Welcome back to The World of Isle of the Blessed. We are at the midway point in this blog series about the history, archaeology and research that are related to Isle of the Blessed, the latest novel in the Eagles and Dragons historical fantasy series.
Last week in Part III, we took a tour of Glastonbury, Somerset and some of the sites that are featured in the novel. If you missed it, you can check it out HERE.
This week, in Part IV, we will be meeting some of the main players in the story, the members of Septimius Severus’ imperial court in Eburacum (modern York) when he spent three years there during the Caledonian campaign. Fans of the series will already be familiar with some, but others will be new, but no less interesting or important to this part of the story.
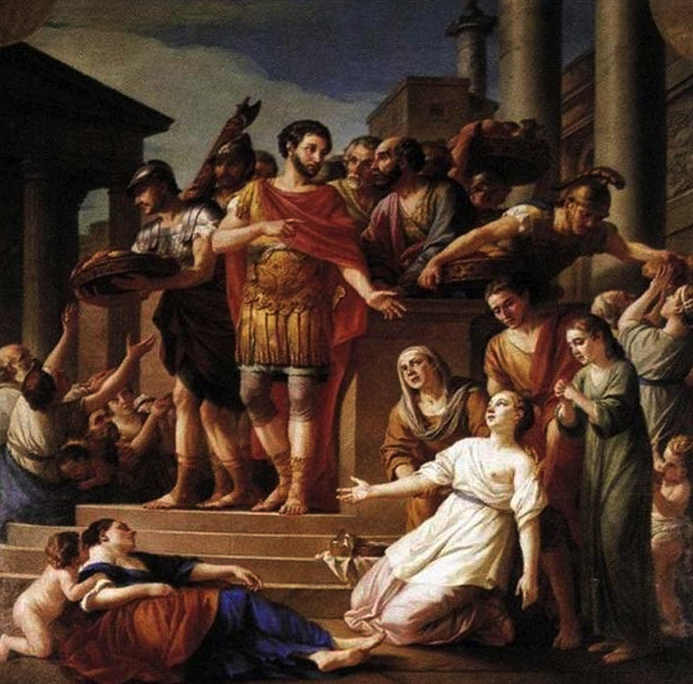

What was it like to be a part of the imperial court?
During the Caledonian campaign, Septimius Severus moved much of his government to Eburacum, the provincial capital of Britannia Inferior, the northern half of the province.
His entourage would have included not only his wife, sons, and other family members, but also an army of slaves, civil servants and more.
With the court moving to Eburacum for over three years, the city would have been bustling with activity. The markets would have been full with merchants and suppliers coming from around the Empire to provide for the great influx of civilians as well as the many thousands of auxiliary troops who came to Caledonia in addition to the legions that were already posted there.
Like any imperial court, however, there were camps with different intentions and interests working in the background. The glens of Scotland were not the only battlefields, and the period of Severus’ rule, perhaps especially during the Caledonian campaign, was a crucial time for the Empire.
So who were the main players at the imperial court, and where did their loyalties lie?
Severus had been ‘dying’ for years, but now, it seemed, the end was near, and the vultures were circling.
First, let us look at the family of Severus himself.
