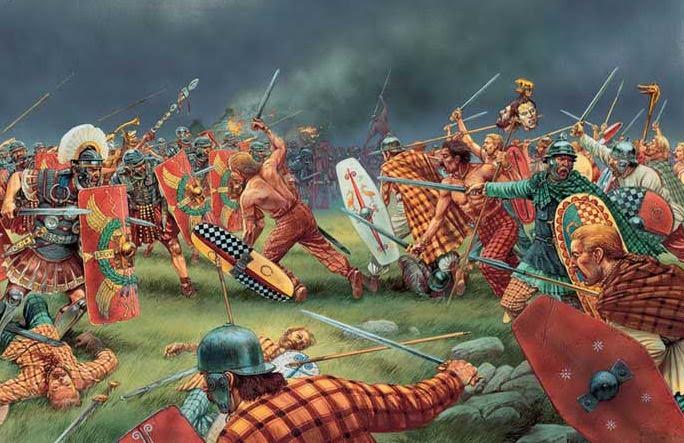
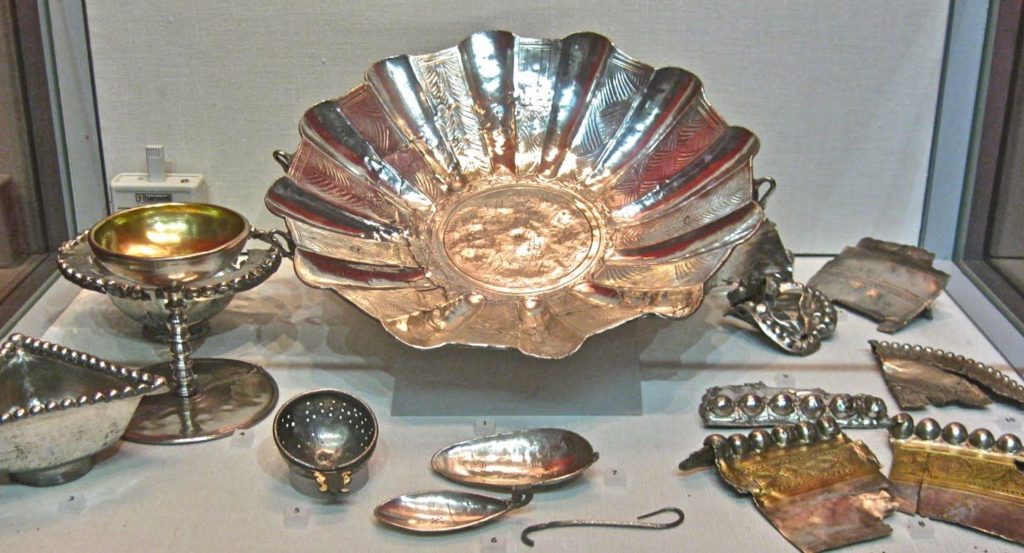
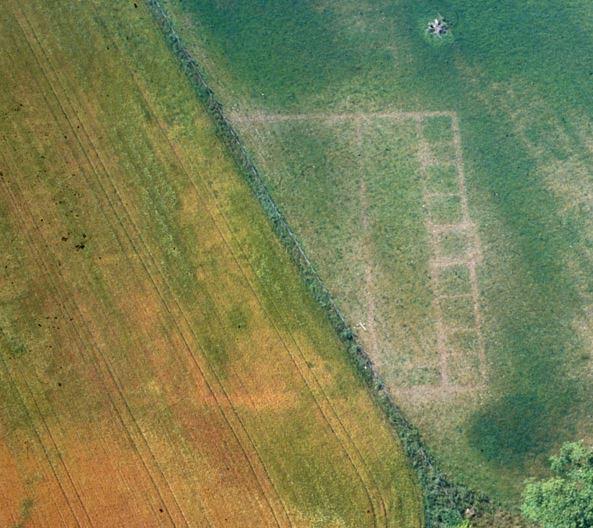
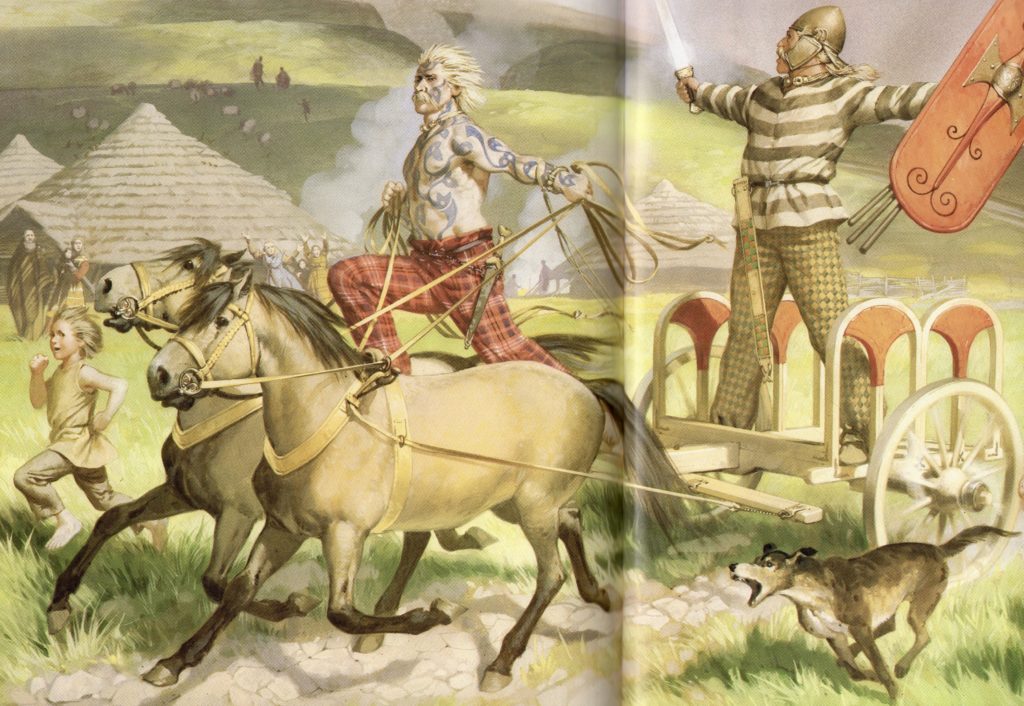
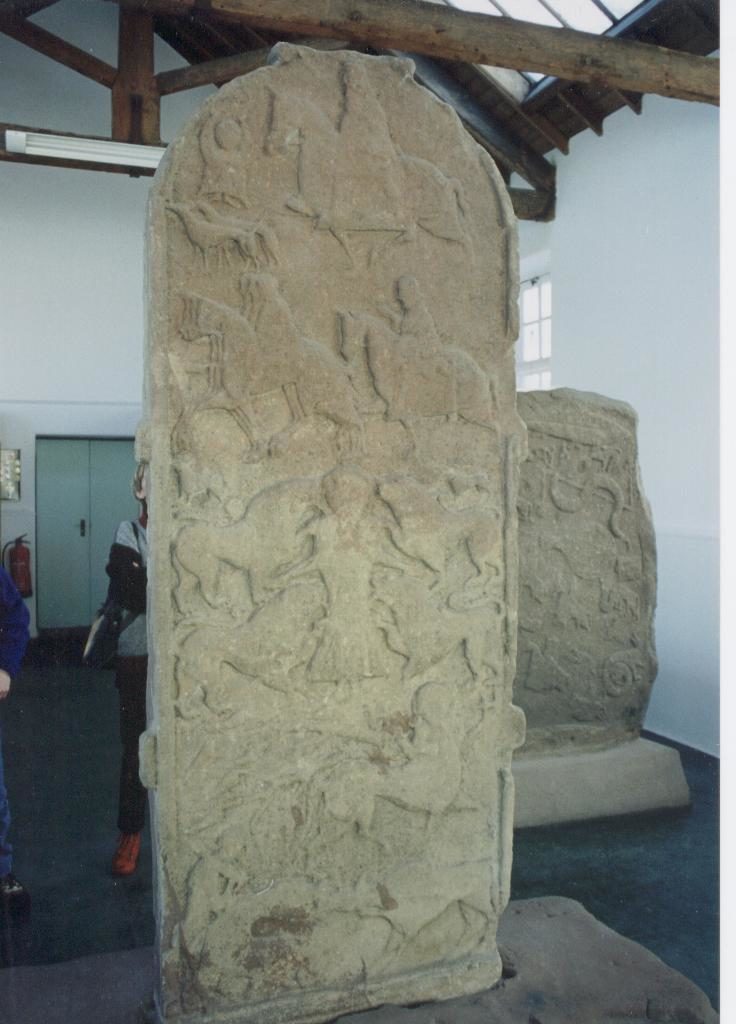
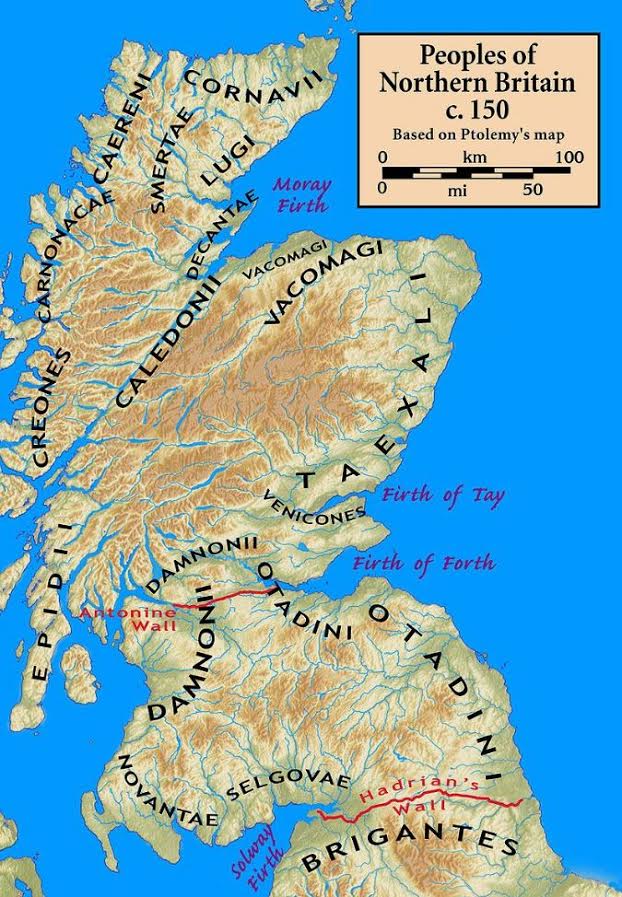
Warriors of Epona is set against the backdrop of the Severan invasion of Caledonia (modern Scotland). It was a massive campaign, and Rome’s last major attempt at subduing the tribes north of the Antonine Wall.
However, this was not the first time Rome had attempted to invade Caledonia. In fact, Septimius Severus’ legions were using the infrastructure of previous campaigns into this wild, northern frontier.
