Greetings Readers and History-Lovers!
Welcome back to The World of Sincerity is a Goddess, the blog series in which we are taking a look at some of the research that went into our latest novel set in ancient Rome.
If you missed Part VII on doctors in the Roman Empire, you can read that by CLICKING HERE.
In Part VIII, we’re going to be exploring one of the major settings in Sincerity is a Goddess: the Theatre of Pompey.
Not only does this theatre play a large role in our story, but it also has a fascinating foundation story in addition to being the site of one of the most infamous moments in the history of Rome.
We hope you enjoy…
When designing a theater, you should include porticoes behind the stage to house the audience when a sudden downpour disrupts the performances, and to provide some open space for the preparation of stage sets. The Pompeian Portico is an example of this.
(Vitruvius, Architecture 5.9.1)
In a previous post in this blog series, we already discussed the history of theatres in ancient Rome and how they started out as temporary wooden stages set up for festivals, only to be torn down at the end of the show. If you missed that post, you can read it HERE.
The Theatre of Pompey, or the Theatrum Pompeii, is different in that it changed the game, so to speak. Its creation not only gave theatre its first permanent home in ancient Rome, but it also changed the architecture and purpose of theatres in general, an influence that can still be felt to this day!

Theatre of Mytilene that inspired Pompey
The Theatre of Pompey was, of course, built by the general and politician Pompey the Great, a contemporary of Julius Caesar who had also been married to Caesar’s daughter, Julia.
In 62 B.C. it is said that on a visit to the island of Mytilene (Lesvos), Pompey was inspired by the theatre there. He was in his second consulship and so, to solidify his popularity he conceived of the idea of building a permanent theatre for the people of Rome.
However, Roman law forbid the building of stone theatres within the pomerium, the sacred boundary of the city of Rome. So, Pompey decided to build his theatre in the ager Romanus, the area outside the boundary of the pomerium, on the Campus Martius, the Field of Mars.
Construction is said to have begun around 61 B.C. with the theatre being completed around 55 B.C.
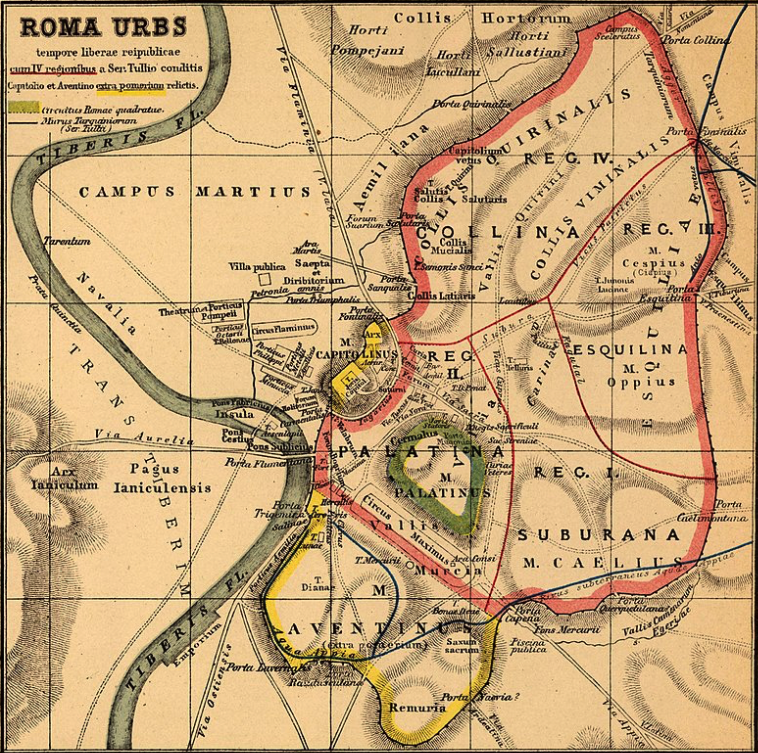
Map of Republican Rome with the borders of the Pomerium in pink.