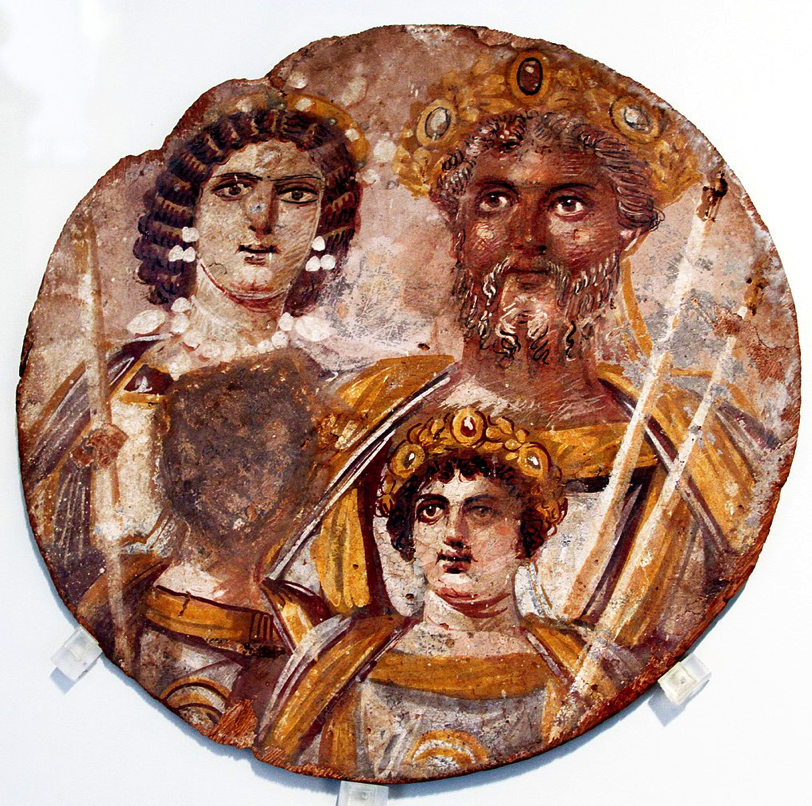

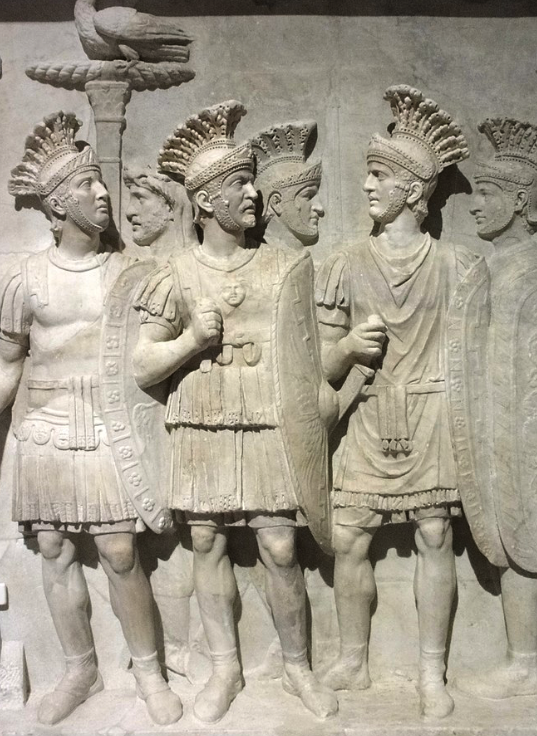
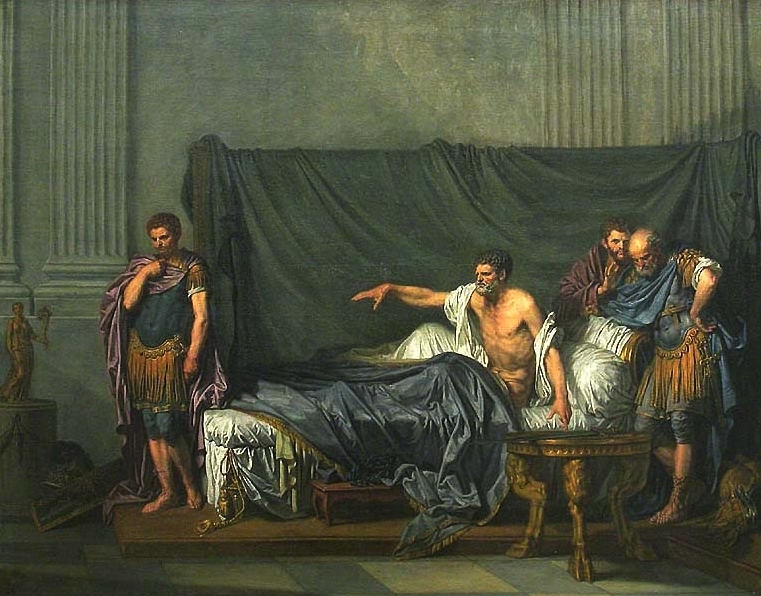
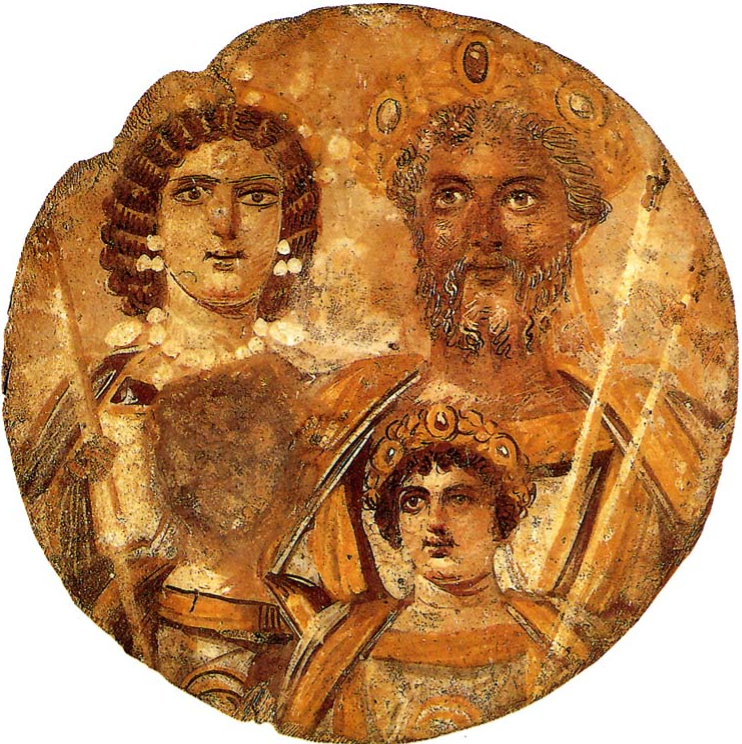
Septimius Severus and his family, Julia Domna, Caracalla and Geta (with face missing)
The Severans were a very interesting family and not without their tales of violence and greed and uniqueness of character. The period is not marked by something so brutal (not yet!) as the psychotic reign of Caligula, but there are certainly many more dimensions. It is a time of militarism, of a weakened Senate, a time of spymasters in various camps. It is a time marked by the rise of lower classes, the presence of powerful women and, over it all, a blanket of religious superstition at the highest levels. Many believe that it is this period in Rome’s history that marks the true beginning of the end of the Roman Empire.
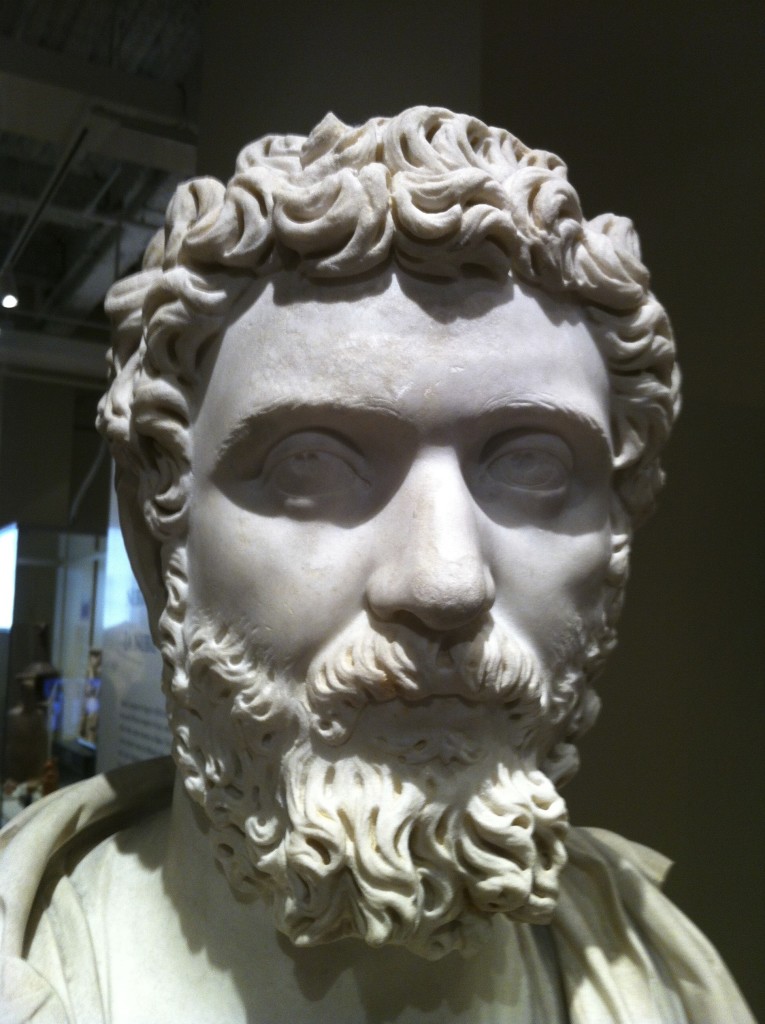