In this fifth and final part of The World of Warriors of Epona, we’re going to look briefly at the Roman actions in Caledonia prior to and including the campaigns of Emperor Septimius Severus.
The full scale conquest of Britannia was undertaken in A.D. 43 under Emperor Claudius, with General Aulus Plautius leading the legions. Campaigns against the British tribes continued under Claudius’ successor, Nero in A.D. 68.
The conquest of the South of Britain involved overcoming the tribes, including Boudicca and the Iceni, the Catuvellauni, the Durotriges, the Brigantes, and others, and the attempted extermination of the Druids on the Isle of Anglesey.
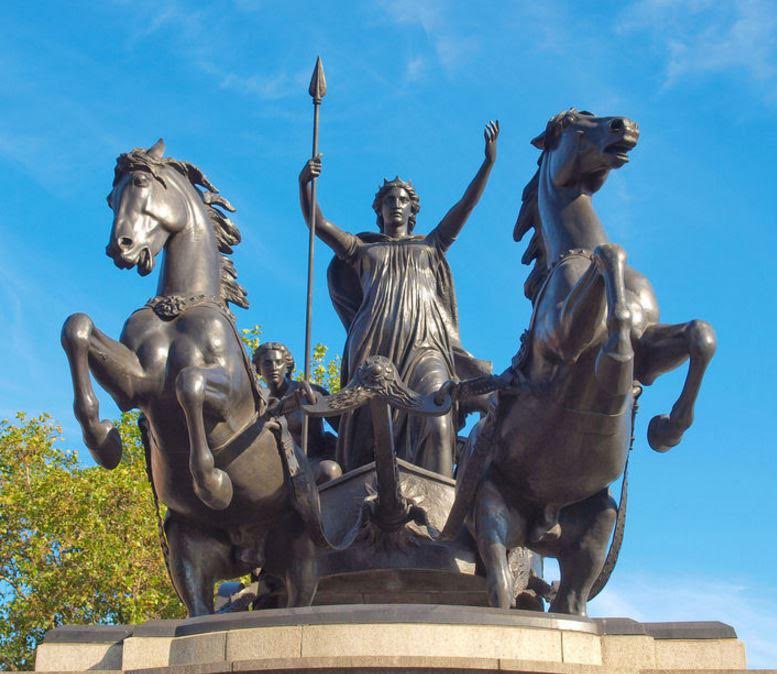

Boudicca
Eventually, after much blood and slaughter, the South was subdued, and the Pax Romana began to take root in that part of Britannia. (It pains me to gloss over so large a part of the history of Roman Britain, but we’re talking about Caledonia here…)
It was not until A.D. 71 that Rome decided it was time to invade Caledonia, and the man assigned this task was Quintus Petillius Cerialis, a veteran of the Boudiccan Revolt, and governor of Britannia at that time.
