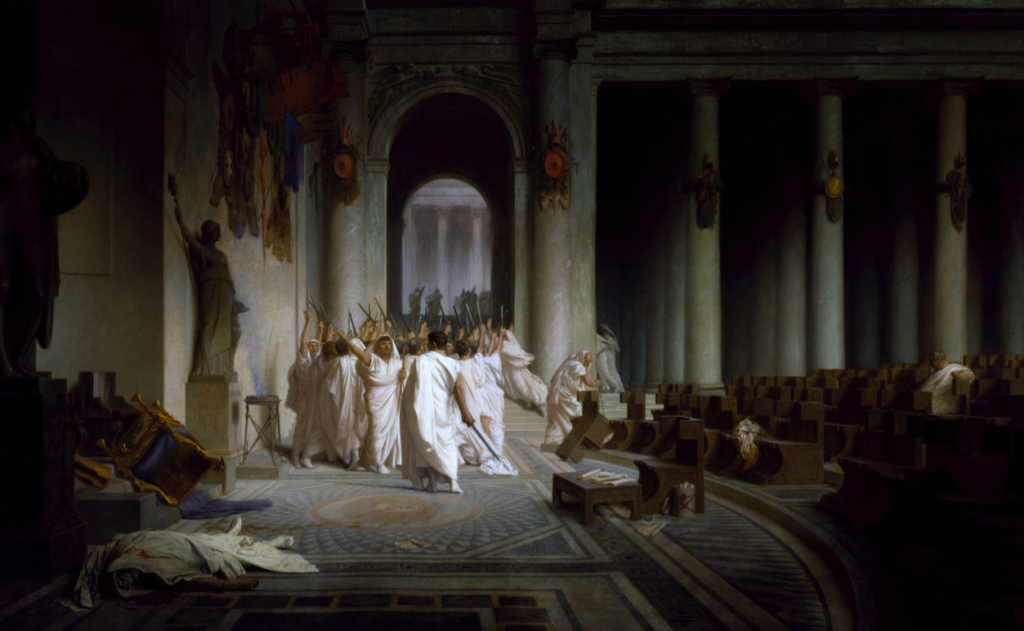

The Death of Caesar (Jean-Léon Gérôme, 1867)
The scene itself of Caesar’s death-struggle and assassination later made it clear to all that some spirit-power [daemon] had taken the event in hand to bring it about. For the meeting-site of the senate that day contained a statue of Caesar’s late rival Pompey, which Pompey himself had dedicated as one more ornament to his theater.…
(Plutarch, Caesar 66.1, 3-7)
The Ides of March were burned into the historical timeline from then on, and it happened at the temple and theatre complex built by Caesar’s one-time friend, son-in-law, and enemy, Pompey the Great.
The Theatre of Pompey had a long and storied history. It saw tragedy, comedy, beauty and bloody murder, and for forty years it was the only permanent theatre in Rome.
Eventually other theatres, such as the Theatre of Balbus (13 B.C.) were built around the Theatre of Pompey, seeking to enliven themselves by proximity to the latter’s splendour. This created a sort of theatre district in ancient Rome, and the Theatre of Pompey was at its heart.
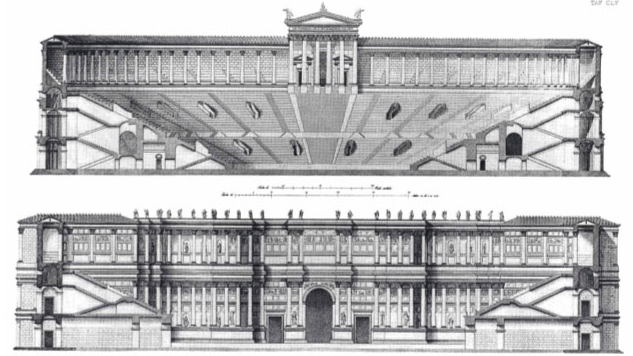
Artist impressions of the cavea (auditorium) with the temple at the top, and of the pulpitum and scaena frons (the stage and stage house).
The building of the Theatre of Pompey in ancient Rome was a turning point in theatre history, for it gave wider acceptance to theatrical performance, as well as a permanent home.
Theatrical groups from across the Roman world, including our fictional Etrurian Players, saw performing in that great place as the pinnacle of their careers, similar to artists getting to perform in places such as La Scala, Royal Albert Hall, or Carnegie Hall today.
The Theatre of Pompey also gave theatre complexes a much broader role in society which not only included that of a religious centre and entertainment venue, but also as an administrative centre, and an attractive public space. The latter is certainly something that is still holds true to this day in modern theatre settings.

