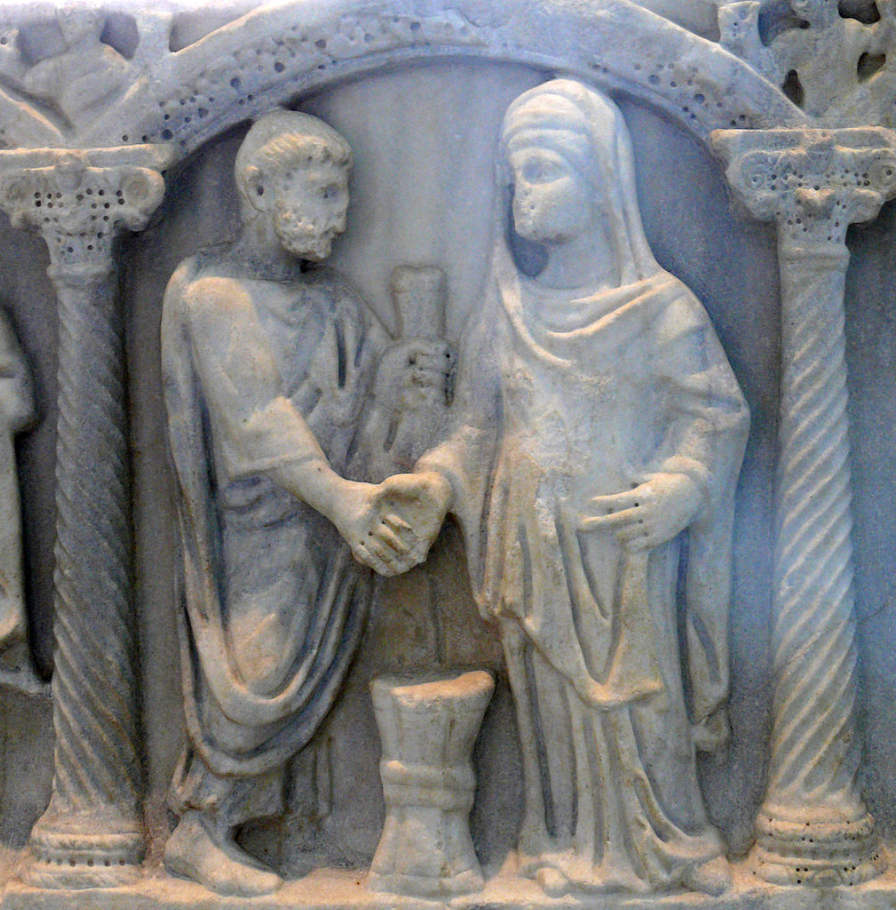
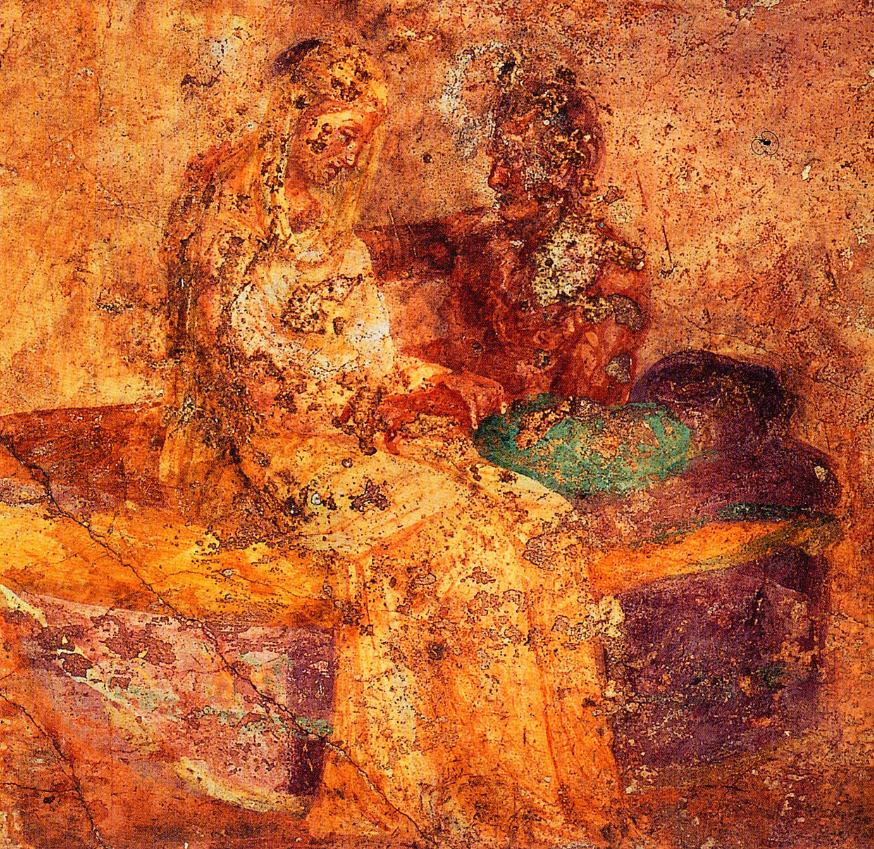
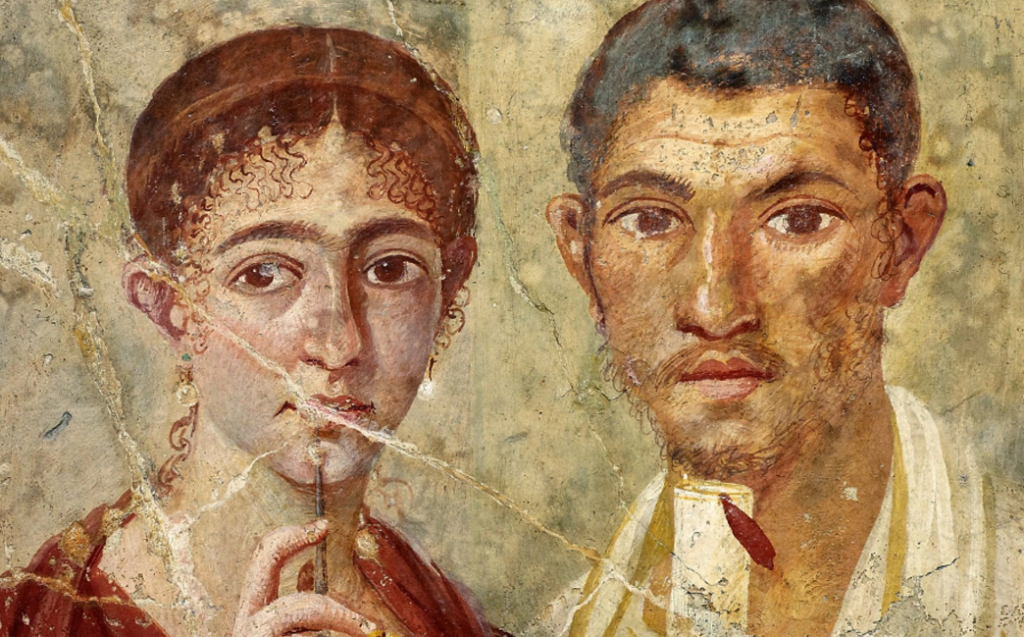
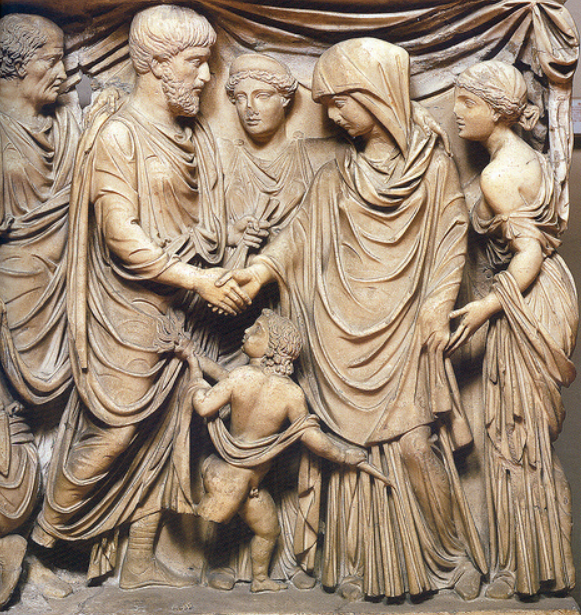
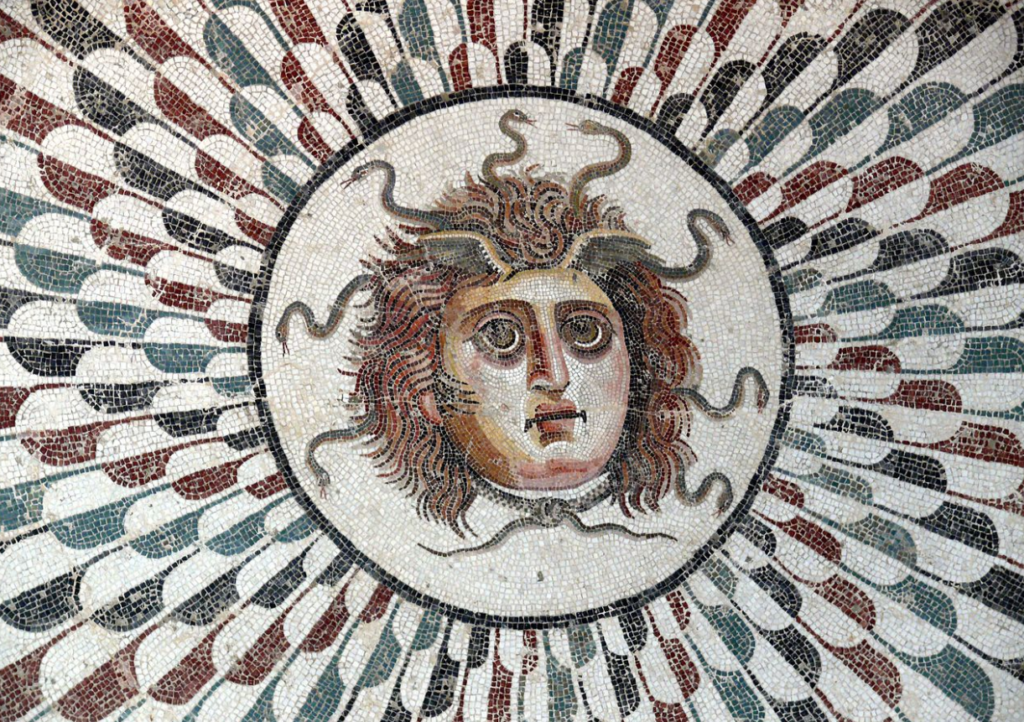
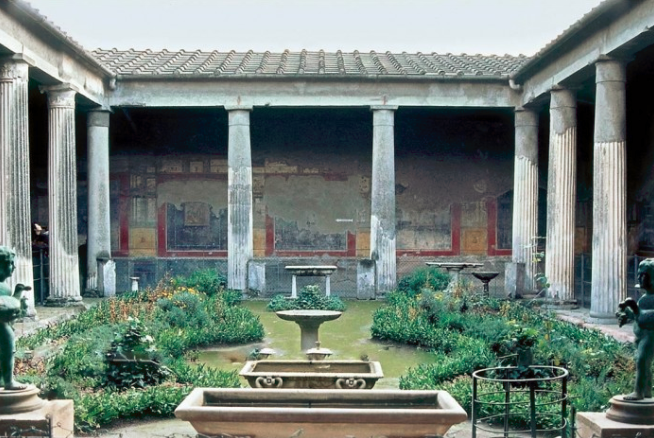
Ancient Rome
Roman Ghosts – Pliny and the Spectral Haircut
Hello History-Lovers!