Once Cerialis’ legions were able to break through the Brigantes, it was time to press north into Caledonia.
The person who is most associated with these initial campaigns in Caledonia is none other than Gnaeus Julius Agricola, who had served in the campaigns against Boudicca in the South and who was also governor of Britannia from A.D. 77-85.

Agricola – Statue at Roman Baths, Bath, England
In around A.D. 80, Emperor Titus (A.D.79-81) ordered Governor Agricola to begin the campaigns into Caledonia by consolidating all of the lands south of the Forth-Clyde (roughly between Edinburgh and Glasgow). This involved taking on the tribes of the Borders, including the Selgovae, Maeatae, Novantae, and Damnonii.
It is in during this campaign that the fort at Trimontium, and many others were established in the Borders.

Commemorative stone at Newstead, in the Scottish Borders
By A.D. 81, Emperor Domitian had decided to order Agricola and his legions into Caledonia, and within two years, Agricola is said to have brought the Caledonians to their knees at the Battle of Mons Graupius.
He [Agricola] sent his fleet ahead to plunder at various points and thus spread uncertainty and terror, and, with an army marching light, which he had reinforced with the bravest of the Britons and those whose loyalty had been proved during a long peace, reached the Graupian Mountain, which he found occupied by the enemy. The Britons were, in fact, undaunted by the loss of the previous battle, and welcomed the choice between revenge and enslavement. They had realized at last that common action was needed to meet the common danger, and had sent round embassies and drawn up treaties to rally the full force of all their states. (Tacitus, Agricola; XXIX)
The Roman historian, Tacitus, was actually Agricola’s son-in-law, and his account, De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae, provides us with the best first-hand account of Agricola and his invasion of Caledonia.
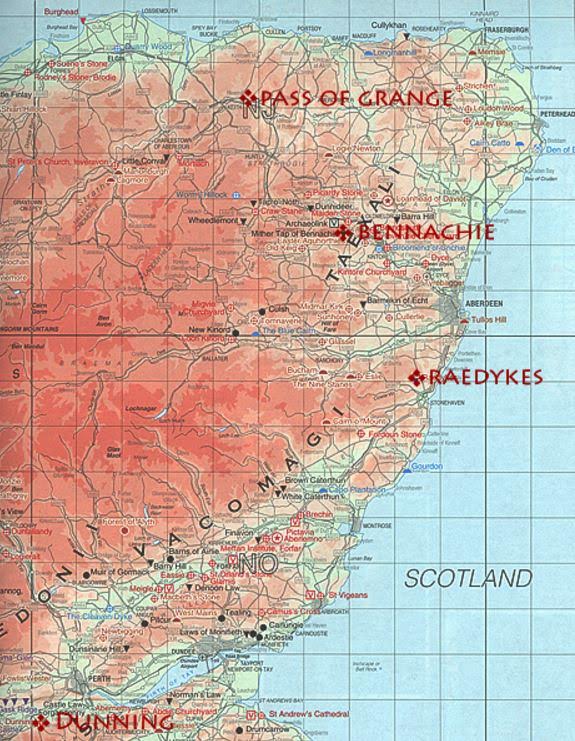
Possible locations for Battle of Mons Graupius
This is a time of legions exploring the unknown reaches of the Empire.
Sadly, the battlefield for Mons Graupius has not been identified, though there are certain candidates.
What is fortunate, however, is that Agricola’s legions left a long train of breadcrumbs in the form of marching camps, legionary bases, watch towers and of course, roads, all the way to northern Scotland.
And it is network of war that was to be used in later invasions of Caledonia.