The Tom Patterson Theatre in Stratford, Ontario carries on the tradition of a theatre that is also a public space and gardens in an urban setting.
In Sincerity is a Goddess, as one of the major settings, the Theatre of Pompey plays a crucial role in the story and in the lives of the players who are destined to perform there.
As in fact and fiction, there is history in that place, and it is keenly felt by all.
Part IX – Plautus: Playwright of the Roman People
In misfortune if you cultivate a cheerful disposition you will reap the advantage of it.
– Plautus
Sincerity is a Goddess was always intended to be a comedy that involved the production of a play, but in the initial stages of research, one of the very first questions I had to pose myself was “What play?”
A lot hinged on the choice. Of course, when one thinks of ancient playwrights, one inevitably thinks of the great Greek playwrights, Aeschylus, Aristophanes, Euripides and others. But I knew that I wanted to use a Roman playwright’s work for this dramatic and romantic comedy, and so the choice inevitably came down to one between Terence and Plautus, the great comic playwrights of Republican Rome whose work was based on Greek New Comedy and subjects dealing with ordinary family life, love, and hilarity.
Terence’s plays are full of feeling. They are tender.
However, Plautus’ plays tended to be more comic and raucous with lots of music, songs, and duets that keep the audience at a distance. One might say that, in his time, Plautus had more popular appeal with the Roman people.
And so, I chose Plautus and his Menaechmi.

Titus Maccius Plautus (c. 254 – 184 B.C.)
Let deeds match words.
-Plautus
Who was Titus Maccius Plautus?
Let’s take a brief look at the man and his origins.
Plautus, who later became the great Roman comedy writer we know of, was originally from Sarsina, a town in northern Italy in Emilia-Romagna.
Early in his life, he moved to Rome where it is believed he worked at a trade in the theatre, either as a stage carpenter or scene-shifter. He also made money at some form of business, perhaps to do with shipping, but that business went under. He also worked as a baker, apparently.
The second century A.D. writer, Gellius, gives us some hints about Plautus’ life before fame:
Now there are in circulation under the name of Plautus about one hundred and thirty comedies; but that most learned of men Lucius Aelius thought that only twenty-five of them were his. However, there is no doubt that those which do not appear to have been written by Plautus but are attached to his name, were the work of poets of old but were revised and touched up by him, and that is why they savour of the Plautine style. Now Varro and several others have recorded that the Saturio, the Addictus, and a third comedy, the name of which I do not now recall, were written by Plautus in a bakery, when, after losing in trade all the money which he had earned in employments connected with the stage, he had returned penniless to Rome, and to earn a livelihood had hired himself out to a baker, to turn a mill, of the kind which is called a “push-mill.”
(Aulus Gellius, Attic Nights)
Luckily, his exposure to theatre is what got hold of him, and it seems that he began to write…and write…and write. We may not know much about Plautus’ personal life, but we are very fortunate indeed that much of his catalogue of plays survived the ages.

Plautine manuscript from 1530
Plautus wrote verse comedies, or fabulae palliatae which were based on Greek New Comedy, and he achieved huge success.
The plays of Plautus are the first substantial surviving written works in Latin and, no doubt thanks to the fact that they were so popular, they were copied frequently.
We know little about the man himself. Some hypothesized that even his name was not his true name and that ‘Maccius’ was actually a corruption of ‘Maccus’ the clown character in the Atellan farces, and that ‘Plautus’ meant ‘flat-foot’, referring to a character in the mimes. However, how many artists use stage names or pseudonyms? Lots, I’d say.
Though Plautus the man may be a mystery, we do know much about his extensive catalogue of works. It is not known exactly how many plays he wrote, but 21 have survived in their entirety, and there are fragments or mentions of an additional 30. In the quote above, Gellius alludes to many more as a possibility.
The metres of Plautus’ verse combined Greek metrical patterns with the stress patterns of the Latin language when spoken. But he went beyond simple translation.
Plautus adapted plays from Greek instead. He added much more music and songs, or cantica, like opera arias, then was normal in New Comedy. The performances were perhaps more like modern musicals which, in turn, partially owe their existence to Plautus’ work. Just think of A Funny Thing Happened on the Way to the Forum, by Stephen Sondheim. That musical is basically a great homage to Plautus!
Plautus’ plays appealed to Roman audiences because they presented a Latinized glimpse of Greek sophistication and outrageous behaviour that was outside of the audience’s experience. After all, theatre should be an escape!
Not by age but by capacity is wisdom acquired.
– Plautus
Plautus’ plays lacked the characterization and refinement of Greek New Comedy. His humour was more about jokes, verbal tricks, puns and alliteration that delighted the audience. He mastered the use of vulgarity, humour, and incongruity.
His stock characters were influenced by the Attelan farces, and included slaves, concubines, soldiers, and doddery old men. He created the ‘clever slave’ which would, in time, come to be known as a ‘Plautine Slave’. Often, the slave was smarter than his master, and even compared to a hero.
The plays involved everything from love and misunderstanding, to ghosts, rogues, tricksters, and braggarts who get humiliated in the end. Plautus only wrote one play based on myth, his Amphitruo. The rest of his plays portray the lives of more everyday people who his audiences could, more or less, relate to.
The Menaechmi itself is a comedy of errors about twins separated in infancy, in a Greek setting with numerous Roman references.
Not only did Plautus adapt Greek plays, he expanded on them and modified them in such a way that he made Greek theatre Roman!
Because he was a man of the people, having experienced their same toils, Plautus’ plays touched a nerve that made them extremely popular. They were performed for centuries after his death, well into the Renaissance, and his work was extremely influential on such greats as William Shakespeare (Comedy of Errors) and Moliere, who made use of many Plautine elements.
Like many comedians to this day, however, Plautus was not immune to criticism. Playwrights have always been rebels. The more conservative elements in Rome accused him of disrespecting the gods because his characters were sometimes compared to the gods either in mockery or praise. Sometimes, his characters even scorned the gods!
Some believe that Plautus was simply reflecting the changing tide of Roman society. He may have been controversial, but not enough to ban or prosecute him. Roman politicians were always keenly aware of the mood of the mob.