It’s been a while since the last post in the Roman Ghosts blog series. Something I was working on recently (a secret to be unleashed this autumn!) made me think of hauntings, and so, here we are.
I’ve also waited because, of all the tips we’ve received about Roman ghost sightings, there were none that took place outside of the UK. The Roman Empire was, of course, vast, and so I found it difficult to believe that there were no accounts outside of Britannia.
So, I did some digging and found one story which I will share with you today.
I am extremely desirous therefore to know whether you believe in the existence of ghosts, and that they have a real form, and are sorts of divinities, or only the visionary impressions of a terrified imagination. (Pliny the Younger, LXXXIII. To Sura)
As it happens, this particular story is not of modern sightings of a ghost, but rather is an ancient ghost story relayed by none other than Pliny the Younger in a letter to Senator Lucius Licinius Sura, from Hispania.
It seems that Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, known to us as Pliny the Younger (c. A.D. 61 – 113), had ghosts on his mind.
Being an educated and inquisitive person like his uncle, Pliny the Elder, he wrote to his friend Sura to see what he thought about ghosts.
Now, we don’t really know why Pliny the Younger had ghosts on his mind, apart from the tales he relays as examples in his letter to Sura.
There are three tales, or examples, of ghost sightings that Pliny relays in his letter. The first is of an apparition that warned the senator, Curtius Rufus, of his rise to power, and also of his death in Africa.
The second story Pliny writes to Sura about is of the Greek philosopher, Athenodorus, who wanted to rent an apartment in Athens but wondered why it was so inexpensive. Apparently, the ghost of an old man kept harassing the occupants of the flat, and so, like an ancient world Ghostbuster, Athenodorus spent the night there to see what happened. The ghost appeared while Athenodorus was working, and insisted that the philosopher follow it to a spot nearby. The next day, Athenodorus asked that a hole be dug there and, sure enough, a putrefied body lay chained within. The remains were reburied with the proper rituals, and the ghost was not seen again.
These first two stories in Pliny’s letter are fascinating, but it is the third story that interests me, because it comes perhaps to the crux of the matter for Pliny – an experience beneath his own roof! Here it is in his words:
I have a freedman named Marcus, who is by no means illiterate. One night, as he and his younger brother were lying together, he fancied he saw somebody upon his bed, who took out a pair of scissors, and cut off the hair from the top part of his own head, and in the morning, it appeared his hair was actually cut, and the clippings lay scattered about the floor. A short time after this, an event of a similar nature contributed to give credit to the former story. A young lad of my family was sleeping in his apartment with the rest of his companions, when two persons clad in white came in, as he says, through the windows, cut off his hair as he lay, and then returned the same way they entered. The next morning it was found that this boy had been served just as the other, and there was the hair again, spread about the room. (Pliny the Younger, LXXXIII. To Sura)
I don’t know about you, but if I woke up to a Roman ghost cutting my hair, I would not be quiet about it!
Obviously, Pliny did not witness the ghost himself, but he does say that “This story I believe upon the credit of others [the previous tale]; what I am going to mention [the current tale], I give you upon my own.”
What would drive Pliny the Younger – an educated and well-respected man and member of Roman society – to believe this tale and even to seek the advice of Senator Sura?
Of course we don’t know what topics of discussion passed previously between Pliny and Sura, what they might have discussed over dinner in times gone by.
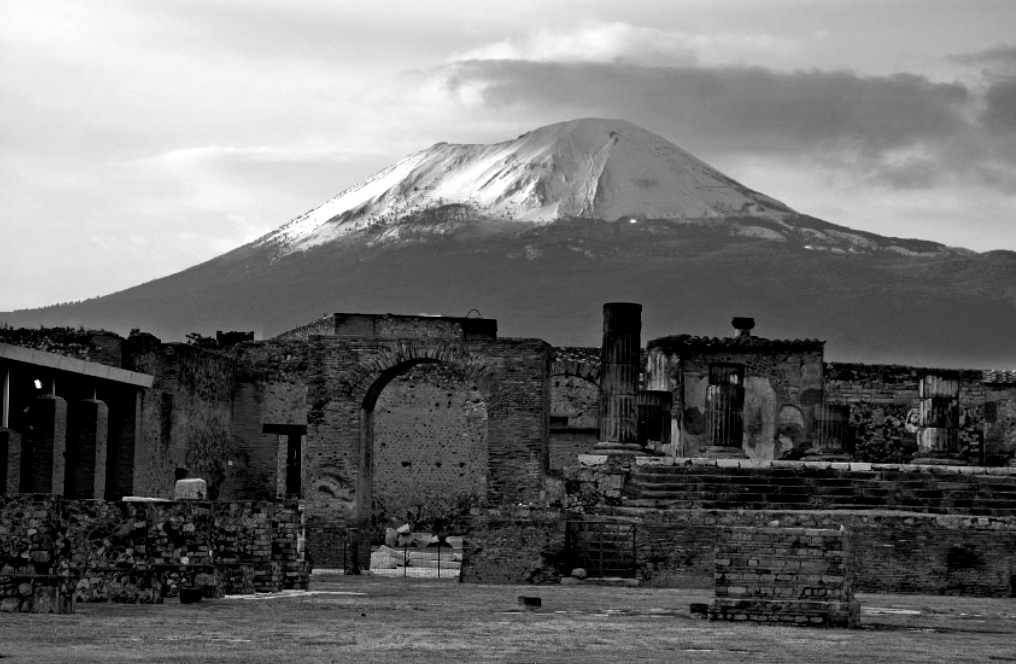
We should bear in mind that Pliny, who was eighteen at the time, bore witness to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, and the deaths of thousands, including his own uncle.
You could hear the shrieks of women, the wailing of infants, and the shouting of men; some were calling their parents, others their children or their wives, trying to recognize them by their voices. People bewailed their own fate or that of their relatives, and there were some who prayed for death in their terror of dying. Many besought the aid of the gods, but still more imagined there were no gods left, and that the universe was plunged into eternal darkness for evermore. (Pliny the Younger, Letter to Tacitus)
Years later, were the ghosts of Pompeii on his mind? Was Pliny haunted by that event, and did he worry about the dead? Perhaps his questions to Sura masked his own fears of the dead? Maybe he felt a great guilt at surviving the cataclysm of Pompeii?
Your guess is as good as mine.
One thing does seem certain from Pliny’s letter to Sura: the respectable Roman was beset by ghosts, or thoughts of them. Why, we can’t be sure, but it is a great Roman Ghost story!
If you would like to read the full text of Pliny the Younger’s letter to Sura, you can do so by CLICKING HERE.
Thank you for reading.
Ancient Everyday – The Siesta
Salvete, dear readers!
I hope you’re all having a brilliant summer so far, or winter if you’re in the southern hemisphere!
The extreme heat that’s been hitting much of the world has not by-passed Toronto either. The air has been thick and humid on several occasions, causing folks to drag their feet and stay indoors if they can, or to seek out the nearest body of water to cool off.
It’s amazing how the heat can drain one’s energy!
So, that got me to thinking about a new Ancient Everyday! If you missed the last post on pets, you can check it out HERE.
Today, we’re going to take a brief look at the siesta!
The idea of the siesta was not something I grew up with. Few people do in North America. You get up, you work through the day, or go to school, and then you come home, eat and sleep.
Most people associate the siesta with Spain or other Spanish-speaking countries, but I first came across the siesta when visiting Greece years ago. As ever, I was out doing the tourist thing, baking myself among the ruins of various archaeological sites, when the world seemed to grow quiet around 2 p.m. or so.
It was midday, but everyone seemed to have retreated. Businesses closed and restaurants emptied (except in the very touristy locations like the Plaka of Athens). There seemed to be a general hush over the world.
It was surreal. It felt like I was in some apocalyptic movie, the only person left in the world!
Well, maybe that’s an exaggeration, but you get the picture. Things grew very quiet.
On subsequent, longer visits to Greece, my family and friends would come home from work for lunch around 1 p.m. or so, they would eat a big lunch, sleep for an hour or two, and then they would go back to work until about 8 p.m. in the evening.
My thinking was, why would they go back to work? You’ve already been!
Enter the siesta!
But this habit of breaking up the day and resting during the hottest hours or mid-way point is not a modern invention.
Though many ancient cultures likely took time out in the middle of the day, it was the Romans who gave it the name we are now familiar with.
The word ‘siesta’ is actually derived from the Latin word sexta, which refers to the sixth hour of daylight. This is approximately 1 p.m. in winter, and 3 p.m. in summer. If you want to know all about Roman time-keeping, you can check out the Ancient Everyday mini-series on that topic by CLICKING HERE.
In ancient Rome, the siestatime of day, the time of sexta, was actually a time to eat and rest, to gather oneself for the second half of the day, whatever that might involve, be it business in the forum, opening your shop for the evening clientele, or loading up a shipment to go to the docks in Ostia. This tradition of day-rest seems to have spread to other cultures across the Roman Empire, including Hispania where it really caught on.
People today might think that the idea of eating a big meal and then taking a long nap in the middle of the working day is ridiculous, but I wouldn’t be too hasty to judge.
There have been plenty of studies to show that midday rest, or naps, are good for productivity and physical and mental performance, they alleviate stress, and are good for the immune system, and of great benefit to cardiovascular and mental health.
Indeed some famous nappers in history were Aristotle, Leonardo da Vinci, Beethoven, Napoleon, Salvador Dali, Einstein, Winston Churchill, and Margaret Thatcher. Whether you like these people and their work or not, you can’t argue that they didn’t get a lot done or have big ideas!
The Romans were certainly a productive lot, and one has to wonder if one of the reasons they conquered so much of the world was because they knew how to take time out. Who knows? It’s possible!
Just another thing the Romans gave to the world. Perhaps it’s time we brought back the siesta in force.
Think about it…
And while you do that, I’m going to take a nap…
Thank you for reading.
Roman BBQ
Salvete readers and history-lovers!
Well, Summer has finally arrived in the northern hemisphere, and that means dining al fresco with friends and family, sunny days (one hopes!), and time spent beside bodies of water.
It also means people will be firing up their barbecues! And so, with the upcoming North American holidays of Canada Day (July 1st) and Independence Day in the USA (July 4th), I thought it would be fun to talk briefly about food!
This isn’t just a history post about food in ancient Rome. It’s a practical post, because at the end I’m going to share a recipe with you that is easily done. But first…
We can’t really have a discussion about food in ancient Rome without talking about one man in particular.
He was the gastronome du jour during the reigns of Augustus and Tiberius, and his recipes were used for hundreds of years after his passing.
I’m speaking, of course, about Apicius, or, more formally Marcus Gavius Apicius (25 B.C. – A.D.37).
Apicius was a man who was largely concerned with fine living and fine food in ancient Rome and his work ‘On Cookery’, also known as ‘Cookery and Dining in Imperial Rome’, which has come down to us, is chock-full of recipes from wines and oils, to desserts, sauces, broths, a lovely array of vegetables, and spices.
There is also a lot about different meats and sea foods, and their preparation and uses, and several of them are quite disturbing if not entertaining.