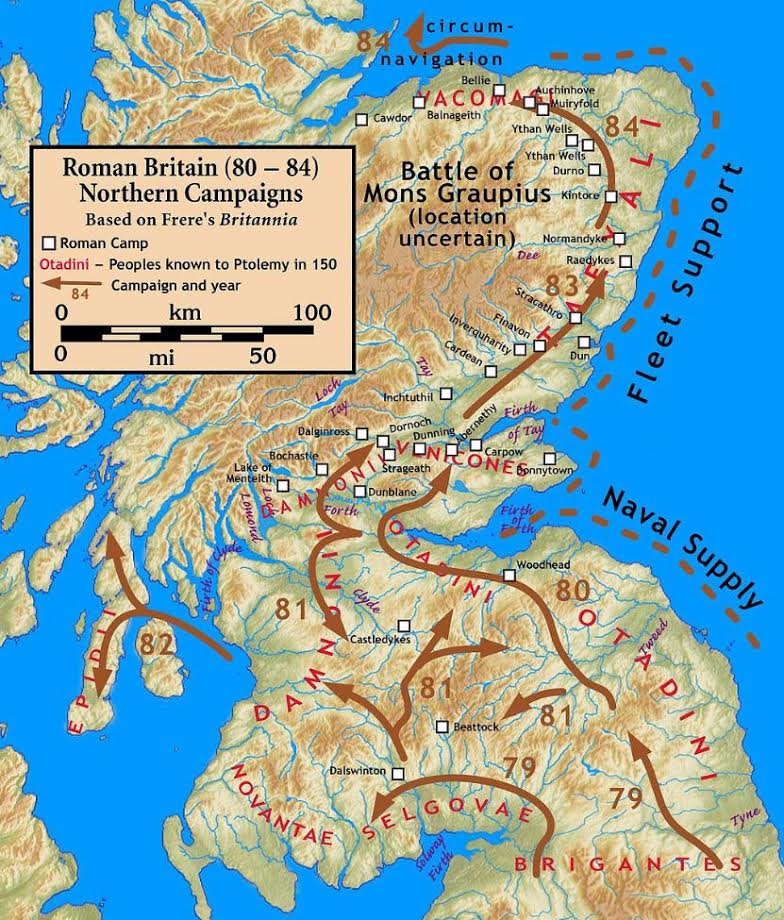
Early Roman campaigns in Caledonia
War broke out again on the Danube frontier at this time, and so Roman man-power was sucked out of Britannia and Caledonia to meet threats elsewhere in the Empire.
And so, the legions in Caledonia went into a period of retrenchment and pulled back to the Forth-Clyde by A.D. 87.
By the time of Emperor Trajan’s reign, c. A.D. 99, Rome had retreated farther to the South to the Tyne-Solway, the future line of Hadrian’s Wall, construction of which began in A.D. 122.
The Caledonian lands for which Agricola and his legions had fought, had been given up for the time being.
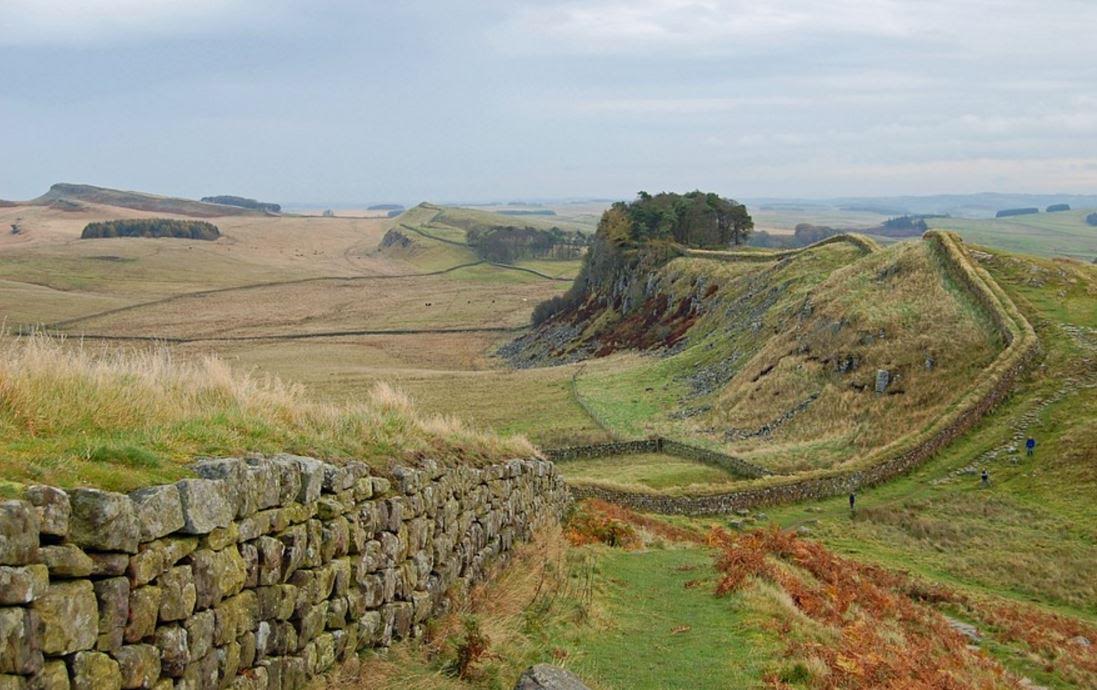

Hadrian’s Wall
As was the case for centuries to come, the lands between the Forth-Clyde line, and the Tyne-Solway line, the area known today as the Scottish Borders, went into a period of push and pull, of occupation, retreat, and re-occupation.