Despite building outside of the pomerium, there were still some conservative parties who opposed the construction of a permanent theatre.
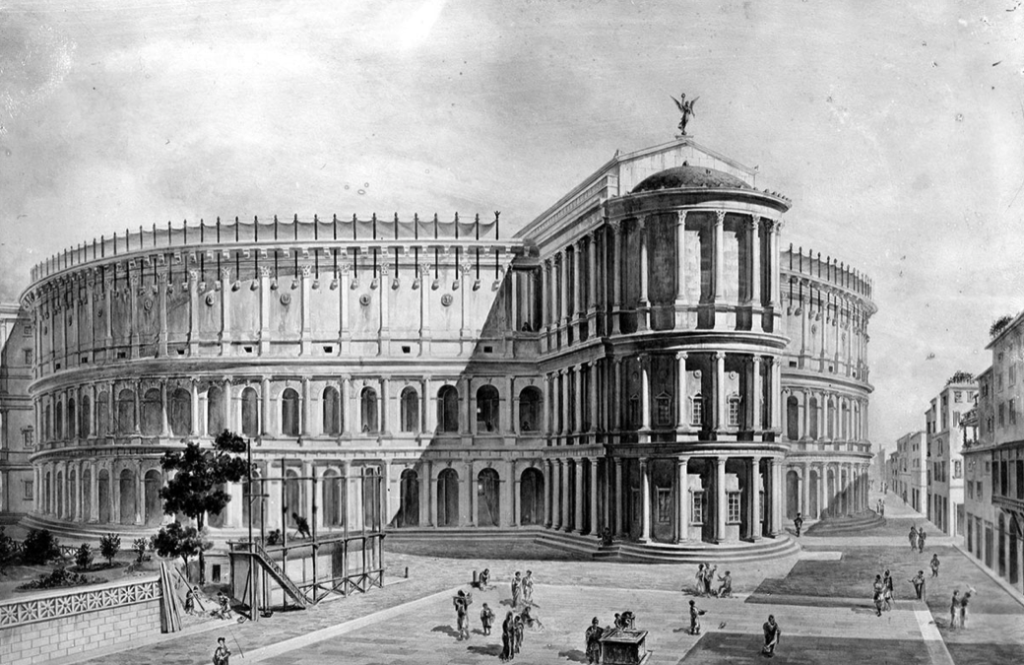
Pompey, cunning general that he was, further circumvented the law against theatres by making the theatre itself a sort of substructure for the temple of his patron goddess, Venus Victrix. Opposite the stage at the top of the cavea, the auditorium, Pompey built a magnificent temple to the goddess. The seats of the auditorium, which had a capacity for well over 22,000 people, provided the steps leading up to the temple!
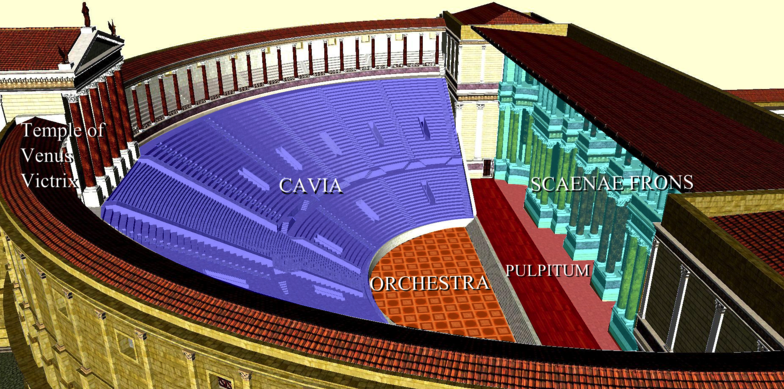
Digital reconstruction of the Theatre of Pompey (Wikimedia Commons)
Now that the structure was mainly a structure dedicated to the goddess Venus herself, none could dare oppose its construction! The Christian writer, Tertullian, writes about this:
I especially wish to demonstrate for other Christians how those traditional spectacles of Roman entertainment are not compatible with the true religion and the true worship of the one true God.…
Let us consider the true nature of theatrical entertainment, beginning with the vice inherent in its setting. The theater, rightly seen, is a shrine to Venus. Indeed, this type of building came into the world in the name of Venus. For originally, even the heathen censors were concerned to destroy theaters as quickly as they arose, foreseeing the serious moral damage that would result from the licentious spirit of the theater.… Because of this attitude, when Pompey the Great (only his theater was greater than he!) had constructed that citadel of every vice and was afraid that because of this his memory might one day suffer from official censure, he added on to his theatre a temple to Venus, and when he summoned the people to the dedication, he did not call the structure a theatre, but a temple “to which we have added,” he said, “some seating for shows.”