Apicius’ ‘book’ might have been a sort of Julia Child cookery book of the ancient world, widely used in the kitchens of well-to-do Romans. Here is a picture of a manuscript copy from the A.D. 900:
When I think of Roman cooking, the first things that I imagine are outlandish dishes and meats that I would never consider eating myself. And if you peruse Apicius, you will indeed read about some things abhorrent to your modern tastes.
Book II of Apicius, dealing with ‘Minces’ includes recipes for Isicia de cerebellis (bain sausage),and Vulvulae Botelli (a dish of sow’s matrix). Or how about Book IV which deals with ‘Miscellanea’ such as Patina Frisilis (vegetable and brain pudding)?
Book VII on ‘Sumptuous Dishes’ has recipes for Vulvae Steriles (spayed sow’s womb), andAliter in Pulmonibus (another way to cook lung). Because I guess, one needs choices when cooking lung!
And then there is everyone’s favourite in Book VIII on ‘Quadrupeds’ which goes into detail about Glires (stuffed dormice).
If you read through the text of Apicius, however, you will see that most of the dishes are quite appealing. There are a lot of wonderful vegetable dishes, and some recipes for meats that would make your mouth water.
With that – and BBQ season – in mind, I thought I would share one of Apicius’ more well-known recipes with you.
What is it?
Hamburgers.
Yes. You heard that correctly. Hamburgers, or, to be more precise, Isicia Omentata.
So, how do you make hamburgers from a 2000 year-old recipe? Let’s see what Apicius says in Book II (chapter 1, 47) on ‘Minces’:
Finely cut pulp of pork is ground with the hearts of winter wheat [fine wheat flour or cream of wheat] and diluted with wine. Flavor lightly with pepper and broth and if you like add a moderate quantity of myrtle berries also crushed, and after you have added crushed nuts and pepper [pepper corns or allspice] shape the forcemeat into small rolls, wrap these in caul, fry, and serve with wine gravy. (Apicius on Cookery)
That’s it. Not much to go on, but the basic ingredients are there. Beef was not as commonly eaten, so it is not surprising that pork was the meat of choice, though you could make this with just about any kind of mince, including a modern veggie mince option.
Another translation of the text reveals some different ingredients too. Here is a simplified version:
500g minced meat (or a vegan mince substitute)
60g pine kernels
3 tsp. Garum (Roman fish sauce – you can use a fish sauce from the grocery store, or just regular sea salt)
Ground pepper
Handful of coriander
Juniper berries (optional) – this is a coniferous berry that is used in cooking, but be sure to buy the edible kind, for some species, like Juniperus sabina, are toxic!
Caul fat (optional) – this is the thin membrane which surrounds the internal organs of some animals
I admit that I had to look up what ‘Caul fat’ is and, well, I think I would leave that part out. The meat will hold together without it if you use bread or wheat in the mixture. As with many Roman dishes in Apicius, the spices are exotic and interesting, so whether you opt for a meaty or meat-free version of this recipe, it should be a tasty treat hot off the grill!
If you try this out, let us know how it goes in the comments, and whether or not you made any adjustments to the recipe.
To read the full text of Apicius, you can do so for free on the Project Gutenberg website here: http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/29728
Have a look at the dishes throughout. You never know! You might just have the makings of a Roman BBQ fit for an emperor!
Thank you for reading!
Roman Ghosts – Sentries of the Saxon Shore
Salvete, Readers!
Today we have our second post in the Roman Ghosts series, and this one is guaranteed to give you shivers.
If you missed the first post about Shades in Eburacum, you can check it out by CLICKING HERE.
Many of you have written to us about Roman ghost sightings in the UK, and we are keen to research them and share with everyone. Rest assured, they’re all on the list! Today’s post comes by way of a tip from Eagles and Dragons reader, Michael Dennis.
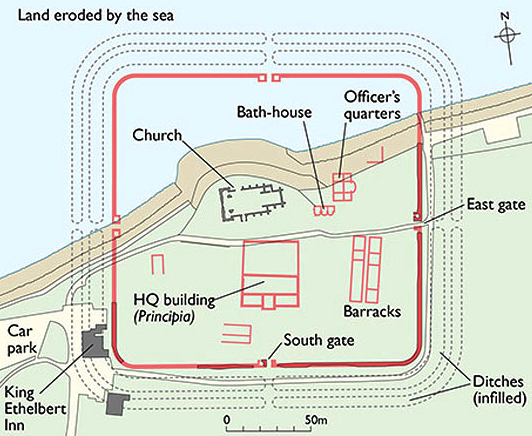
This particular look at Roman ghosts takes us to Reculver on the Kentish coast in England, in particular a site on the promontory at the mouth of the Watsum Channel, facing the Isle of Thanet.
Before we get into the spectral sightings associated with this remote location, we should, of course, look briefly at the history of the place.
Reculver was the site of Roman Regulbium which comes from the Celtic name meaning ‘at the promontory’.
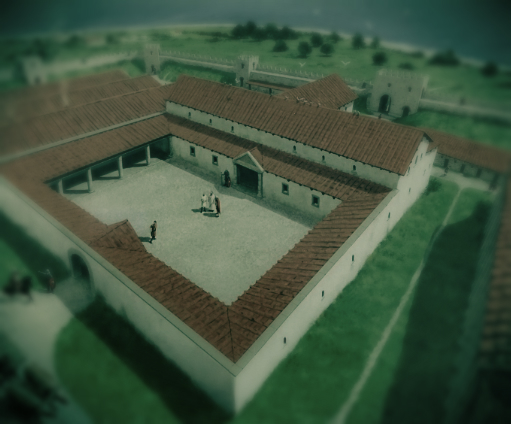
It was on this site during the Claudian invasion of Britain in A.D. 43 that a Roman fortlet was first built. Tense times in the land, of course. Eventually, the fort was connected by road to the settlement of Durovernum, modern Canterbury.
Eventually, in the late second century, a larger Roman castrum was built on the site, and this included a basilica as part of the principia (headquarters building), barracks, a bathhouse, and even a nearby oven which was located outside the walls. The walls themselves were almost fifteen feet high and ten feet thick. Sadly, much of the fort has been lost to the sea and erosion.
What does remain are two of the Roman towers which were incorporated into the early medieval Saxon church of St. Mary’s. More on these towers later…
The Notitia Dignitatum, the great Roman administrative document of the early fifth century, indicates that the Cohors I Baetasiorum was stationed at Regulbium. These troops of the Baetasii tribe inhabiting the lands between the Rhine and the Meuse, in Germania Inferior, were a good distance from their homes.
Regulbium was apparently abandoned after A.D. 360, but from what we have been reading, it may well be that some of the troops never went home.
Try and imagine a soldier, or a cohort of soldiers, based in a specific location for an extended period of time. Routine and disciplina, as the Romans called it, were central to a soldier’s life. Sometimes they lived and died in a specific place, had families, lost loved ones, took life and shed blood.
Well, in Regulbium to this day, it seems that some of the Roman soldiers are determined to keep to their schedules and their posts.
There have been many reports of Roman soldiers seen on patrol at Reculver fort (Regulbium) or keeping ghostly sentry duty there, so much so that visitors, even in summer, claim that there is something very ‘wrong’ about the place.
Apparently, the site of the Roman fort is so haunted that it has become a destination for amateur ghost hunters!
But it isn’t just the ghosts of groups of Roman soldiers on patrol that people have reported seeing. There have also been chilling reports of a lone Roman soldier standing stolidly at his sentry post somewhere between the two remaining towers that stand there to this day.
What might the shade of that Roman be looking out for? A returning patrol? Raiding Saxon ships coming into the isle between the fort and Thanet?
Who knows? One thing is for sure, there are more than just the shades of Roman soldiers lurking around the fort.
There have also been numerous reports of phantom babies crying on the wind when people have visited the fort!
One might think that this is just the gusting wind playing tricks on visitors to the fort. Then again, perhaps not.
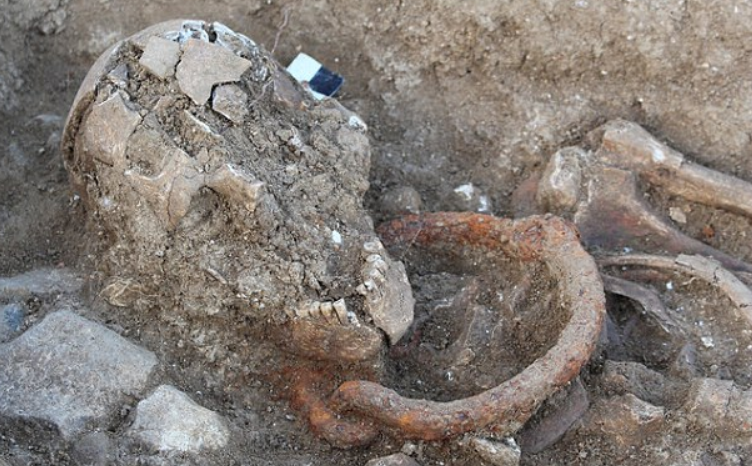
When excavations were carried out at the fort, the burials of ten infants were found within the fort itself, and six of these were associated with specifically Roman buildings.
There are some theories that the infants were part of a ritual sacrifice there, but it is not known if they were dead already (stillborn), or if they were killed as part of the ritual.
Seeing as Romans more or less frowned on human sacrifice (apart from in the arena), the slaying of babies does seem to be a bit of a stretch, but one never knows. Perhaps the Baetasii tribe from the Rhine region did that sort of thing, perhaps not.
Either way, the remains of infants have been found, and whatever the circumstances of their deaths, it seems likely that the wailing of their little shades at the fort would be enough to turn the legs of the toughest legionary to mush.
Have you been to the ruins of Regulbium? Would you go after reading this?
I’m not sure I would.
We hope you’ve enjoyed this second post in the Roman Ghosts series. For more information on the haunted site you can check out the book Haunted Kent, by Janet Cameron.
For information about the archaeology and ruins of Roman Regulbium, you can check out the Historic England page by CLICKING HERE.
Remember, if you know of any Roman ghost stories in any part of the former Roman Empire that you would like to share, just send us an email through the Contact Uspage of the website and we’ll look into it.
Thank you for reading!
Ancient Everyday – Pets in Ancient Rome
Salvete Romanophiles!
We’re back for a new Ancient Everyday post. If you missed the last one on coinage in the Roman world, you can check it out HERE.
This week, we’re looking at pets in the Roman world, and let me tell you, this turned out to be a much bigger, more complex topic than I had imagined! So, this will be something of an introduction to a topic that could well take up an entire book.
A quick shout-out to Jenny Villar who suggested this topic.
The first thing most of us picture when we think of animals in ancient Rome is no doubt the display bloody entertainment in amphitheatres like the Colosseum. But that is only part of the picture.
Before we discuss household pets, we should first take a look at the relationship ancient Romans actually had with animals.
Romans, it seems, were absolutely fascinated with animals!
They also had a strange, contradictory relationship with animals. They admired and were in awe of wildlife, and yet they used them to death, quite literally.
Animals served many purposes in the Roman world.
We have already alluded to entertainments in the amphitheatres and circuses of the Empire where any number of grisly pairings of beasts took place. But this category would also have included using animals for hunting (as both hunter and prey), in the wild or in the arena. Romans loved to watch animals be hunted, fight, and be killed, whether in the amphitheatre, or a private cock-fighting pit.
Animals were also labourers in the city, the countryside, and in the ranks of Rome’s legions across the Empire as beasts of burden and more.
One area that is sometimes overlooked is the use of animals for religious purposes. Animals were sacrificed to the gods on a daily basis for a variety of reasons, and were often specifically bred for this purpose. As examples, only the whitest of doves might have been offered to Venus, Goddess of Love, or the blackest of sheep to chthonic gods such as Dis.