It was during the reign of Antoninus Pius (A.D. 138-161) that it was deemed necessary to re-occupy the lands lost during the Flavian period, and so the army advanced again across the borders, using those same roads and forts that had been constructed by Agricola, and constructing new ones.
Twenty years after construction began on Hadrian’s Wall, Antoninus Pius ordered the construction of a new wall in Caledonia itelf in A.D. 142. This was the Antonine Wall, and it’s earth and timber ramparts ran the width of Caledonia from the Forth to the Clyde in an attempt to hem the raucous tribes in on their highlands.
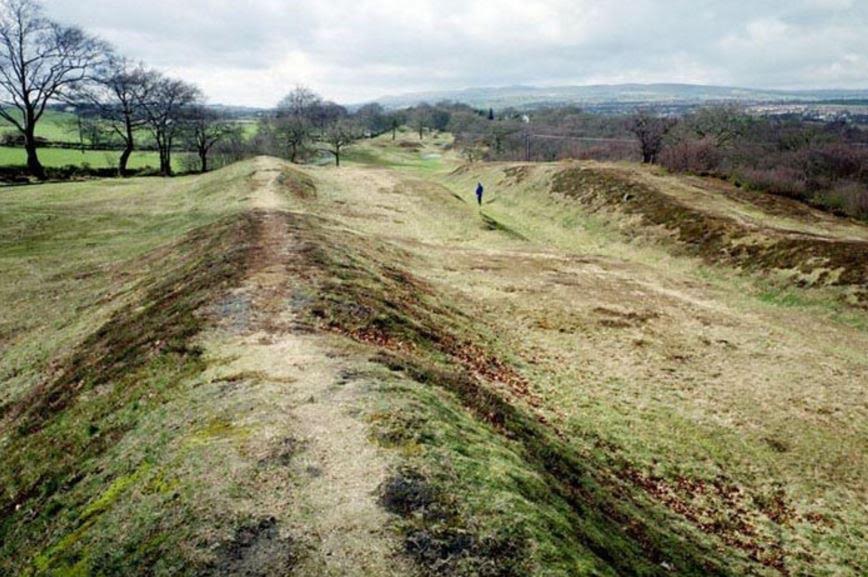

The Antonine Wall
But, after more campaigning and entrenchment by Rome, the Antonine Wall was abandoned during the reign of Marcus Aurelius in around A.D. 163.
A few outposts remained in use to the north of Hadrian’s Wall, but for the most part, the bones of the Empire were left to rot and be overwhelmed by the Caledonians and their allies.
For the next forty years, the northern tribes became a menace, breaking through the frontier defences twice, once during the reign of Commodus (c. A.D. 184) and then again during the early part of Septimius Severus’ reign in A.D. 197.