In writing the Eagles and Dragons series, it has become obvious that Septimius Severus (A.D. 193-211) was, perhaps, one of the better emperors in Rome’s history. Sure, he was not Antoninus Pius (few were), but he was far better than say, Tiberius.
He was the son of an Equestrian from Leptis Magna in North Africa. When Commodus was killed in A.D. 192, Severus was governor of Pannonia. When the Praetorians decided to auction the imperial seat a short time later, Severus’ legions declared him Emperor. He subsequently defeated his two opponents who had also declared themselves Emperor: Clodius Albinus and Pescennius Niger. A purge of his opponents’ followers in the Senate and Rome made Severus sole ruler of the largest empire in the world.
Septimius Severus was a martial emperor, the army was his power and he knew how to use it, how to keep the legions loyal and happy. During his reign, he increased troops’ pay and in a radical move, allowed soldiers to get married. Severus was good to his troops, his Pannonian Legions and victorious Parthian veterans, some of whom fought for him in Caledonia. He promoted equestrians to ranks previously reserved for aristocrats and lower ranks to equestrian status. There was a lot of mobility within the rank system at the time due to Severus ‘democratization’ of the army. Remember, this was an emperor who favoured his troops, especially those who distinguished themselves. However, as Lucius Metellus Anguis discovers in Isle of the Blessed, there are prices to be paid. No favour is free, and being close to the imperial court can be perilous.
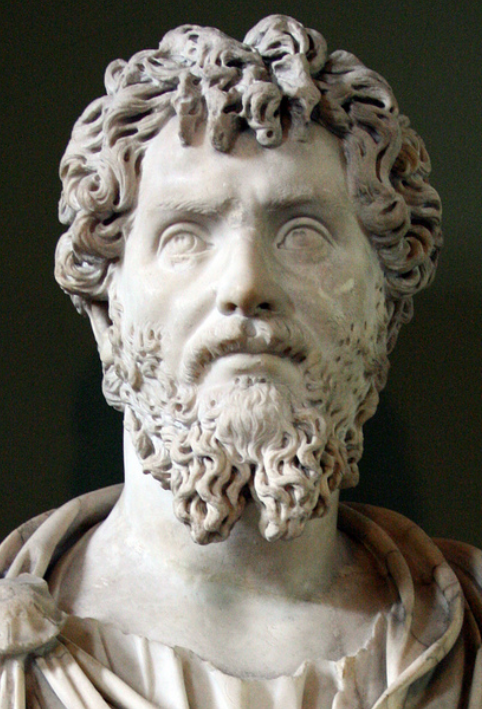

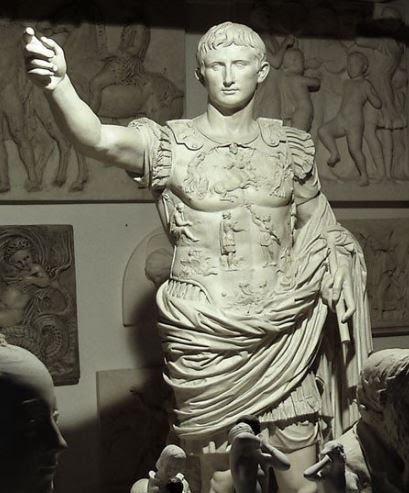
Emperor Septimius Severus
One of the most interesting characters of the period is Empress Julia Domna. She appears as one of the strongest women in Rome’s history, an equal partner in power with her husband who heeded her advice but also respected her. Julia Domna was the first of the so-called ‘Syrian women’, hailing from Antioch where her father had been the respected high priest of Baal at Emesa (Homs in modern Syria).