Animals were also used as ornaments in the Roman world, especially in the homes and villas of the rich and powerful. The emperors Domitian and Caracalla are both said to have had pet lions that followed them around, and some wealthy Romans even had elephants, the most exotic symbol of Roman power, to transport them to dinner parties.
What the valet slave would do with that, I don’t know!
What seems apparent is that exotic animals were as much a show of Roman wealth and power as the most expensive jewels, and some rich Romans had gardens filled with various exotic animals – a sort of ancient equivalent to a nineteenth-century menagerie.
Included in the long list of animals that appeared in the amphitheatres or homes of the Roman world were parrots, ostriches, monkeys, lions, leopards, lynxes, tigers, elephants, rhinos from Asia and Africa, and more.
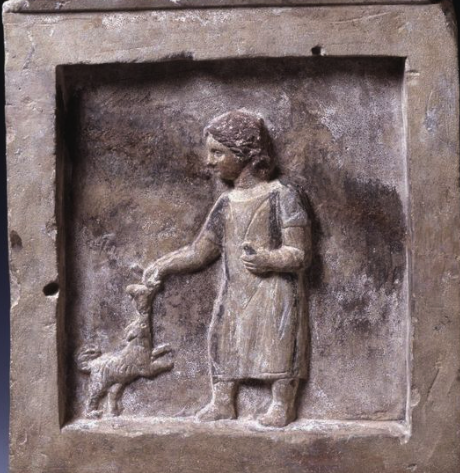
But we’re here to discuss animals as pets, specifically. In doing so, we might expect the usual array of animals we’re familiar with today, but, as ever, the Romans have put a twist on things for us. For instance, some children were said to have had pet goats or deer who were sometimes hooked up to little wagons or carts to pull them around.
We’ll go through a few of the animals that were said to have been kept as pets in ancient Rome.
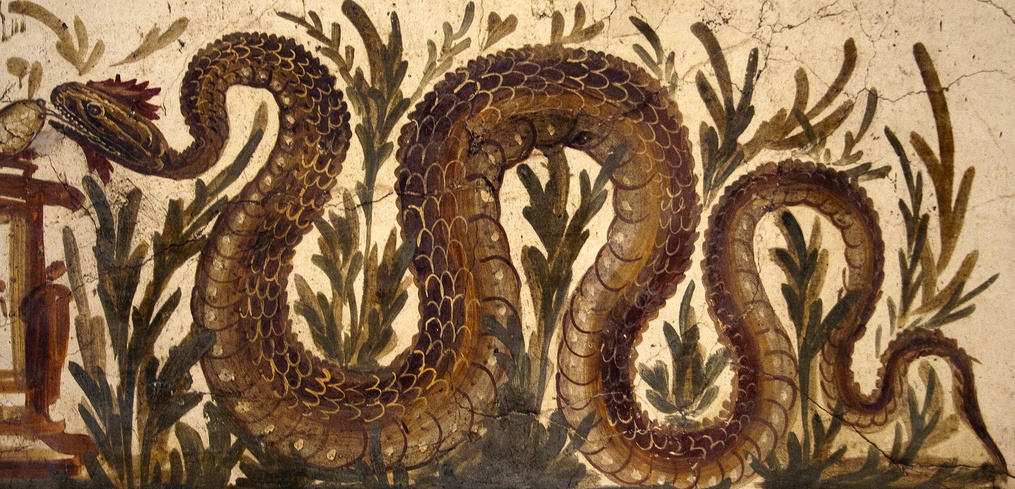
Snakes. Let’s just get this one out of the way now. Yes. The Romans had pet snakes. In fact, the idea of a household with a resident snake is quite ancient.
In the ancient world, snakes were not only useful in destroying vermin such as mice and rats. They were also sacred, and strongly associated with healing. Think of the god Asclepius who is often pictured with a snake around a staff, that symbol which has been adopted by the medical profession.
In ancient Greece, many households had a snake which acted as a sort of household guardian. In fact, in certain parts of the Mediterranean to this day, it is considered bad luck to kill a snake.
In ancient Rome, emperors had sent to Epidaurus and the Sanctuary of Asclepius there for some of the sacred snakes used in healing, and these were kept on Tiber Island. The emperors Tiberius, Nero, and Elagabalus all kept snakes.
Now, whether or not the residents of Suburan tenement blocks kept snakes, I’m not sure. One hears of people with pet snakes today, so I imagine the idea is not so far-fetched.
Fish were also kept as pets, but these appear to have been something relegated to the upper classes who had the space and land for large fish ponds. One wonders how attached some became to these fish, for surely they would have ended up on the tricliniumtable at some point.
Sparrow! my pet’s delicious joy,
Wherewith in bosom nurst to toy
She loves, and gives her finger-tip
For sharp-nib’d greeding neb to nip,
Were she who my desire withstood
To seek some pet of merry mood,
As crumb o’ comfort for her grief,
Methinks her burning lowe’s relief:
Could I, as plays she, play with thee,
That mind might win from misery free!
…
To me t’were grateful (as they say),
Gold codling was to fleet-foot May,
Whose long-bound zone it loosed for aye.
(Catullus, Lesbia’s Sparrow)
Birds appear to have been much more popular a pet in ancient Rome than they are today. In the quote above, we hear from Catullus about Lesbia’s sparrow, or ‘passer’, which she adores.
When it comes to birds, with the length and breadth of the Empire, there was opportunity for an impressive array of species from ducks and geese to ostriches, peacocks, budgies and parrots. In the case of the latter, things get a bit odd when one considers the fact that parrot tongues were something of a delicacy. Again, the contradictory relationship Romans had with their animals.
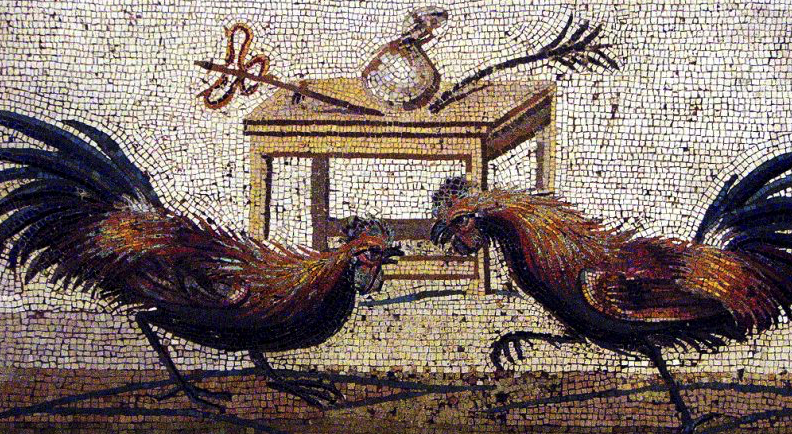
One popular pastime was, of course, cock fighting. This still goes on in certain parts of the world today, but in ancient Rome, it was also a sport for the upper classes. Plutarch describes how Octavianus always beat Mark Antony at cock fighting:
…we are told that whenever, by way of diversion, lots were cast or dice thrown to decide matters in which they were engaged, Antony came off worsted. They would often match cocks, and often fighting quails, and Caesar’s would always be victorious. (Plutarch, Life of Antony)
I suppose Octavian had to be better at something than Mark Antony, and I imagine that it rankled Marcus Antonius to have Octavianus’ cock beat his own.
Anyway…moving on…
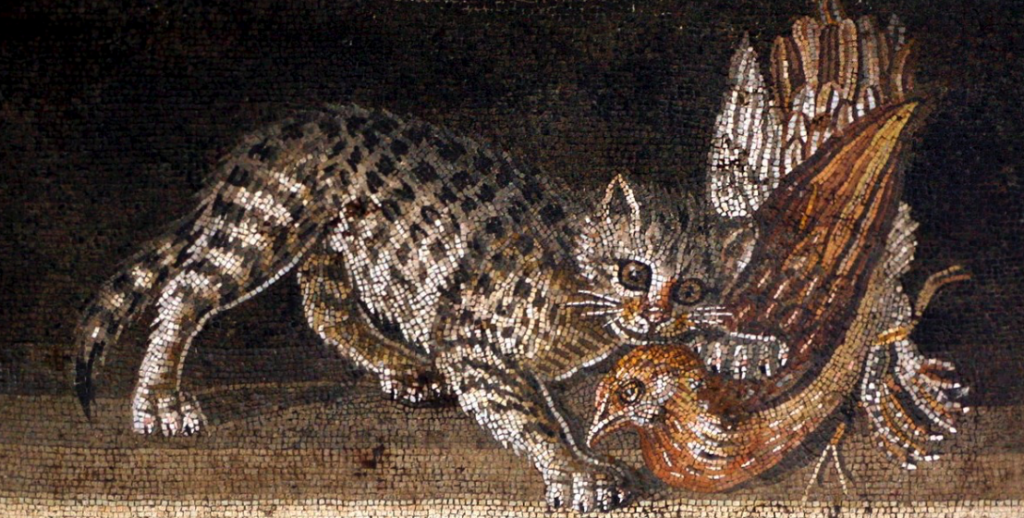
Now we come to the felines of the Empire.
Certainly, exotic big cats were prized in the arenas and menageries, and we have already mentioned Domitian and Caracalla’s pet lions.
But let’s talk about cats as we know them. Today, cats are a very popular pet, but in the world of ancient Rome, they were not so adored as you might expect. Birds and dogs were more popular than cats, though if you walk the streets of Rome or Athens today, you’d think cats had taken over the world.
In ancient Rome, cats served a more utilitarian purpose. They were kept as pets, but it was more for the purpose of catching vermin. There were plenty of mice and rats to go around in Rome, of that we can be sure, though there is mention of another use. The ancient writer Palladius points out that the cattus (Palladius was apparently the first to use the word ‘cattus’) was very good for catching moles in artichoke beds!
I didn’t even know moles liked artichokes.
There was of course one part of the Empire where cats were revered above all other animals, and that was Egypt. Cats were sacred there, and in my research I even read that when cats were smuggled out of Egypt, a ransom was paid to get them back! I wonder if some entrepreneurial Romans ever created a cat-ransom racket to take advantage of the Egyptians’ love of felines?
Of course we cannot discuss animals in the Roman Empire without touching on what was considered a most noble animal – the horse.
Horses were extremely important in the ancient world. Not only were they used as beasts of burden and farm animals, but they were also essential on military campaign as pack animals or in the ranks as auxiliary cavalry.
They were also central to entertainment in the Roman world as chariot racing in the hippodromes of the Empire, like the Circus Maximus in Rome, was the most popular sport around. You can read more about chariot racing HERE. Champion horses were well-treated and even received a pension and luxurious retirement at the end of their careers.
Horses were pets too, and one of the main activities for those in the countryside, rich and poor, was riding for leisure.
Probably one of the most famous instances of a pet horse from the Roman world is Caligula’s horse Incitatus. Suetonius goes into some detail:
He used to send his soldiers on the day before the games and order silence in the neighbourhood, to prevent the horse Incitatusfrom being disturbed. Besides a stall of marble, a manger of ivory, purple blankets and a collar of precious stones, he even gave this horse a house, a troop of slaves and furniture, for the more elegant entertainment of the guests invited in his name; and it is also said that he planned to make him consul. (Suetonius, Life of Caligula)
We’ve looked at a few species of animal that were popular among ancient Romans as pets, but none of those mentioned above were more popular as pets in the ancient world than dogs.