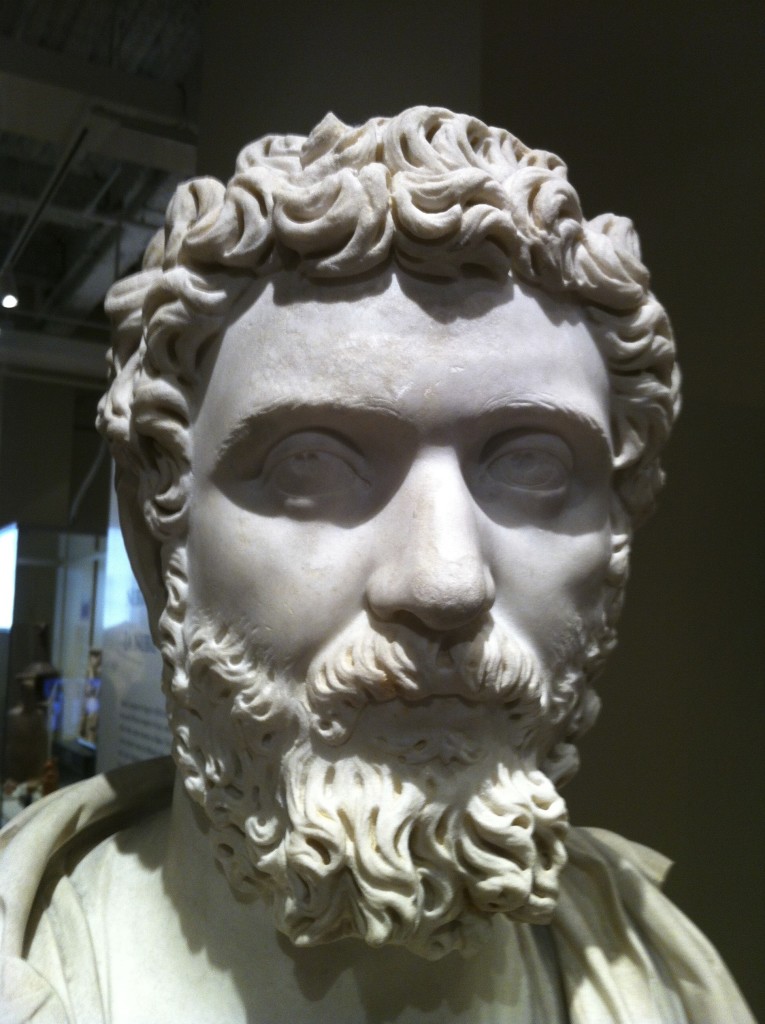

Septimius Severus
When Septimius Severus took the imperial throne, he was immediately engaged in consolidating the Empire after the civil war, and then taking on the Parthian Empire. He was a military emperor, and he knew how to keep his troops busy, and how to reward them.
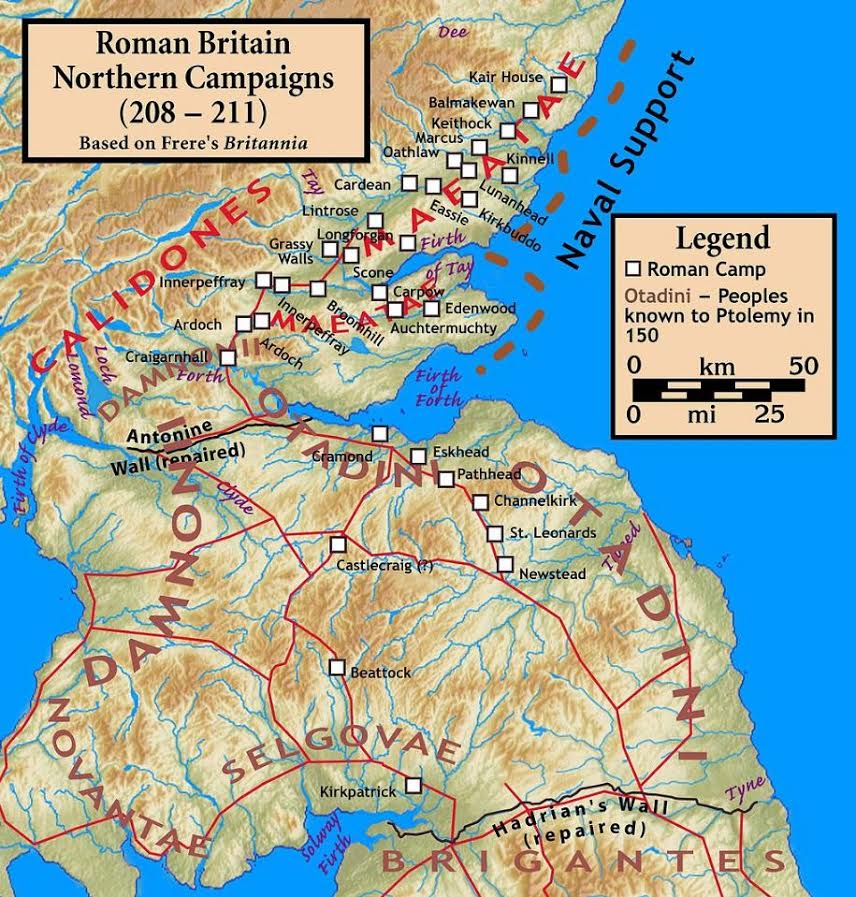
The Caledonians had been a thorn in Rome’s side for a long while at that time, but it was not until A.D. 208 that Severus was finally able to deal with them. And so, the imperial army moved to northern Britannia, poised to take on the Caledonians once again.