Artist impression of the Second Macedonian War
Conquered, we conquer.
-Plautus
War is a subject that seems constant throughout history. We are certainly aware of it today (sadly), as were Plautus and the Roman people.
During Plautus’ lifetime, the Roman people endured three great wars: the Second Punic War against Hannibal, and the First and Second Macedonian Wars against Philip V and Greece.
With the Second Punic War, the Roman Republic and people were fighting for their lives with the enemy being literally at their gates at one point. When it finally ended, they were exhausted by war, tired of it.
When certain powers in Rome wished to wage a successive war on Greece and Philip V of Macedon, the Roman people were not as supportive, and Plautus reflected these popular, anti-war sentiments in his plays such as Miles Gloriosus, and Stichus.
Many Romans did not want another war, and Plautus championed them in a way by giving voice to their anti-war voices and touching on themes of economic hardship forced on the citizens by the wars.
Sounds strangely familiar to us today, doesn’t it?
One could say that the greatest contribution of Plautus’ work, his genius even, was to take up the cause of the average Roman through comedy.
He was saying that the state should take care of its suffering people at home before undertaking military actions abroad.
We should bear in mind too that at this time in Roman history, when the Roman Republic was expanding and gathering power, Roman theatre was still in its infancy.
Plautus broke new ground in Rome. He made the people laugh, but he also gave them an important voice.
Since he has passed to the grave, for Plautus Comedy sorrows;
Now is the stage deserted; and Play, and Jesting, and Laughter,
Dirges, though written in numbers yet numberless, join in lamenting.
– Epitaph for Plautus, attributed to Plautus by Gellius and Varro
We have but scratched the surface of Plautus’ life and plays. Little more is known of him personally but, as with any writer, we can perhaps discern something of the man from the stories he put into the world.
There can be no doubt that the Roman world mourned his death on some level, as is attested by the moving epitaph shared by his fellow writers.
In a sense though, because so much of his work has survived time, and continues to be performed, to influence other art, Plautus is perhaps one of the most immortal of Romans.

Renaissance representation of Plautus
The plays of Plautus are fun to read, even today, and I would encourage you to delve into them.
For my part, I truly enjoyed reading and re-reading the Menaechmi, and by incorporating it into Sincerity is a Goddess, by diving deep into the study of it, it has given me a new and wonderful insight into Roman theatre, and the man who was truly the playwright of the Roman people.
Thank you for reading.
Well, that is the end of The World of Sincerity is a Goddess. The curtain has fallen (or risen out of the ground, as was the case in Roman theatres!).
We hope you have enjoyed this blog series, and that you enjoy Sincerity is a Goddess if you read it. If you have read it, please leave a review on the Eagles and Dragons Publishing website or on the store where you purchased the book. Reviews are a wonderful way for new readers to find this dramatic and romantic comedy of ancient Rome!
Sincerity is a Goddess is available in hardcover, paperback, and ebook from all major online retailers, independent bookstores, brick and mortar chains, and your local public library.
CLICK HERE to buy a copy and get ISBN#s for the edition of your choice.