As far as pets, dogs were the favourite, and they had an age-old relationship with humans. They were friends, workers, and family members. Dogs were even worthy of serving the gods – think of Diana and her hunting hounds.
The oldest mention of a dog by name is in the Odyssey when there is reference to Odysseus’ dog, Argus.
‘This dog,’ answered Eumaios, ‘belonged to him who has died in a far country. If he were what he was when Odysseus left for Troy, he would soon show you what he could do. There was not a wild beast in the forest that could get away from him when he was once on its tracks. But now he has fallen on evil times, for his master is dead and gone, and the women take no care of him. Servants never do their work when their master’s hand is no longer over them, for Zeus takes half the goodness out of a man when he makes a slave of him.’
So saying he entered the well-built mansion, and made straight for the riotous pretenders in the hall. But Argos passed into the darkness of death, now that he had fulfilled his destiny of faith and seen his master once more after twenty years. (Homer, The Odyssey, Book 17)
There were different breeds for different purposes in ancient Rome. There were dogs for entertainment, fighting in the arena. These dogs were known as canes pugnaces. There were dogs in the Roman army, usually a breed of mastiff, and also for use as guard dogs.
The Roman agriculture writer, Grattius, goes into some detail about various breeds of dogs:
Dogs belong to a thousand lands and they each have characteristics derived from their origin. The Median dog, though undisciplined, is a great fighter, and great glory exalts the far-distant Celtic dogs. Those of the Geloni, on the other hand, shirk a combat and dislike fighting, but they have wise instincts: the Persian is quick in both respects. Some rear Chinese dogs, a breed of unmanageable ferocity; but the Lycaonians, on the other hand, are easy-tempered and big in limb. The Hyrcanian dog, however, is not content with all the energy belonging to his stock: the females of their own will seek unions with wild beasts in the woods: Venus grants them meetings and joins them in the alliance of love. Then the savage paramour wanders safely amid the pens of tame cattle, and the bitch, freely daring to approach the formidable tiger, produces offspring of nobler blood. The whelp, however, has headlong courage: you will find him a‑hunting in the very yard and growing at the expense of much of the cattle’s blood. Still you should rear him: whatever enormities he has placed to his charge at home, he will obliterate them as a mighty combatant on gaining the forest. But that same Umbrian dog which has tracked wild beasts flees from facing them. Would that with his fidelity and shrewdness in scent he could have corresponding courage and corresponding will-power in the conflict! What if you visit the straits of the Morini, tide-swept by a wayward sea, and choose to penetrate even among the Britons? O how great your reward, how great your gain beyond any outlays! If you are not bent on looks and deceptive graces (this is the one defect of the British whelps), at any rate when serious work has come, when bravery must be shown, and the impetuous War-god calls in the utmost hazard, then you could not admire the renowned Molossians so much. (Grattius, Cynegeticon)
Wolfhounds and greyhounds were used for hunting by Romans, and there were even dogs used for religious sacrifice.
Apart from the larger breeds used for the purposes mentioned above, smaller lapdogs were very popular house pets in the Roman world. These were most likely similar to today’s maltese breed of dog.
There are several examples of beloved dogs on grave monuments for family or children that survive. The fact that Romans even did this is testament to the importance placed upon them.
We have but scratched the surface of this vast topic on pets and animals in the Roman world. I hope you’ve found it interesting.
At the end of the day, the wide array of animals that served as pets, workers, food, religious sacrifice and more was as vast and varied a reflection of the world as the Roman Empire itself.
Thank you for reading.
Inspiration for Writing the Past – An Eagles and Dragons Playlist
Music brings a warm glow to my vision, thawing mind and muscle from their endless wintering.― Haruki Murakami
How does music help you? How does it affect you and your creativity? Has it helped you to overcome obstacles and see the world from a different angle?
The answers to these questions will vary from person to person.
This week on the blog, I want to share something different with you, something related to my own creative process, particularly when it comes to writing historical fiction.
For the entirety of my life to this point, music has played an influential role at every stage. I grew up in a household where music was ever-present and appreciated. Whether it was classical or movie music, opera, folk, rock’n roll, period music or punk rock, music was always there. It was always marking big events in my mind, accompanying me on my journeys, accenting my experiences.
When I sift through my own memories, there is always music to go with them.
Who hears music, feels his solitude, Peopled at once.― Robert Browning
Since the beginning of my writing career in my mid-teens, music has always been a part of my creative process.
I write to music, pure and simple. I have to.
Every writer is different, and among those who do write to music I’m sure there is a vast array of musical types that inspire.
For me, the music of choice for writing has always been movie soundtracks. They’re highly emotive and varied, different tracks suited to different types of scenes.
Music is like a dream. One that I cannot hear.― Ludwig van Beethoven
I can’t just write to any type of movie soundtrack, however. You won’t find me listening to Star Wars, Indiana Jones or The Lord of the Rings soundtracks while writing. The images of those films are burned onto my memory and I know the exact part of the movie where every note is played. That would unduly affect my own storytelling.
But there are countless movie soundtracks that, to me, evoke something of the ancient world, are a bit more exotic, and have the power to transport me out of the modern world and into the past.
For each writing project, I create a separate playlist which I will listen to when doing research, riding on the subway to work, driving in my car, or when I’m out for a walk. The music is there at all times when I’m thinking about my work-in-progress.
Today I want to share with you the most prominent soundtracks on my playlist for the book I’m currently writing, Isle of the Blessed (Eagles and Dragons Book IV).
Some of these might be familiar to you, others not, but I hope you will enjoy all of them. Where available, I’ve embedded samples from some of the soundtracks (the samples are often uploaded by individual fans and not the composers, hence the pictures).
*There are a lot of embedded audio files below, so when you first load the page, you will probably need to click ‘refresh’ once on your web browser so that the SoundCl0ud players show up.
(A quick note here in the interests of transparency that the Amazon and iTunes links are affiliate links – this means Eagles and Dragons Publishing will get a small portion of the proceeds if you purchase it)
I hope you enjoy this musical peek into the creative process behind a book I know many of you are waiting for…
Fans of ancient Greece among you will be familiar with the 300 movies, and the soundtrack from the first film has some powerful, really driving tracks. But there are also some wonderfully solemn tracks that make me feel as if I am standing in the shadow of Mt. Taygetus outside of Sparta itself. This soundtrack has been with me on a couple books, from battles to quiet moments with Lucius Metellus himself. The track that particularly stands out to me is ‘Message for the Queen’. (Please forgive the picture this person uploaded – it has nothing to do with the movie!)
(Amazon and iTunes)
It goes without saying that as the Eagles and Dragons series is set in the Roman Empire, that some of the soundtracks should be from movies set there as well. I thought Pompeii was a decent film but it is not one that I watch over and over again, so it was easy for me to separate the images of the film from the music. This movie has some great street scenes in it that really do evoke the hustle and bustle of Pompeii. The track I like for that, is aptly named ‘Streets of Pompeii’.
(Amazon and iTunes)
This is the only non-period movie on the playlist. Hans Zimmer, who is one of the great film composers of our time, really created a fantastic soundtrack with Black Hawk Down. I’ve used this in the past for all previous Eagles and Dragons novels, especially as it evokes the desert and the East for me. However, the track I love most is the very moving ‘Leave No Man Behind’. When writing about soldiers and brotherhood, whether in the ancient world or the present, this track makes you feel.
(Amazon and iTunes)
If you haven’t seen the film Centurion, then you will definitely want to check it out. It’s showing on Netflix at the moment if you’re interested. Obviously this movie takes place during the Roman Empire and Ilan Eshkeri’s soundtrack is a fabulous journey of intensity and despair. One track that I sometimes play on repeat because of its sublime intimacy and ‘moment of calm’ aspect, is the track called ‘Necromancer’. Have a listen. It’s beautiful.
(Amazon and iTunes)
We’re back to the 300 movies, this time with the second one entitled 300: Rise of an Empire, music composed by Junkie XL.
This soundtrack has been one of the most influential on my writing of late, and in addition to inspiring the battle scenes in Warriors of Epona (Eagles and Dragons Book III), and scenes in Isle of the Blessed, it was also a huge inspiration for me when writing the climactic scene for Heart of Fire: A Novel of the Ancient Olympics. The track ‘History of the Greeks’ gives me chills every time. Every track has something to offer here, so you won’t want to miss this one. Here is a sample of several tracks from the album.
(Amazon and iTunes)
One movie that I don’t think got the recognition it deserved is Dracula Untold, and the music for this is no different. Ramin Djawadi, most famous for his soundtracks for the Game of Thrones series, created a fantastic soundtrack for Dracula with glorious highs and lows. One of my favourite tracks on this one is ‘Mirena’. If you like Dracula films with history thrown in, you have to check this out.
(Amazon and iTunes)
Those of you who have known me for a while will know that I’m a big fan of all things Arthurian. When I first saw the BBC series Merlin, I was a bit sceptical at first, but after a few episodes, I was hooked. The series is dramatic, funny, tragic and uplifting and the music and themes created by Rob Lane and Rohan Stevenson are no different. As Isle of the Blessed takes place in Britannia, the music fits nicely with the mystery of the setting. The track ‘Gwen and Arthur’ is a particularly moving one.
(Amazon and iTunes)
Speaking of Ramin Djawadi, it was inevitable that at least one of the Game of Thrones soundtracks should be on my playlist. Actually, the music for both season one and two are on the list. I’m not a super fan of the television series, though I do enjoy it. I am, however, a super fan of the music. The vast array of themes for different characters and settings, countries and more that Ramin Djawadi has created is truly mind-blowing. There’s something for everyone and every situation in the music for Game of Thrones. I am hard-pressed to pick just one track but I have to say that I am post partial to the ‘Winterfell’ theme.
(Amazon and iTunes)
One movie that got absolutely panned at the cinema was Immortals, the movie about Theseus. Now, I have to admit that I actually like this movie quite a bit. Granted, it’s more of a big-time fantasy movie that a serious take on mythology, but that’s ok. These tales are meant to be reinvented. That’s why they’ve lasted so long! Trevor Morris is a composer whose work I’ve enjoyed for a few years and his soundtrack to Immortals is one of my favourites. It just transports me to another time and place and makes me feel like the gods are standing right there with me. The track ‘Do Not Forsake Mankind’ is the track to listen to on this, though they are all pretty fantastic.
(Amazon and iTunes)
Composer Joseph LoDuca is no stranger to television soundtracks, having written the music for the Hercules: The Legendary Journeys and Xena: Warrior Princess shows back in the nineties. He’s been a favourite in our family as my own mother, a former opera singer, performed on the Xena Season Four soundtrack. Joseph LoDuca’s music is fantastically exotic, quirky and emotional. More recently, he composed the music for the television series, Spartacus: Blood and Sand.
Spartacus was a fantastic and gritty series and LoDuca’s music fit the bill perfectly. You really do feel like you are in ancient Rome, on the sands of the amphitheatre, or in the characters’ private dwellings. Check out the soundtrack for the first season, in particular for me, the track ‘No Life Without You’.
(Amazon and iTunes)
A more recent history-themed show is Vikings. This epic series has found quite a bit of success, and the atmosphere that the film makers have created is only enhanced by the music of Trevor Morris. I’ve only delved into the first season’s soundtrack for this series, but it is a wonderfully sprawling and mysterious soundscape. There are so many tracks to choose from, but at the moment, one of my favourites is ‘Ragnar Takes the Throne’.