(Tertullian, Pagan Entertainments 1, 10)
Rome had received its first, permanent, stone theatre complete with a large, wide stage, or pulpitum, aulaeum, the curtain that rose out of the ground before the stage, and a towering decorative scaena frons which provided the backdrop for performances, complete with doorways for the plays, and niches with statues above.
The Theatre of Pompey had it all!
According to the sources, the performances that were put on as part of the theatre’s dedication were Accius’ Clytemnestra, and Equos Troianus by either Andronicus or Naevius. It was a big event, such that the famous actor Clodius Aesopus was brought out of his retirement to perform in the opening show which was, of course, accompanied by gladiatorial matches with exotic animals. It was Rome, after all!
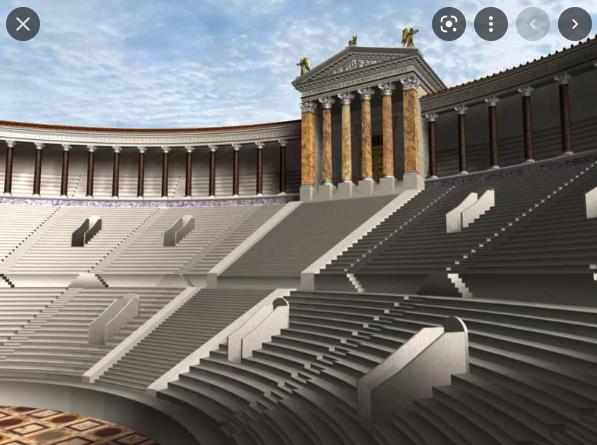

Digital Recreation of the temple of Venus Victrix at the top of the auditorium.
The Theatre of Pompey, however, was much more than a theatre, or a temple for that matter. It was an entertainment and administrative complex where the elite of Rome could meet, and where citizens could gather. It was something of an oasis in the city of Rome. Even poets praised its beauty…
Why, Cynthia, do you flee the city for smaller towns nearby?
I suppose the Portico of Pompey, with its columns of shade
And tapestries of threaded gold, seems squalid to you,
With its solid rows of plane trees shaped to an even height,
The streams of flowing water that slide off the Slumbering Satyr,
And the liquid sounds of splashing around the entire basin
When Triton suddenly blows the water from his mouth.
(Propertius, Elegies 2.32.11-16)
Connected to the theatre was a large area known as the quadriporticus which comprised an enormous area of groomed gardens with magnificent statues and fountains surrounded by columned porticoes.