Julia Domna was also highly intelligent, known as a philosopher, and had a group of leading scholars and rhetoricians about her. They came from around the Empire to be a part of her circle, to win commissions from her. Her strength also bought her a great many enemies, including the previous Praetorian Prefect and kinsman to Severus, Gaius Fulvius Plautianus. In Caledonia however, years after the death of Plautianus, with her husband’s health deteriorating rapidly, she must have worried a great deal about the dual succession of their sons, Caracalla and Geta, both of whom brought a tenseness to the court.
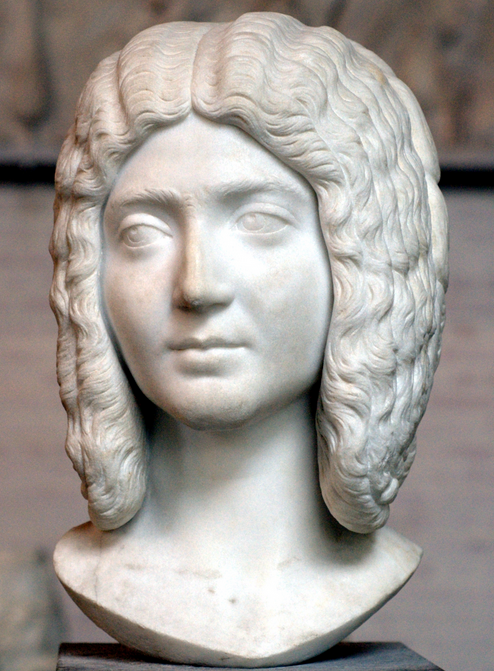

Julia Domna
By all accounts Caracalla and Geta, Severus’ heirs, were both at odds much of the time. The two brothers seem to have tolerated each other’s presence and competed fiercely back in Rome, even in the hippodrome where at one point they raced each other so aggressively on their chariots that they ended up with several broken bones, almost leaving their father without a successor.
Caracalla seems to have been the favourite of the empress, though in later years Julia Domna does come to Geta’s defence, however much in vain.
One of the main reasons the sources give for the Caledonian campaign was that Septimius Severus believed it would be good for his sons, a way to teach them, give them focus, and prepare them to succeed him together. If anything, however, the angry chasm between the brothers grew worse the more their father’s light faded.

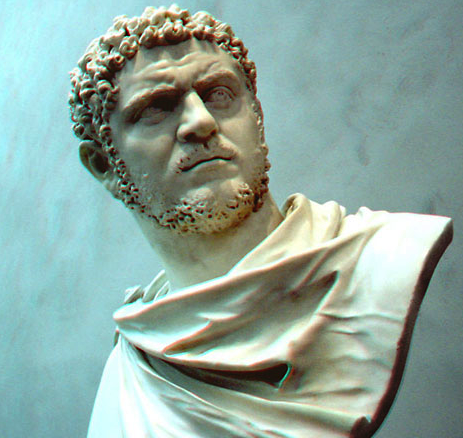
Caracalla
Caracalla, the older of the two brothers and about twenty-two at the time of the campaign, was the more martial of the pair. While Geta was appointed to administer the province from Eburacum, Caracalla went north to fight alongside the troops.