(Amazon and iTunes)
One of my more recent soundtrack acquisitions is from the Arthurian-themed movie Tristan and Isolde. This is quite simply, a beautiful tragic tale that does this story of doomed-love utmost justice. Composer Anne Dudley has such a knack for inserting gut-wrenching feeling into the most intimate, quiet scenes. This soundtrack has been a big inspiration for Isle of the Blessed. You need to listen to this one right now. I’m especially enjoying the track ‘None Can Die’.
(Amazon – but not available on iTunes)
And finally…
I would be utterly remiss without mentioning the soundtrack that has been with me almost from the beginning of the Eagles and Dragons series – Gladiator.
This is the soundtrack that brought the names of Hans Zimmer and Lisa Gerrard (of Dead Can Dance fame) to the fore, and for good reason. Whenever I write about the grandeur of the Roman Empire, the frontiers of Numidia or Africa Proconsularis, or even Severus’ war in Caledonia, the music from Gladiator is churning in my brain.
I know this movie well, having watched it so many times, so it is strange to me that the images from the film do not intrude on my own conjurings. Hans Zimmer and Lisa Gerrard’s music has succeeded even in transcending director Ridley Scott’s vision and Russell Crowe’s outstanding performance.
I suspect that this soundtrack will be with me for many more books. All the tracks are good, but if you want to hear one of the more haunting ones, listen to ‘The Wheat’.
(Amazon and iTunes)
Music, when soft voices die, vibrates in the memory.― Percy Bysshe Shelley
I hope you’ve enjoyed this peek at the creative process and the wonderful music that is accompanying me on this very personal journey writing Isle of the Blessed.
Like the music, there are highs and lows, moments of inspiration, and times of despair, and that’s the beauty of the creative process, that we get to feel the full range of human emotion. With hope, I can impart the full measure of that to all of you, just as these wonderful composers have done for me.
Thank you for reading.
A man should hear a little music, read a little poetry, and see a fine picture every day of his life, in order that worldly cares may not obliterate the sense of the beautiful which God has implanted in the human soul.― Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Ancient Everyday – Coinage in Ancient Rome
Greetings ancient history lovers!
It’s been a while since the last Ancient Everyday blog post. If you missed the last one on Roman oil lamps, you can read it HERE.
Today we’re going to take a brief look at coinage in Ancient Rome from it’s inception to the early Imperial period and reforms of Emperor Augustus.
One of the reasons I love writing the Ancient Everyday series is that it shows is how much we actually have in common with the Roman world as far as our daily experiences.
Now, while we might not all have a big cache of loot lying buried in our back gardens, we do use money in some way shape or form on a daily basis.
Romans were no different in that regard, and whether they were getting paid for their legionary service, shopping in the markets of Trajan, or paying for the company of a lovely lupa in the streets of Pompeii, money was exchanged, and that usually in the form of coin.
But coins did not always exist in Rome, indeed not really across most of the early Mediterranean world.
In the ancient world, coins were first produced in the Greek cities of Asia Minor in the late 7th century B.C. These first coins were made of something called ‘electrum’ which was a mixture of gold and silver with simple designs upon them.
Eventually, by about 500 B.C. coin production had spread across the Aegean and to the Greek colonies of southern Italy. These first coins were of pure silver, but the mints of these southern Italian Greeks also produced the first coins made of bronze.
However, before coins were common across Italy, the currency usually came in the form of irregular-shaped lumps of bronze known as aes rude. These were valued by weight.
By the 4th century B.C. bronze was being cast in regular-sized, cast bars, and then by the 3rd century B.C. standard weights were introduced and bars were stamped with images. These were known as aes signatum.
During the Republic, c. 289 B.C., aes grave were introduced. These were pieces of bronze about four inches in diameter that were cast in molds. They superseded the previous, larger bronze bars and became known as an as, or aes, the name given to one of the later denominations of Roman coin.
The as was then divided into smaller values such as a semis (half-as), a triens (a third), a quadrans (a quarter), a sextans (a sixth), and an uncia (a twelfth). These were quite small, but perhaps they would have got you a honeyed pastry in the forum!
As Rome grew in power and wealth, the coinage seemed to follow suit. In the early 3rd century B.C., Roman silver coins began to appear, and these were based on Greek designs coming out of southern Italy. It appears that the first silver coins were struck in Rome itself from about 269 B.C., and the first silver denarii were issued around 211 B.C.
Eventually, silver became the standard for coinage over the previous bronze, and the denarius became the main silver coin of the Roman world.
Other changes were afoot too…
The as was reduced in size so that 1 denarius was equal to 10 asses in the second century B.C. And, around the time of the Second Punic War, gold coins were first issued.
Around 24 B.C. the Emperor Augustus established a standard system of coinage, and under this system, the minting of gold and silver coins was a monopoly of the emperor, and bronze coinage was issued by the Senate of Rome.
Under this new system, four metals were used in coinage: gold, silver, brass, and bronze or copper.
Gold and silver coins were for official uses like salaries, and the baser coins were for everyday uses like market shopping or tipping the attendant at the baths. Augustus knew what he was doing as when a soldier was paid in silver or gold, then the emperor’s face was staring right back at him from that shiny surface. The troops knew who was paying them!
Over time, largely because of increased military spending, the silver denarius, the backbone of the Roman monetary system, became debased until, during the reign of Emperor Severus, a denarius contained only 40-50% silver and the rest was bronze.
But how much were the actual coins worth during the early Empire? Here are the approximate values of the various coins equal to one golden aureus:
You needed 25 silver denarii to equal 1 aureus.
100 brass sestertii were equal to 1 aureus.
You needed 200 brass dupondii for one aureus.
400 bronze asses equaled one golden aureus.
800 brass semis were needed to equal 1 aureus.
And a whopping 1600 bronze quadrans were needed to equal the value of one aureus!
I imagine that the purses of the rich were much easier to carry around than those of the poorer classes in ancient Rome. That’s a lot of bronze to equal just one gold coin!
Of course, in the later Empire, some new denominations came into effect, such as the argenteus, the follis, the solidus, and the centenionalis. Values fluctuated and metals were debased depending on which way the Roman economy veered. Not unlike today, I suppose.
There is one aspect that we should touch on too, and that is the powerful marketing tool coinage was for emperors. Coins were everywhere and in everyone’s hands, and what better way to let the people of the Empire know who was their master and protector than to put your face on the very coins they sought to collect and use to pay for things in their daily lives.
With coinage, the Emperor’s face was with you at all times, reminding you who was in charge. Coins gave you their likeness and also helped to commemorate victories over Rome’s enemies.
One thing is for sure…
In the world of Imperial Rome, for better or worse, money was one of the things that made the wheels of the Empire turn, and coin passed through the hands of rich and poor alike. Only some had more of it than others.
Thank you for reading.
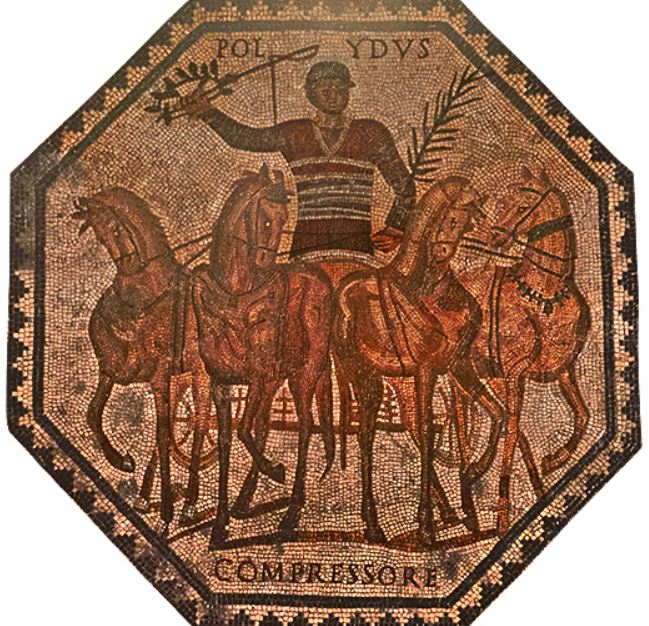
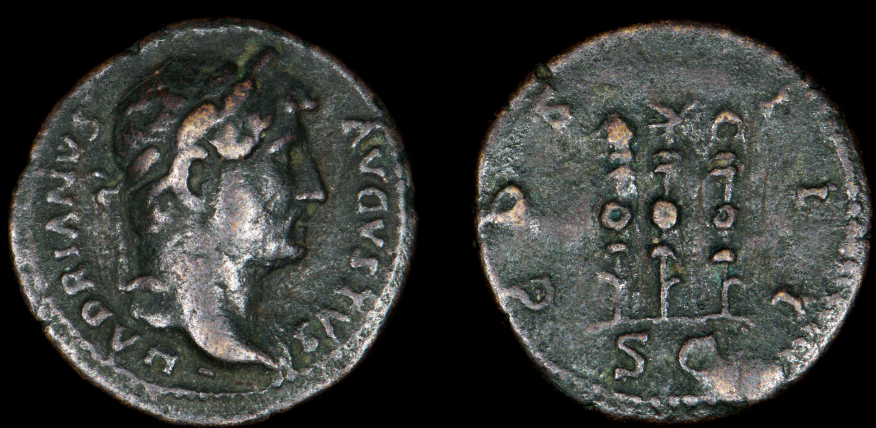
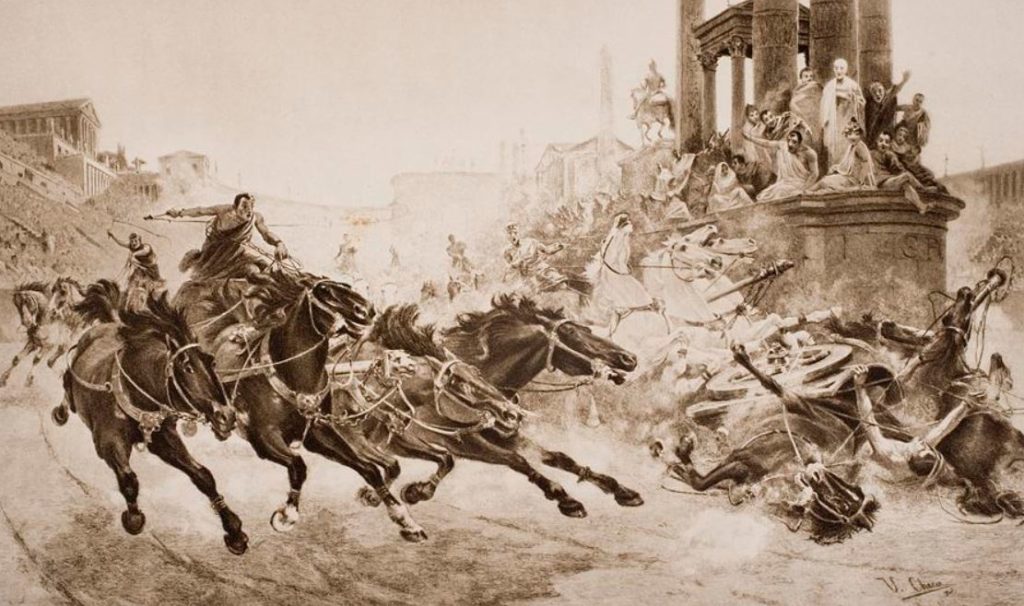
Chariot Racing in Ancient Rome
See you not, when in headlong contest the chariots have seized upon the plain, and stream in a torrent from the barrier, when the young drivers’ hopes are high, and throbbing fear drains each bounding heart? On they press with circling lash, bending forward to slacken rein; fiercely flies the glowing wheel. Now sinking low, now raised aloft, they seem to be borne through empty air and to soar skyward. No rest, not stay is there; but a cloud of yellow sand mounts aloft, and they are wet with the foam and the breath of those in pursuit: so strong is their love of renown, so dear is triumph. (Virgil, Georgics III-IV)
When we think of the raucous world of sport in ancient Rome, the images we conjure are most often of blood-soaked gladiatorial combat, or of chariot racing.