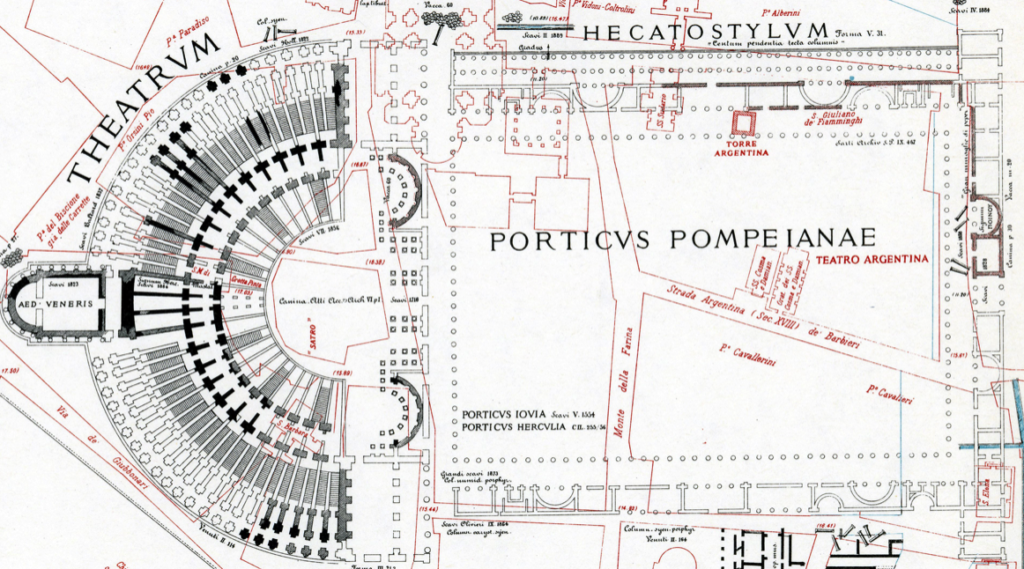
Architectural plan of the theatre and quadriporticus of the complex.
Outside the far end of the quadriporticus, opposite the theatre, another temple complex was incorporated. This sacred area included more ancient temples to Juturna (A – 241 B.C.), the Aedes Fortunae (B – 101 B.C.), Feronia (C – 4th century B.C.), and the Lares Permarini (D – 2nd century B.C.).
As was often the case in ancient Rome, religious belief was a part of the everyday, including theatre.
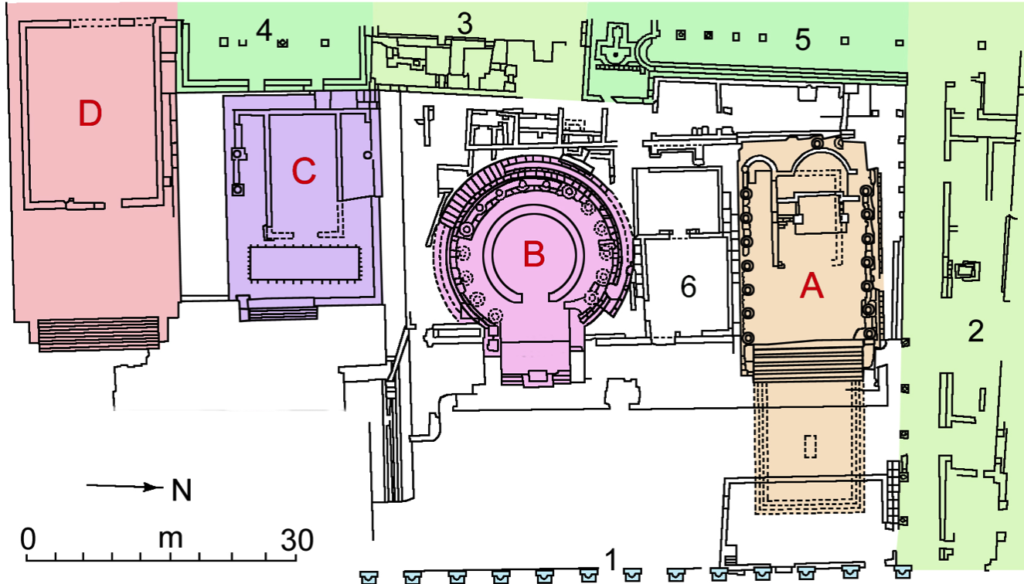
Republican-era temples in the sacred area at the far end of the quadriporticus. (Wikimedia Commons)
As we mentioned, Pompey’s wonderful theatre complex was much more than an entertainment and social venue. It was also an administrative centre.