Did resentment build in the young Caesar as he fought, away from the court? Suspicion? Paranoia? Perhaps it was all of that and more? During the first phase of the Caledonian campaign, when Severus was about to agree to peace with Argentocoxus, the Caledonian leader, it is said that Caracalla nearly murdered his father in front of everyone, an episode that plays out in the previous novel, Warriors of Epona.
Caracalla was eager for the imperial throne, so much so that, as Herodian tell us, “he tried to persuade the physicians to harm the old man in their treatments so that he would be rid of him more quickly.”
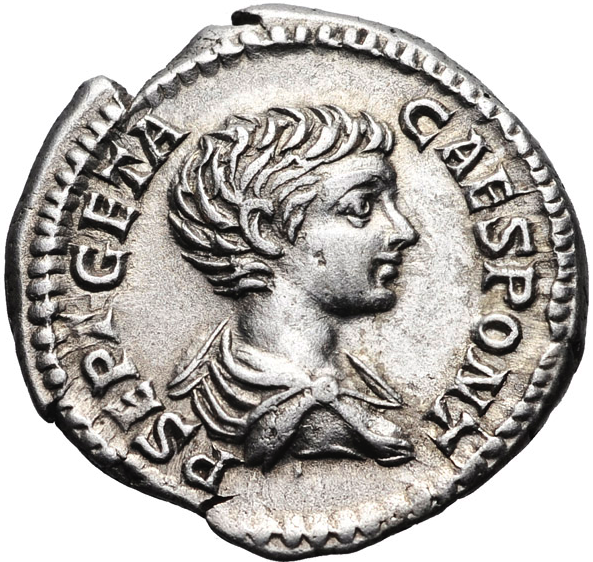

Denarius of Publius Septimius Geta
And what of Geta, Severus’ younger son and heir?
He seems to have been entrusted with much as far as the administration of Britannia during the Caledonian campaign, so he must have been skilled to some extent. However, from what little we know of him, he was not the survivor that his brother was, and most likely lacked the ambition that was needed in the imperial court.
He was respected by people at court and by the army, but this was perhaps due more to his parentage and position than his actions over the course of his short life.
Whatever impact Geta had over the years, perhaps the most prominent was his ability to anger his brother by way of his mere existence.

Aemilius Papinianus
One of the main players at the imperial court was Aemilius Papinianus, or ‘Papinian’ (A.D. 150-212), Prefect of the Praetorian Guard.
Papinianus is a fascinating man, a man of intelligence who was thrust, perhaps unwillingly, into one of the most powerful and perilous positions in the Roman Empire.
After the death of Gaius Fulvius Plautianus in A.D. 205, as told in Killing the Hydra, Severus appointed Papinianus as prefect of the guard. Before that, he had been a brilliant jurist (lawyer), legal expert, and had served as Severus’ main secretary. He was Syrian, and it seems likely that he was a cousin of the empress, Julia Domna. Perhaps that is why he was so trusted.
Papinianus, in his day, wrote many legal texts and was a great believer in the equity of the law. But what must he have thought to see the risk of all that Severus built over the years – with his advice – turning to ash after the succession of Caracalla and Geta?
It must have been dark days for the reluctant Praetorian Prefect.

Domitius Ulpianus
Lurking in the shadows of Papinianus was his long-time apprentice and fellow jurist, Domitius Ulpianus, or ‘Ulpian’ (A.D. 170-223).
It seems that Ulpianus was also a brilliant lawyer who served as a secretary under Severus (beneath Papinianus), and then became Papinianus’ right hand when the latter was made Praetorian Prefect.
Interestingly, Ulpianus’ writings were very influential on Roman law and later, on the laws of Medieval Europe.