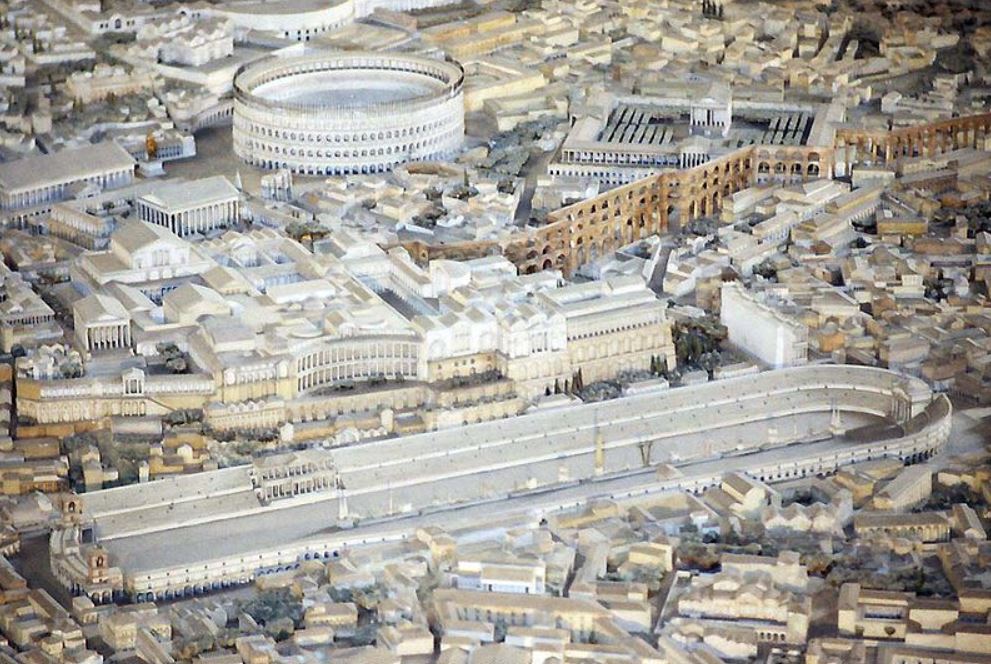
Today, we might think that gladiatorial combat was the most popular sport amongst the people of Rome, but in truth, nothing was more sensational than the chariot races put on in the great circus of Rome – the Circus Maximus.
In this post, we’re going to take a brief look at the circus itself, the charioteers, the horses, the fans, equipment, and what teams stood to win…and lose.
Their temple, dwelling, meeting-place, in fact the centre of all their hopes and desires, is the Circus Maximus. (Ammianus Marcellinus on Plebs and the Circus, XXVIII.4)
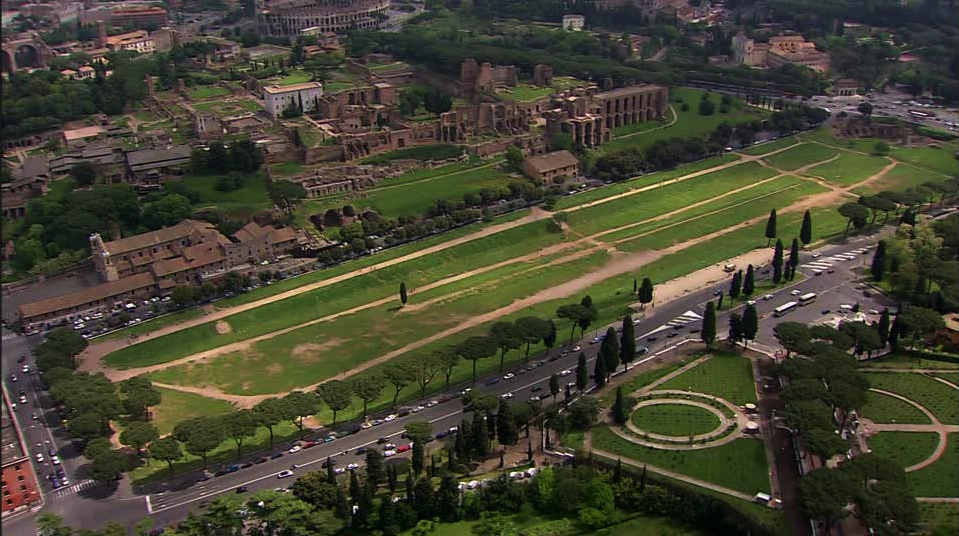
Chariot racing was an ancient sport handed down from the Greeks to the Etruscans and Romans early in the history of Rome, the races in the city of Rome being held in a dip in the land between the Palatine and Aventine Hills. Over time, the Circus Maximus was built upon by successive senates and emperors, making it the largest in the Roman world.
Rome’s great circus had an area of 45,000 square meters, making it twelve times larger than the Colosseum, and it could hold at least 150,000 spectators. With the addition of temporary wooden seating, the capacity was said to have reached 250,000!
The Circus Maximus was the largest and most expensive entertainment venue in Rome. Buildings had been added to it from the fourth century B.C. onward, going from wood to stone, and a major renovation was done in the first century B.C. Before the Colosseum was built, the Circus Maximus also hosted gladiatorial combats, wild animal hunts, and other games.
The Circus Maximus certainly owns its name, for by the time of Emperor Trajan, it was about 550-580 meters long, and about 80-125 meters wide. At the start of the track, there were twelve carceres, starting boxes, with ostia (gates) from which the teams would shoot out and charge the first 170 meters toward the central spina, which divided the course and which is what the teams raced around. The spina was 335 meters in length and 8 meters wide, and at each end of it were metae, the turning posts which the riders sped around. The spina was also ornamented with statues of the gods, towering palms, and obelisks from Rome’s campaigns in Egypt.
There were also large frames on the spina with mechanisms with suspended dolphins and eggs to count down the laps for a race. The total distance of a race of seven laps was about 5,200 meters over the packed earth and gravel track.
When it came to putting on games, or ludi as they were known, in the Circus Maximus, hundreds of staff were required in addition to the aurigae, the charioteers themselves. There were stable boys, grooms, cartwrights, saddlers, doctors, veterinarians, men at each of the starting gates (which were each six meters wide in Rome), men to clear the debris after crashes, lap counters, musicians, and even performers between races usually comprised of riders or acrobats.
That’s a lot of people to keep things running, but it was worth it to those who put on the games, for the people of Rome loved their chariot teams.
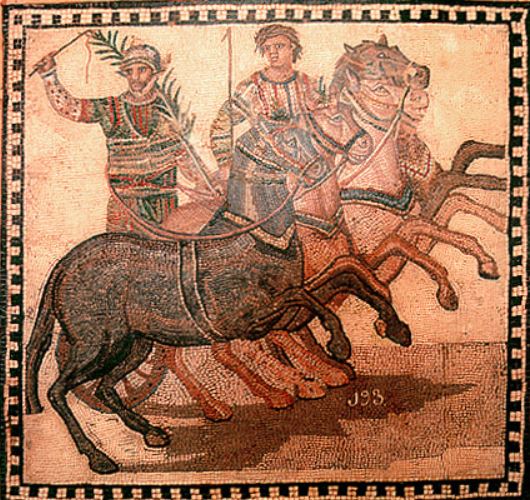
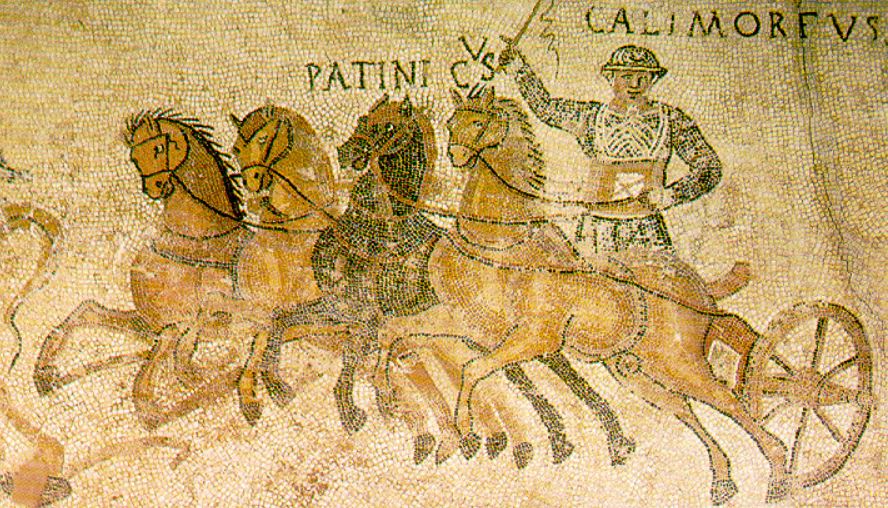
One might think that fans usually cheered for their favourite charioteers, but in truth, Romans were fans of their favourite factions, or factiones as they were known. There were four chariot factions in Rome: the Veneti (Blues), the Prasini (Greens), the Russati (Reds) and the Albati (Whites).
The four chariot factions of Rome were managed by the domini factionis, the ‘faction masters’ who were usually men of the Equestrian class. They would have sought out potential charioteers, made deals with others, and generally seen to the running of the faction and its success. The domini factionis were similar to the lanista of a gladiatorial school, or ludus.
In Rome, the factions had their headquarters, the stabula factionum, which contained accommodation and stables, on the Campus Martius, but their breeding grounds and training camps were located in the countryside.
People were wild for their factions, and there could be violence between the followers of each. During a race, each faction could enter either one, two, or three separate teams so that a full race could comprise up to twelve chariot teams running at a single time.
But who were the men who drove the factions to victory or defeat? Who were the charioteers of Rome?
O Rome, I am Scorpus, the glory of your noisy circus, the object of your applause, your short-lived favourite. The envious Lachesis, when she cut me off in my twenty-seventh year, accounted me, in judging by the number of my victories, to be an old man.
(Martial, Epigrammata, LIII. Epitaph of the charioteer Scorpus)
Outside of Rome, in the hippodromes of distant provinces, it was possible for individual owners to enter teams or even race themselves, but in Rome’s circus, it was the factions who entered the teams, and the professional charioteers, the aurigae, who raced for each faction.
The aurigae were usually slaves or freedmen, low on the status scale the same as gladiators, but they could achieve great fame and wealth.
In his Epigrammata, the poet Martial tells us of a famed auriga named Scorpus who was one of the few charioteers to achieve the status of miliarius. The miliarii were those who had won over one thousand races – Scorpus was said to have won 2,048!
Ancient chariot racing in Rome was not dissimilar to modern sports. People were loyal to their faction, their ‘team’ so to speak, and charioteers, like pro sports players today, might be traded to or wooed by other factions. It was not uncommon for a charioteer to move factions several times before settling down in the latter half of his career.