In fact, included in the complex of the quadriporticus was the Curia of Pompey. This meeting space was sometimes used as a place for the Senate of Rome to meet.
This is exactly what was happening on March 15th, 44 B.C.
Because of work being done on the Senate house in the Forum Romanum, the Senate of Rome was meeting in the Curia of Pompey. It was a day that would shake the Roman world, and set off another bloody civil war.
As Julius Caesar arrived at the Curia of Pompey for the meeting of the Senate, he was surrounded by a conspiring group of Roman senators and murdered.
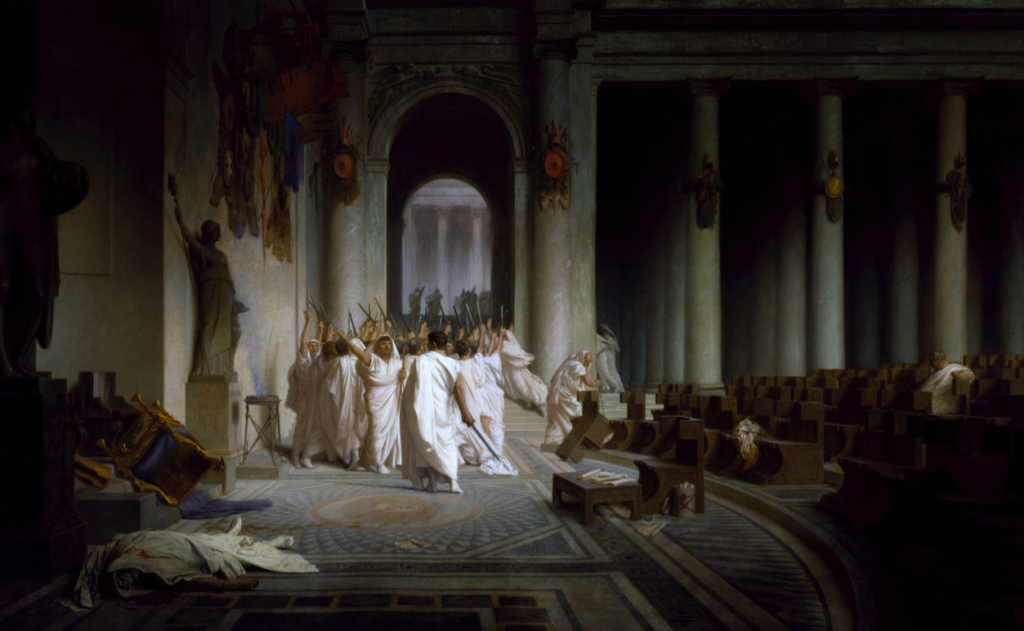

The Death of Caesar (Jean-Léon Gérôme, 1867)
The scene itself of Caesar’s death-struggle and assassination later made it clear to all that some spirit-power [daemon] had taken the event in hand to bring it about. For the meeting-site of the senate that day contained a statue of Caesar’s late rival Pompey, which Pompey himself had dedicated as one more ornament to his theater.…
(Plutarch, Caesar 66.1, 3-7)
The Ides of March were burned into the historical timeline from then on, and it happened at the temple and theatre complex built by Caesar’s one-time friend, son-in-law, and enemy, Pompey the Great.
The Theatre of Pompey had a long and storied history. It saw tragedy, comedy, beauty and bloody murder, and for forty years it was the only permanent theatre in Rome.
Eventually other theatres, such as the Theatre of Balbus (13 B.C.) were built around the Theatre of Pompey, seeking to enliven themselves by proximity to the latter’s splendour. This created a sort of theatre district in ancient Rome, and the Theatre of Pompey was at its heart.