But what must he have thought constantly playing second to Papinianus? Did the apprentice ever feel jealous of the master, or try to outdo him? We don’t know for certain, but what we do know is that he survived the tough years ahead, and so he must have been close to Caracalla. In fact, Ulpianus went on to become sole Praetorian Prefect in A.D. 223 under Emperor Severus Alexander. He must have been a survivor.

A Roman tutor and his students
There are two other men who played a very prominent role at the imperial court, who had the emperor and empress’ utmost trust, but who had also incurred the wrath of Caracalla.
Euodus, was the long-time tutor of Caracalla and Geta, and was still with the family when they went north during the Caledonian campaign. It seems that life was easier when the young caesars were smaller, but as the years went by and the animosity between them grew worse, Euodus’ job was more to try and nurture harmony between the brothers, something he evidently failed at.
This man may have felt he had much influence at court, and perhaps he did. But his constant attentions, his preachings perhaps, would prove to be more of an aggravation to Caracalla. Euodus would pay for it.

Roman freedmen
Likewise, Castor, who was Septimius Severus’ most trusted chamberlain, had a prominent role at court. He was a freedman of Severus’, elevated from a lowly rank to having the emperor’s ear, and his confidence, on a daily basis.
It is said that Castor was one of the imperial court members who most annoyed Caracalla. He was there at every turn, even when Severus reprimanded his son for attempting to kill him in front of the Caledonii at the end of the first campaign.
As Cassius Dio tell us, both Castor and Euodus did not fare well when Severus finally passed.
Astrology played an enormous role in the life and decisions of Septimius Severus
There were others who played a crucial role in the imperial court and would have been present at Eburacum during Severus’ time there.
As almost fanatical believers in astrology, Septimius Severus and Julia Domna would have had their primary astrologer, possibly named Artemidoros, with them at all times. He would have done daily readings for them, advised on any action, civic, personal, or military, and was probably the one who determined the date of Severus’ death before they even left Rome.
The sources say little to nothing about him, but his role would have been an important one, his influence upon the emperor and empress great.
Artist impression of a Roman doctor at work
As someone who would have been ill for many years, Septimius Severus would have required medical attention on a daily basis, especially at the end. His physicians would have been there, at the heart of imperial politics, hearing and seeing much, including Caracalla’s aforementioned request to speed his father’s passing.
These doctors, who had refused Caracalla’s request (threat?), likely grew extremely wary as their patient’s health deteriorated more by the day in the British climate.
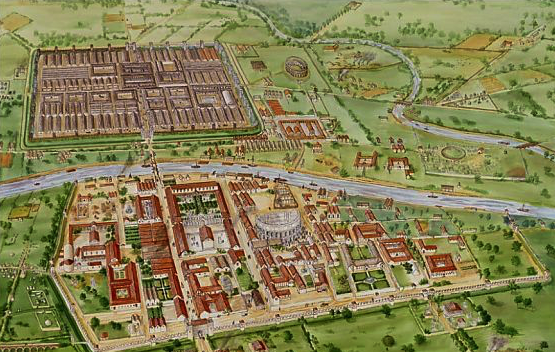
Roman York (Eburacum), c. A.D. 210. Aerial reconstruction by Tracy Croft, English Heritage
To this point, we’ve discussed the people whom we know to have been present at the imperial court. In truth, however, there would have been many hundreds (thousands?) who were a part of the imperial machine and civil service who were present in Eburacum. After all, the Empire was being administered from there during that time.
There are also some other key players who may have been present.
It is quite possible that Julia Domna’s sister, Julia Maesa, may have been present. After her sister, Julia Maesa was perhaps one of the most influential of the ‘Syrian Woman’. She and her daughters, Julia Soaemias Bassiana and Julia Avita Mamaea (mother of later Emperor Severus Alexander) would be extremely influential in the years to come.
It would not be surprising if Julia Maesa were present at court, close to the heart of things. She was apparently close to Caracalla too, and this would have protected her and her daughters. She survived until A.D. 226.