Servants’ hands hold mouth and reins and with knotted cords force the twisted manes to hide themselves, and all the while they incite the steeds, eagerly cheering them with encouraging pats and instilling a rapturous frenzy. There behind the barriers chafe those beasts, pressing against the fastenings, while a vapoury blast comes forth between the wooden bars and even before the race the field they have not yet entered is filled with their panting breath. They push, they bustle, they drag, they struggle, they rage, they jump, they fear and are feared; never are their feet still, but restlessly they lash the hardened timber.
At last the herald with loud blare of trumpet calls forth the impatient teams and launches the fleet chariots into the field. (Sidonius Apollinaris, To Consentius)
It wasn’t just the aurigae who achieved fame in the Circus Maximus. Horses too could be just as famous as their drivers, and oftentimes equine heroes were met with adoration.
Winning horses received palm branches, but also modii, which were measures of grain, with barley thrown into the mix. They were no doubt pampered back at the stabula factionum, and those horses who ran their factions to victory after victory enjoyed retirement in the countryside on a pension. They even received a burial with honour.
Race horses were bred and trained on private, and later imperial, stud farms, and the most successful breeds to race in the Circus Maximus were Lusitanos and Andalusian breeds from North Africa and Spain.
Though the horses were well-cared for by the factions, the racing was hard on their joints because of the tight turns of almost 180 degrees around the metae, and of course the great risk of injury.
Animal losses were high in the circus of Rome.
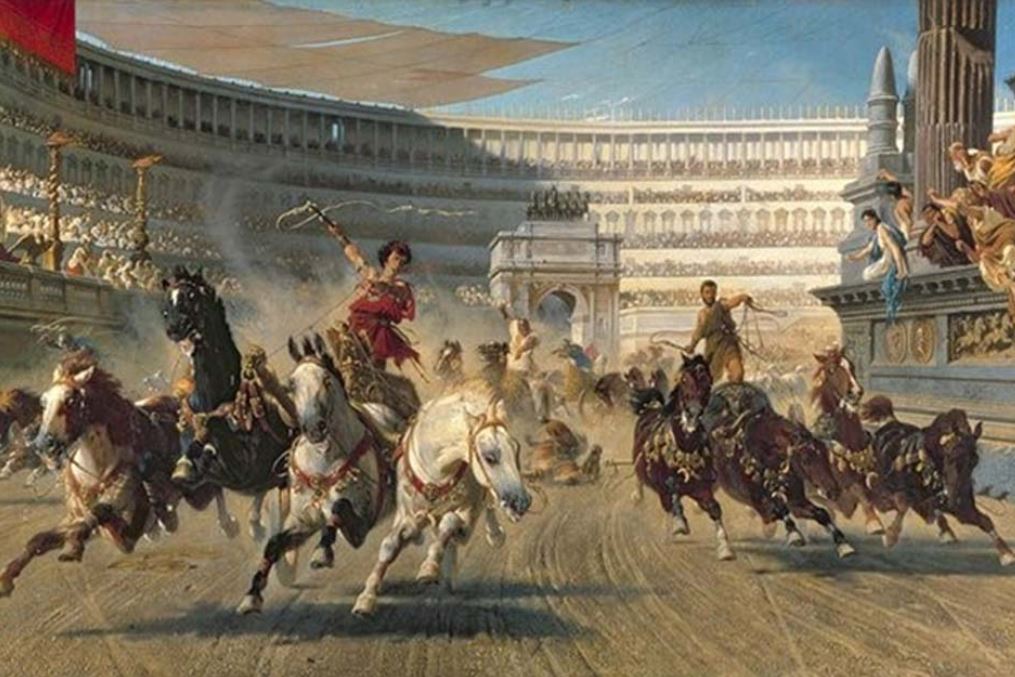
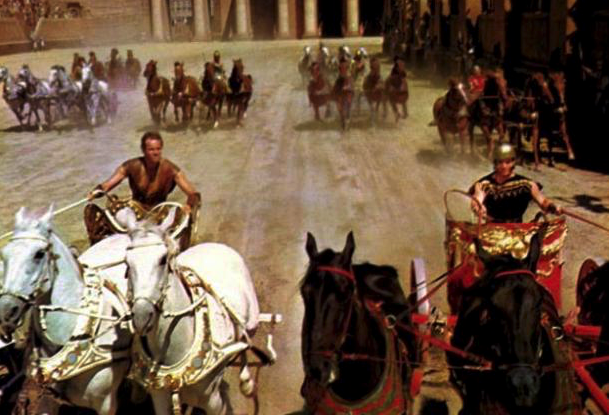
When it comes to the chariots and equipment used for the sport of chariot racing in ancient Rome, the movies have often been misleading.
In movies like Ben Hur (pictured above) the chariots are massive, some with long blades sticking out of the wheels. The chariots used in the movie made for some exciting film making and a great scene, but they were not at all accurate as far as what was really used.

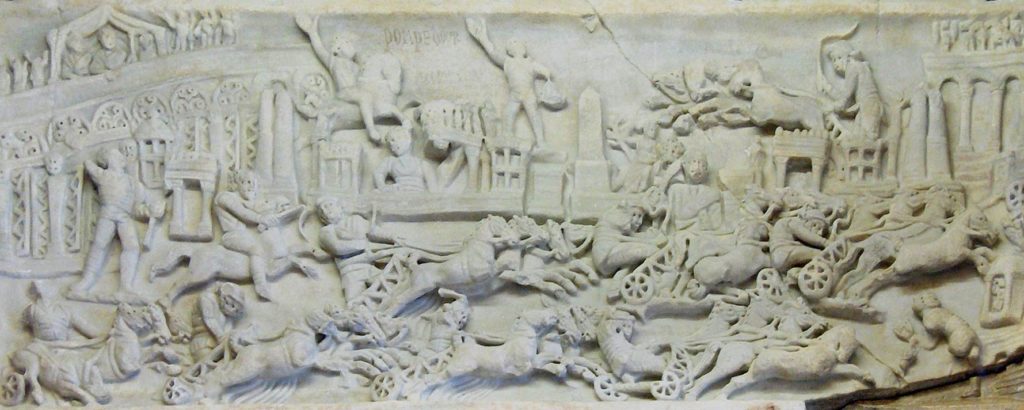
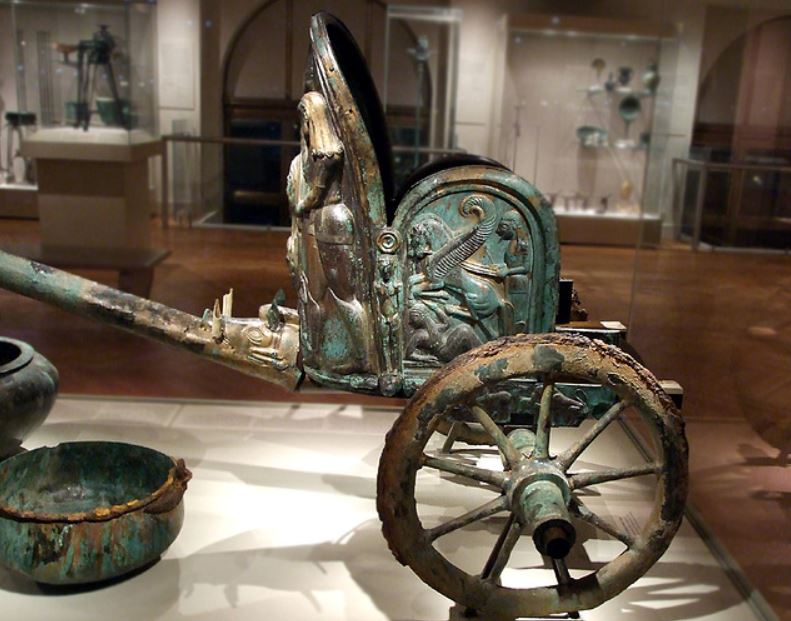
Statue of a Roman biga (two-horse chariot) found in the Tiber. Note how much smaller the chariots actually were compared to what we see in the movies
Roman racing chariots, which were adapted from the ancient Greek and Etruscan chariots, were light-weight affairs, consisting of a slight wooden frame bound with strips of leather or linen, and small wheels with 6-8 spokes.
The most common chariot was the quadriga, a four-horse chariot from ancient Greece. The other commonly-used chariot was the biga, a Roman two-horse chariot. These two types were what were raced most often in the Circus Maximus in Rome. However, there were said to have been six-horse chariots (seiugae), eight-horse chariots (octoviugae), and even a ten-horse chariot (decemiugae).
Unfortunately, no remains of an imperial Roman chariot have been found, so we are forced to rely on artwork for an idea of their appearance. However, the tombs of Etruscan nobility have yielded some two-hundred and fifty examples of chariots.
In ancient Greece, charioteers wore only a long chiton with a belt when they raced, but Roman and Etruscan aurigae wore a short chiton, a protective skull cap or leather helm, and a wide leather belt composed of many straps. They also wore linen or leather wrappings on their legs and carried a curved dagger on them.
Why did they carry a dagger?
Well, it wasn’t to attack each other during the races. The reason for the dagger was that unlike Greek charioteers who held the reins in their hands, Roman charioteers wrapped the reins around their waists in order to use their whole body to steer the team and have one hand completely free for the whip.
If they ever got into a naufragia, a ‘shipwreck’ as chariot accidents were called, the dagger was supposed to be used to cut oneself free of the reins that were wrapped about you. It certainly was a risk when driving a team of four horses up to 75 kms per hour while trying to cut off your opponents going into the turns and so on.
One thing’s for sure, Roman chariot racing was extremely dangerous, though perhaps not as hazardous to one’s life as gladiatorial combat.
Games, or ludi, were the highlight of the Roman calendar, and chariot racing in the Circus Maximus was always the main event. During imperial games, there were usually up to twenty-four races per day at Rome, and that could include up to 1,152 horses.
This was always an event on a titanic scale, and the people of Rome loved it!
People were fanatical about their factions, and the charioteers who risked their lives in the Circus Maximus must have felt near to gods when the adoration of the crowd shone full upon their faces.
Apart from the traditional victory palm, winning charioteers and their factions could receive massive fortunes for their success.
In Rome, prizes ranged from 15,000 to 60,000 sestercii per race! That’s far more than the annual pay for a legionary soldier who received about 900 sestercii per year during the early Empire.
One charioteer by the name of Gaius Appuleius Diocles was said to have won almost 1,500 races and when he retired at the age of forty-two, he had a fortune of 35.5 million sestercii!
I guess some things don’t change, as the salary of military personnel today is far outstripped by that of the average sports star.
It seems that those who are destined entertain us, whether a modern sports star or an ancient charioteer in the circus of Rome, are going to be raised above the average person in society. Victory brings great reward, it seems, and ancient Rome was no different in that respect.
Bread and circuses!
There’s a reason Juvenal wrote those words back in the first century A.D.
Thank you for reading
For those of you who are interested, the Timeline documentary below talks about the history and technical specs of ancient Roman chariot racing while training four modern equestrian experts to become charioteers and then race each other. You might want to check this out!
A Turn of the Thumb: Gladiators and the Thumbs Up
Greetings ancient history fans! We hope you enjoyed last week’s blog post on the origins of gladiatorial combat and the different types of gladiators. If you didn’t read it, you can check it out by CLICKING HERE.
This week we’re venturing farther into the world of gladiators with a special guest post by archaeologist Raven Todd Da Silva.
Everyone who is familiar with popular representations of gladiators and gladiatorial combat will be familiar with the ‘turn of the thumb’ gesture, but do you know how that expression came about? Is it historically correct? Why was the thumb so important to Romans?
Well, Raven is going to demystify that for us. Take it away, Raven!