We’ve already touched on Severus’ campaign in previous parts of this blog series. However, it’s important to note that this is believed to be the last real attempt by Rome to take a full army into the heart of barbarian territory.
Severus moved on the Caledonians with the greatest land force in the history of Roman Britain, making use of his predecessors’ fortifications (such as the Gask Ridge frontier) and roads, and penetrating almost as far as Agricola’s legions over a hundred years before.
According to Cassius Dio, when the inhabitants of the island revolted a second time, Severus:
…summoned the soldiers and ordered them to invade the rebels’ country, killing everybody they met; and he quoted these words: ‘Let no one escape sheer destruction, No one our hands, not even the babe in the womb of the mother, If it be male; let it nevertheless not escape sheer destruction.
Rome was poised for a final push, and ultimate victory over the Caledonians.

Goddess Fortuna
But Fortuna was not on Severus’ side, for it was at that time that his chronic health problems finally got the better of him.
In A.D. 211, the man who had won a brutal civil war, and who had finally brought the Parthians to heel, died at Eburacum (modern York) in Britannia.
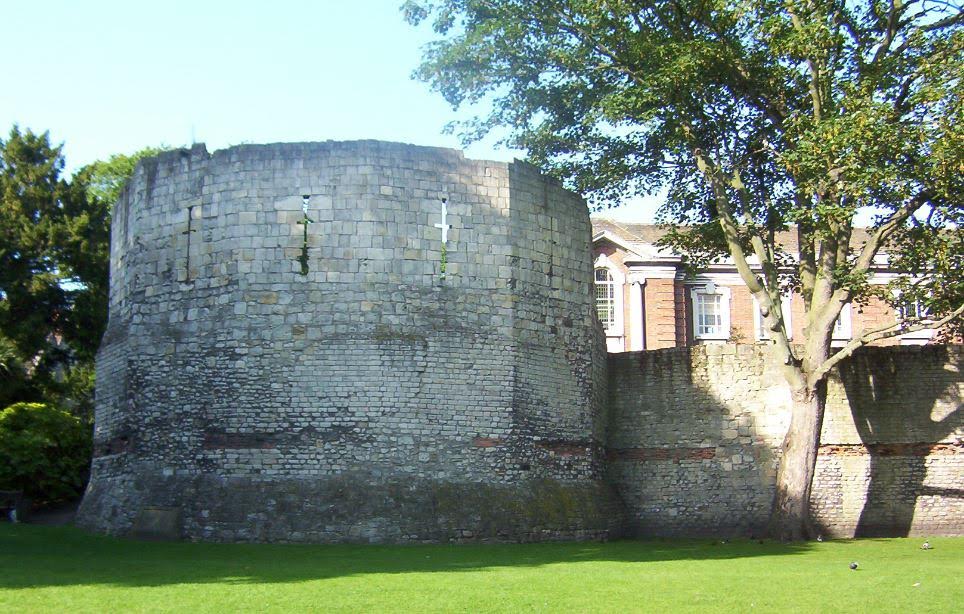

Roman Tower at Eburacum (York)
His son, Caracalla, who was ill-equipped to handle the situation, struck a deal with the Caledonians, abandoning all the headway his father had made in that northern land, and all of the blood shed by fifty-thousand Romans in the Severan campaign.
What happened after the death of Severus is for another story (i.e. for the next book!). However the Severan conquests in Caledonia did usher in a fleeting period of tranquility.
Later expeditions into the North were mounted in c. A.D. 296 by Constantius Chlorus, and by his son, the future Emperor Constantine, in A.D. 306. However, neither of these campaigns were on a scale comparable to the Severan campaign.
Like other remote corners of the Empire, Caledonia must have seemed like a lost cause.

Roman Cavalry