Gold ‘aureus’ of Julia Maesa
With much of the government following the emperor, one has to wonder if there were not also a certain number of senators present in Eburacum as well.
If so, it is possible that Cassius Dio was there. As the primary, contemporary source for the reign of Septimius Severus, it would not be surprising if he were present in Britannia for at least a portion of the campaign.

How many Roman senators might have been present in Eburacum? Was Cassius Dio among them?
Then there is Caracalla’s wife, Plautilla, and her brother Plautius. Were they present? Or did Caracalla want to keep her as far from him as possible, as it was said that she was ever an annoyance to him in previous years.
If the names of Plautilla and Plautius are somewhat familiar to you, it may be that that is because they are the children of Gaius Fulvius Plautianus, the traitorous Praetorian Prefect who was dispatched by Caracalla and others in a plot in A.D. 205, with Julia Domna no doubt working toward that end in the background.
As for his wife and brother-in-law, Cassius Dio said that Caracalla had them killed when to took power, but whether it was immediately, or upon his return to Rome is not stated.
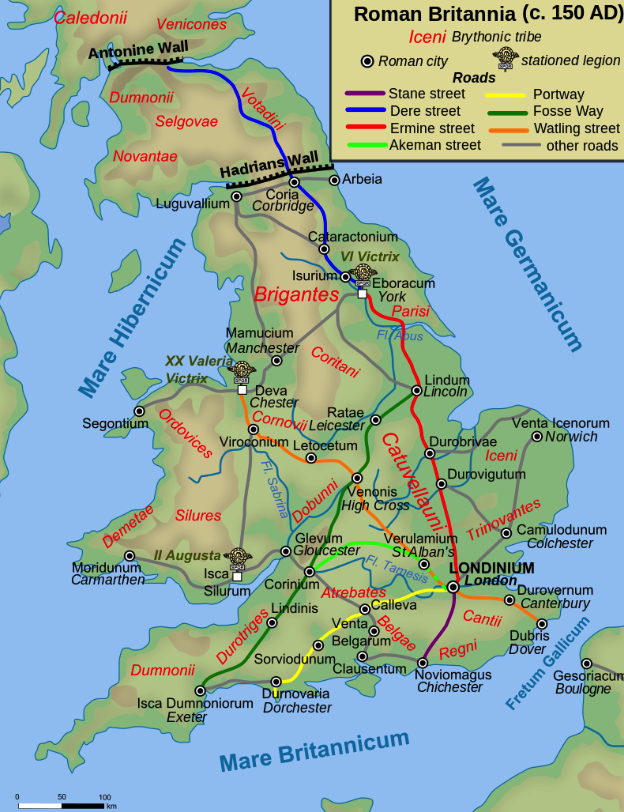
Map of Roman Britain prior to reign of Severus (Wikimedia Commons)
Another person who may have been in Eburacum for much of the time, and who may have found his work partially hi-jacked by the presence of the imperial family and the administrations of Geta, was Gaius Junius Faustinus Postumianus. He was the provincial governor of Britannia Superior, based in Londinium.
Faustinus was an officer in the army previously, before being appointed governor. What did he think about the presence of the imperial court in Britannia, or the waging of war at the borders of his province? No doubt the situation brought him many benefits, but also many headaches, especially when Severus passed from the world.
Of one thing we can be certain, and that is that an imperial court was not a place for the faint of heart.
Who survived, and who fell? Did being close to Severus’ sun mean you would get burned, or thrive?
For a writer of historical fiction, these are interesting questions to be explored with different answers for each player in the drama.
If anything, life at the court of Severus in Eburacum would have been anything but dull, despite the fact that they were on the virtual edge of the Empire.
Thank you for reading.

Isle of the Blessed is now available in e-book and paperback from all major on-line retailers. If you haven’t read any books in the Eagles and Dragons series yet, you can start with the #1 bestselling A Dragon among the Eagles for just 0.99! Or get the first prequel novel, The Dragon: Genesis, for free by signing-up for the newsletter HERE.