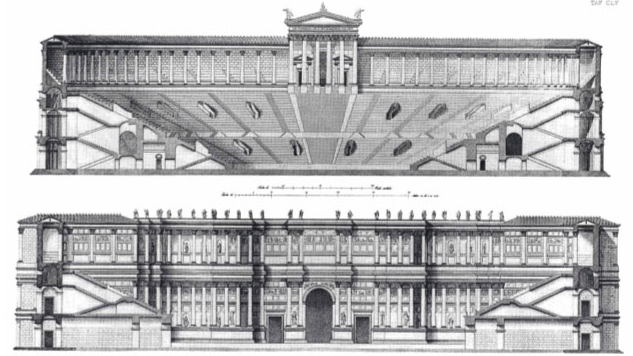
Artist impressions of the cavea (auditorium) with the temple at the top, and of the pulpitum and scaena frons (the stage and stage house).
The building of the Theatre of Pompey in ancient Rome was a turning point in theatre history, for it gave wider acceptance to theatrical performance, as well as a permanent home.
Theatrical groups from across the Roman world, including our fictional Etrurian Players, saw performing in that great place as the pinnacle of their careers, similar to artists getting to perform in places such as La Scala, Royal Albert Hall, or Carnegie Hall today.
The Theatre of Pompey also gave theatre complexes a much broader role in society which not only included that of a religious centre and entertainment venue, but also as an administrative centre, and an attractive public space. The latter is certainly something that is still holds true to this day in modern theatre settings.
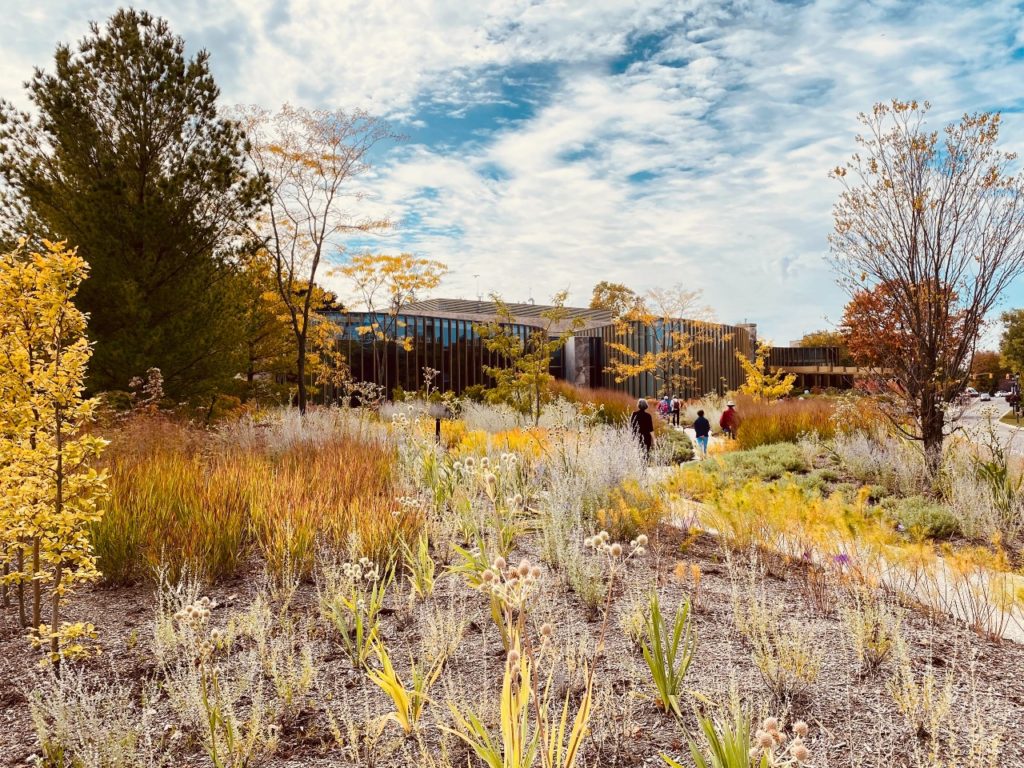

The Tom Patterson Theatre in Stratford, Ontario carries on the tradition of a theatre that is also a public space and gardens in an urban setting.




